A substation is a part of an electrical grid. Its job is to take electricity from the power plant and send it out to homes and businesses. substations step down the voltage so that it can be used by customers, and they also provide a place where utilities can connect and disconnect customers.
If you’re in the market for a substation, you have a few different options to choose from. The type of substation you’ll need depends on the application it will be used for. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of substations:
– Transmission Substation: A transmission substation is used to connect two or more parts of a power grid. It steps up or steps down voltages and can also regulate voltage and current levels.
– Distribution Substations: A distribution substation connects the secondary circuit of a transformer to the distribution system.
It reduces voltage so that it can be distributed safely to homes and businesses.
– Industrial Substations: An industrial substation is used to supply power to an industrial plant or complex. They are often located near sources of high demand, such as factories or mines.
How Do Substations Work?
Which Type of Substation is Widely Used?
Most substations are of the outdoor type, often located in a rural area where land is plentiful. Because they require less maintenance than indoor substations, they are generally more economical to operate.
What is Substation And Types of Substations?
A substation is a type of power plant where electricity is generated. There are many different types of substations, each with its own unique purpose. The most common type of substation is the power plant itself, which generates electricity from coal, natural gas, or nuclear fuel.
Other types of substations include hydroelectric dams, wind farms, and solar arrays.
The purpose of a substation is to take the electricity generated at the power plant and distribute it to homes and businesses through the electrical grid. Substations are also responsible for providing voltage regulation and power quality control.
Without these critical functions, the electrical grid would be less reliable and susceptible to blackouts.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and switching. Transmission substations take high-voltage electricity from the power plant and step it down to a lower voltage that can be transported over long distances without losing too much energy.
Distribution substations then take this lower-voltage electricity and step it down even further before sending it out to homes and businesses through medium-voltage lines. Switching substations act as junction points on the electrical grid, allowing for easy reconfiguration in case of an outage or other emergency situation.
What are the Three Different Types of Substations And Its Purposes?
A substation is an electrical installation where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. The three types of substations are power, distribution, and switching.
Power substations step down extra-high voltages (EHV) from the transmission system to a level that can be used by the local distribution system.
They also provide an interface between generation and transmission.
Distribution substations distribute electricity at lower voltages to consumers. They receive their power from either a power station or a larger substation and deliver it to several feeders.
Switching substations do not change voltage levels; they simply connect or disconnect sections of the network as needed. This type of substation is usually found near load centers where there is a significant amount of demand for electricity.
What Does Substation Do?
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. substations take the high-voltage electricity from transmission lines and step it down to a lower voltage so it can be distributed to consumers. Substations also help regulate voltage and improve power quality.

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
Types of Substation
In electric power distribution, a substation is a junction point where two or more circuits meet. The word “substation” can refer to either the buildings housing the equipment or the equipment itself. A substation may be as simple as a transformer for changing voltage from low to high, or as complex as a grid control center with computer-assisted controls and monitoring devices.
There are several different types of substations which serve different purposes:
1) Transmission Substation: These are located between generation plants and distribution networks. Their purpose is to step up voltage from generation level (usually 115 kV) to transmission level (345 kV), in order to transmit electricity over long distances with minimal energy losses.
2) Distribution Substation: These receive power from transmission lines at high voltage levels and transform it into lower voltages for distribution to local customers via lower-voltage distribution lines.
3) Substations serving large loads: Large loads such as factories or office complexes often have their own on-site substations which receive power directly from the utility company at high voltage and then distribute it internally at lower voltages. This avoids having to run many miles of distribution line back to the nearest standard distribution substation.
4) Mobile Substations: These are used when there is an emergency need for additional capacity due to an unexpected outage elsewhere in the system, or during planned maintenance activities when one section of the system needs to be taken offline for work while still providing electricity service to customers. They consist of portable transformers, switches, and other electrical equipment mounted on trucks or trailers so they can be quickly transported and set up where needed.
Electrical Substation
What is an Electrical Substation?
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a collection of equipment that transforms high-voltage electricity from the transmission system to lower voltages that can be used by consumers.
Substations also play an important role in providing voltage support and regulating the flow of electricity on the grid.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and combined. Transmission substations step down high-voltage electricity from the transmission system for use on the distribution system.
Distribution substations further reduce voltage levels and deliver electricity to businesses and homes. Combined substations perform both functions.
Substations must be designed to withstand extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes, ice storms, and earthquakes.
They must also be able to protect against human threats, such as vandalism and terrorism. To do this, substations are typically surrounded by fences or walls and have security cameras and other security measures in place.
