A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then transmitted to an area. The substation connects to the power grid and distributes electricity to homes and businesses.
What is a Substation?
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. It serves as a junction point between transmission lines and distribution lines. The substation transforms high-voltage electricity from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses served by the distribution line.
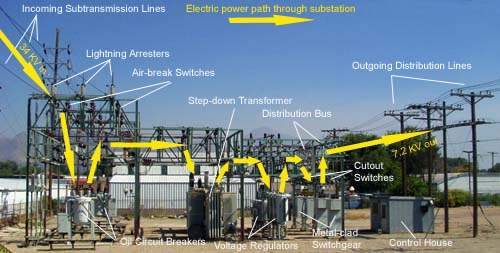
Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but all contain key components that perform important functions. These components include power transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, capacitor banks, and surge arrestors.
The power transformer is the heart of the substation.
Its job is to step down or step up the voltage of electricity coming into the substation from the transmission line. This transformation allows the electricity to flow safely through various other components in the substation before being sent out on the distribution lines.
Circuit breakers are also critical components.
They protect equipment within the substation by automatically opening and closing circuits as needed. If there is an overload on a circuit, for example, circuit breakers will open to prevent damage. Disconnect switches provide another layer of protection by allowing operators to manually open and close circuits when necessary.
Capacitor banks are used to store energy so that it can be released when needed. This helps regulate voltage levels within the substation and can provide a boost of power during times of peak demand.
What is Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electric power grid. It is a collection of equipment that helps to generate, distribute, and use electricity. The substation usually contains transformers, breakers, and switches.
The substation’s job is to take the high-voltage electricity from the transmission lines and convert it into a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses. The substation also protects equipment and people from power surges by automatically disconnecting the power when there is an overload.
Substations come in all shapes and sizes.
Some are as small as a closet, while others can be as large as a football field. They are typically located near where the electricity is needed, such as near a city or town.
Large Substations: These are normally built for high voltages (138kv – 765 kv) uses giant transformers to change voltages levels so that it can be used at our homes(220 volts).
These types of Substations will have many acres of land with several buildings on site including offices for engineers who work there.
Medium Substations: These types of Substations will have medium voltage (13kv – 25 kv) uses slightly smaller transformers than those found at large Substations but they serve the same purpose which is changing voltage levels before it enters our homes(220 volts). These Substations tend to occupy ¼ to ½ an acre with one or two buildings on site depending on its size with some having offices inside while others do not because they may not require full time employees manning them at all times like their larger counterparts do.
. Small Substations: As you guessed these types of Substations will have low voltage (600 volts or less) just like those found in our neighborhoods going into each home(220 volts). These often times don’t even have any buildings on site due too their size which could range anywhere from occupying just a few meters to around 200 meters.
. Now that we know what each type looks like based on size lets talk about how each Substation gets its power?
All three types get their electricity from either generators using coal ,oil ,natural gas or renewable resources like wind turbines ,solar panels ,or hydroelectric dams .
Substation Components
A substation is a crucial part of the electric power grid. It is a collection of electrical equipment that serves as a junction point between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. The substation components include transformers, circuit breakers, voltage regulators, capacitors, and reactors.
The transformer is the most important component in a substation. Its primary purpose is to change the voltage of electricity flowing through it. This is done by using coils of wire to increase or decrease the magnetic field around the conductor, which in turn increases or decreases the voltage.
Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to excessive current flow. They work by automatically opening and closing circuits in response to changes in current flow.
Voltage regulators are used to maintain a constant voltage level within a given range.
This is accomplished by either increasing or decreasing resistance in the circuit, depending on whether the voltage is too high or too low.
Capacitors are used to store electrical energy and release it when needed. They work by storing charge on their plates and then releasing it when the voltage drops below a certain level.
Reactors are used to limit currents flowing through them.
Function of Substation
In power systems, a substation is a component of an electrical grid. Its main function is to take high-voltage electricity from the transmission system and transform it into lower voltages so that it can be used by consumers. The substation also serves as a switchyard where power flows in different directions depending on demand.
Substations are typically located near population centers because that is where the demand for electricity is highest. They may also be located near sources of generation, such as hydroelectric dams or thermal power plants, to minimize transmission losses.
Inside the substation, there are many pieces of equipment that work together to perform the transformation of voltage.
These include circuit breakers, busbars, transformers, and grounding devices. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or faults in the system. Busbars are conductors that carry large currents between circuit breakers and other equipment within the substation.
Transformers change the voltage level of electricity so that it can be used by consumers without damaging appliances or causing fires. Grounding devices provide a safe path for fault current to flow to ground in order to protect equipment and personnel from electric shocks.
The layout of a substation depends on its specific purpose, but all must have adequate space for housing all of the necessary equipment and for workers to safely move around inside.
Substations may be enclosed by walls or fences to keep unauthorized people out and prevent interference with sensitive electronic equipment from outside sources like lightning strikes.
Distribution Substation
A distribution substation is a power substation that reduces voltage from a higher transmission voltage to a lower secondary distribution voltage used in the local distribution network. The first stage in the delivery of electricity to end consumers, it is located between the primary grid and the local network.
reduce voltage from high tension lines for use in lower secondary voltages for local distribution networks.
These are typically located between the primary grid and customer connections.