What is Substation
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then sent to an electric grid. The substation converts the high-voltage electricity from the grid into the lower-voltage electricity that is used by homes and businesses.
Types of Substation Pdf
A substation is a crucial part of the power grid. Without substations, electricity would not be able to flow from generation facilities to our homes and businesses. Substations come in many different shapes and sizes, but all play an important role in keeping the lights on.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and service. Transmission substations take high-voltage electricity from generation facilities and step it down to a lower voltage that can be transported over long distances without losing too much power. Distribution substations then take this lower voltage electricity and step it down even further so that it can be sent to homes and businesses through medium-voltage power lines.
Service substations are the final stop for electricity before it enters our homes and buildings. These substations step down the voltage one last time so that it can be used safely by our appliances and lights.
Substations are an essential part of the power grid, but they can also be dangerous places.
High voltages flowing through these stations can pose a serious hazard to workers and passersby if proper safety precautions are not taken. It is important to always respect posted warning signs and never enter a substation without permission from the utility company that owns it.
Distribution Substation
electric power distribution substation is a utility installation that serves as a junction between high-voltage transmission lines and lower voltage distribution lines. The primary purpose of a distribution substation is to step down the voltage of the transmission line to an level that is safe for distribution to end users. A typical distribution substation will have one or more transformers, along with associated switchgear, controls, and other equipment.
A secondary purpose of some distribution substations is to provide switching capability so that circuits can be reconfigured without interrupting service. This allows for maintenance on individual circuits without affecting the rest of the system. Distribution substations are typically located at strategic points within an electric power grid so that they can serve large numbers of consumers in their service area.
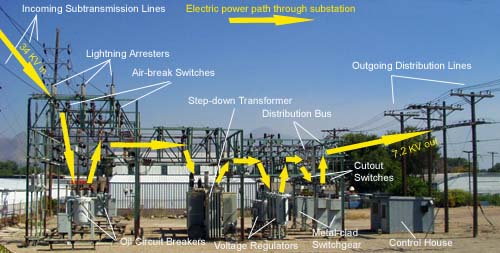
Components of Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is a collection of electrical equipment that transforms, switches, and controls the flow of electricity. The four major components of a substation are:
1. Transformers – Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity passing through the substation. Higher voltages are needed to transmit electricity over long distances, so transformers step up the voltage before it leaves the substation.
2. Switchgear – Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity passing through the substation.
It consists of high-voltage circuit breakers, switches, and fuses that can be used to isolate parts of the substation for maintenance or repair.
3. Capacitors and Reactors – Capacitors and reactors are used to store or release energy into the system to help regulate voltage levels.
Electrical Substation near Me
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. Without it, electricity couldn’t be delivered to homes and businesses. Substations transform high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to the lower voltages used by consumers.
They also regulate voltage and improve power quality.
Substations are usually located near large loads, like cities or industrial areas. This is because substations need to be close to where the electricity is being used.
Substations come in all shapes and sizes, but they typically have several key components:
Transformers – Transformers convert high-voltage electricity into lower voltages so it can be used by consumers. Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers protect equipment and prevent outages by automatically disconnecting circuits when there’s an overload or fault.
Capacitors – Capacitors store energy and help improve power quality by regulating voltage levels. Inductors – Inductors smooth out fluctuations in current, which helps protect equipment and improve power quality. Busbars – Busbars are thick metal bars that carry electricity from one circuit to another inside the substation.
Cables – Cables connect different parts of the substation and carry electricity between them. Grounding grids – Grounding grids provide a safe path for excess current to flow into the ground in case of a fault or overload situation.
If you’re ever curious about what’s going on at your local substation, most utility companies offer tours upon request!
Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a type of electrical substation that contains one or more transformers. A transformer is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) from one voltage level to another. Transformer substations are used to change the voltage level of electricity being transmitted from one area to another.
There are three main types of transformer substations:
-Step-up transformer substations increase the voltage level of electricity.
-Step-down transformer substations decrease the voltage level of electricity.
-Regulating transformer substations maintain a consistent voltage level.
Transformer substations are essential in ensuring that electricity can be safely and efficiently transmitted over long distances. Without these devices, power grids would not be able to function properly.
Conclusion
There are many different types of substations and the type you need will depend on the specific application. The most common types of substations are distribution, transmission, and generation substations. Each type has its own unique purpose and function.
A distribution substation takes power from the transmission grid and steps it down to a lower voltage so that it can be distributed to consumers. A transmission substation steps up the voltage so that it can be transported over long distances without losing power. And a generation substation connects generators to the grid.