Substation Pdf
A substation is an electrical installation where power lines and equipment are connected in order to distribute electricity. The distribution of electricity requires a high voltage, which is why the substation must have a transformer. A substation can be as simple as a single transformer connected to a few power lines, or it can be much more complex, with multiple transformers, circuit breakers, and other devices.
The first step in designing a substation is to determine the voltage levels that will be used. The voltages used in most substations are either 115 kV or 230 kV. Once the voltage levels have been determined, the next step is to select the type of transformer that will be used.
There are two basic types of transformers: air-cooled and water-cooled. Air-cooled transformers are less expensive and require less maintenance than water-cooled transformers, but they are not suitable for use in all environments. Water-cooled transformers are more expensive but can be used in any environment.
After the type of transformer has been selected, the next step is to choose the type of switchgear that will be used. Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within a substation. There are two basic types of switchgear: low-voltage and high-voltage.
Low-voltage switchgear is less expensive but cannot handle as much electrical current as high-voltage switchgear. High-voltage switchgear is more expensive but can handle larger amounts of electrical current.
Once theswitchgear has been selected,the final step is to choose the type of cabling that will be used to connect everything together.
Cables come in different sizes and insulation levels depending on their intended use; however, most cables used in substations are either copper or aluminum conductor cable with PVC insulation .
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. Substations transform high-voltage, long-distance transmission lines to lower voltages for distribution to customers. They also connect generation resources to the grid.
Substations are typically located where transmission and distribution lines intersect.
Components
The three basic types of components in a substation are:
Transformers – Converts high voltage to low voltage or vice versa
Circuit breakers – Opens and closes circuits as needed to protect equipment and maintain service
Transmission Substation
A transmission substation is a type of electrical substation that is used to switch between different types of transmission lines. Transmission substations are typically located at the boundaries between different power networks. They may also be located at major load centers, or at other points where the capacity of the transmission system needs to be increased or decreased.
Transmission substations are usually much larger than distribution substations, and they often have a variety of different types of equipment installed in them. This equipment includes transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and protective relays. Transmission substations typically have a high voltage (HV) side and a low voltage (LV) side.
The HV side is used to connect to the high-voltage transmission lines, while the LV side is used to connect to the lower-voltage distribution lines.
One important function of transmission substations is to provide impedance matching between the transmission line and the load. Impedance mismatch can cause significant losses in the system, so it is important to minimize it wherever possible.
Another function of transmission substations is to provide voltage regulation. Voltage regulation is necessary because the voltages on the transmission lines can vary significantly due to changes in load or generation levels. By regulating the voltage at the substation, these variations can be minimized and kept within acceptable limits.
Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a type of electrical substation that includes one or more transformers. These devices are used to change the voltage level of an alternating current (AC) in order to match it with the voltage required by the equipment being powered. Transformer substations can be found in a variety of settings, including power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks.
The most common type of transformer used in these substations is the air-cooled transformer. This device uses fans to circulate air around the transformer windings in order to keep them cool. Other types of transformers, such as oil-filled transformers, may also be used in some cases.
The main components of a typical transformer substation include a control house, one or moretransformers, circuit breakers, and disconnect switches. The control house houses the equipment needed to monitor and operate the substation. The transformers step up or step down the voltage level as needed.
Circuit breakers are used to protect the equipment from damage due to excessive currents, while disconnect switches allow for safe maintenance and repair work on the substation components.
Credit: www.osha.gov
What is the Purpose of a Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. Its purpose is to take high-voltage electricity from the transmission system and lower the voltage so it can be used by consumers.
Substations also play an important role in ensuring the quality of electricity supplied to customers.
They house equipment that can regulate voltage and remove any fluctuations or interruptions in the power supply. This results in a more consistent flow of electricity to customers, which reduces disruptions and keeps everyone safe.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
There are three types of substations: transmission, distribution, and service. Transmission substations step up the voltage from generation plants to the extremely high voltages used in long-distance power transmission lines. These substations typically use transformers to increase the voltage.
Distribution substations take the high voltage electricity from transmission lines and step it down to a lower voltage for use in local distribution circuits. Service substations provide a connection point between customer’s facilities and the utility grid. These substations typically have transformers that step down the voltage for customer use.
What is the Difference between a Substation And a Transformer?
A substation is an electrical installation where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. A transformer is a device that changes the voltage of an alternating current (AC) by inductively coupling between its primary winding and secondary winding circuits.
Can You Live near a Substation?
Yes, you can live near a substation. In fact, many people do! However, there are some things to keep in mind if you choose to live near one.
First of all, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with living near a substation. While the risk of an accident at a substation is relatively low, it is still important to be aware of the possibility. If an accident were to occur, it could result in damage to property and even injuries or fatalities.
Secondly, living near a substation can also be noisy. The equipment inside a substation produces a lot of noise, which can be disruptive for residents nearby. If noise is a concern for you, it may be worth considering another location.
Finally, living near a substation does have its perks! For example, many utility companies offer discounts for customers who live close to their facilities. Additionally, being close to a substation means that you will have quick and easy access to power in case of an emergency situation.
Conclusion
A substation is a type of power plant that converts electricity from one voltage to another. It is an important part of the electrical grid, as it ensures that electricity can be transported safely and efficiently between different parts of the country. A substation typically consists of a number of transformers, which are used to raise or lower the voltage of the electricity, as well as other equipment such as switches and circuit breakers.


