There are many reasons to use electric power in a substation. One reason is that electric power is more efficient than other forms of energy, such as oil or gas. Electric power can be generated at a central location and then distributed to the substation, which eliminates the need to transport fuel to the site.
Additionally, electric power is cleaner than other forms of energy and produces no emissions.
There are many reasons to use electric in substation. First, electric is more efficient than other forms of energy, so it can save money on your energy bill. Second, electric is cleaner and more environmentally friendly than other forms of energy, so it can help reduce your carbon footprint.
Third, electric is more reliable and less likely to cause outages than other forms of energy. Finally, using electric in substation can help improve the safety of your employees and customers by reducing the risk of fire and explosion.
Electrical Substation & It's purpose | Explained | TheElectricalGuy
Types of Substation
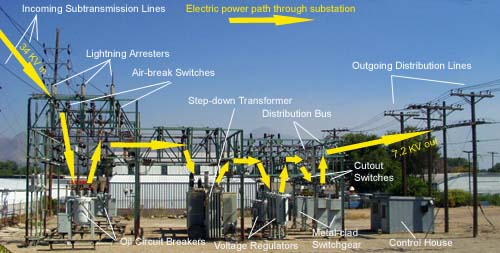
A substation is a power system facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. Substations are also used to change alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or vice versa. The energy in a substation is generally managed by circuit breakers, fuses and switches so that components can be isolated for repair or replacement.
There are three types of Substations:
1. Transmission Substation
2. Distribution Substation
3. Substations for Switchgear
Transmission Substation: A transmission substation increases the voltage of an electric power line so that it can be transmitted over long distances with minimal losses. These substations are usually located near generation plants and use large transformers to convert between low voltages at the plant and high voltages for transmission.
The primary equipment in a transmission substation includes power transformers, circuit breakers and disconnects, bus work, metering equipment, and control devices .
Distribution Substation: A distribution substation reduces the voltage of an electric power line so that it can be distributed safely and efficiently to consumers via smaller lines. These substations are usually located near population centers and use smaller transformers than those found in transmission substations .
The primary equipment in a distribution substation includes power transformers, circuit breakers , reclosers , taps , capacitors , voltage regulators ,drain pipes Secondary Equipment such as grounding grids and earth electrodes may also be present . Switchgear: Substations that contain only switchgear are typically used as collection points in radial distribution systems where several feeder lines converge . The switchgear controls the flow of electricity from each feeder line to the main distribution line .
This type of substation does not include anytransformational equipment and therefore cannot increase or decrease voltages .
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electricity grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines and where the voltage is transformed from one level to another. Substations can be found in both urban and rural areas, often near power plants or load centers.
A typical substation includes a number of components:
Transformers – to change the voltage level
Circuit breakers – to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or faults Capacitors – to improve power factor Regulators – to control voltage levels Disconnect switches – to isolate equipment for maintenance Inductors – to smooth out fluctuations in current Measuring devices – for monitoring purposes Control panels – for operator use Communication systems – for remote monitoring and control
Substations must be designed with safety in mind. All electrical equipment is enclosed in metal cabinets or surrounded by fencing. Grounding rods are used to dissipate any stray currents and minimize the risk of shock.
Warning signs are posted around the perimeter of the substation, and access is typically restricted to authorized personnel only.
What is a Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where high-voltage power lines from generating stations are connected to lower-voltage distribution lines. This transformation of voltage allows electricity to be sent over long distances without losing power.
Substations also have switchgear, which helps protect equipment and maintain voltage levels, as well as devices that measure and record data about electricity flow.
Electrical Substation Components
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and distribute electricity to end users. Without substations, the electric power grid would not be able to function.
There are four main components of an electrical substation:
-Transformers
-Circuit breakers
-Capacitors
-Grounding equipment
Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity passing through the substation.
The three types of transformers are step-up, step-down, and isolation. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage caused by overloads or faults in the system. Capacitors store energy that can be released during short circuit conditions to help stabilize voltage.
Grounding equipment provides a safe path for current to flow in case of a fault.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes depending on their purpose and location. Some common types include transmission, distribution, rectifier, converter, and switchgear substations.
Function of Substation
A substation is a part of an electrical grid that transforms power from one voltage to another, or that connects different parts of the grid. A substation can also be used to connect two different grids.
Substations are usually located where power lines come together, or where they connect to other parts of the grid.
They often have transformers, which step up or step down the voltage of the electricity so that it can be used by consumers.
Substations may also have equipment for controlling the flow of electricity and for protecting equipment and people in case of an electrical fault.
Electrical Substation near Me
If you live in a city or town, chances are there is an electrical substation nearby. If you’re not sure what that is, it’s basically a facility where electricity is generated, transformed and distributed to homes and businesses. These substations are usually operated by the local utility company.
While most of us don’t give them much thought, these substations play an important role in keeping our lights on and our appliances running. And if you’ve ever wondered what goes on inside one of these facilities, wonder no more! Here’s a behind-the-scenes look at an electrical substation:
The first step in the process is generating electricity at a power plant. This can be done using various energy sources, such as coal, natural gas, nuclear power or renewable resources like solar and wind power. The electricity produced at the power plant is then sent through high-voltage transmission lines to the substation.
Once the electricity reaches the substation, it goes through a transformer which reduces the voltage so it can be safely distributed to homes and businesses within the community. From there, the electricity flows through secondary wires to distribution circuits before finally reaching your home or office via service drop wires.
That’s how electricity makes its way from the power plant to your light bulb!
Next time you see an electrical substation near you, remember all the hard work that goes into keeping your lights on each day.
Distribution Substation
A distribution substation is a power substation that provides electricity to lower-voltage distribution lines. These are the lines that carry electricity to customers’ homes and businesses. A typical distribution substation has two parts:
The first part is the step-down transformer. This device lowers the voltage of the electricity coming from the high-voltage transmission line so it can be used safely on the lower-voltage distribution line.
The second part of a distribution substation is called a switchgear.
This equipment includes switches, fuses and other devices that help protect and control the flow of electricity on the distribution line.
Types of Substation Pdf
A substation is an electrical installation where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. Substations are also used to switch between different voltages, such as when alternating current (AC) needs to be converted into direct current (DC). The word “substation” can also refer to the buildings that house these installations.
There are three types of substations: transmission, distribution, and switching. Transmission substations connect parts of the high-voltage national grid. They step down the voltage so that it can be used by local distribution networks.
Distribution substations distribute electricity around towns and cities. Switching substations automatically switch circuits so that maintenance can be carried out on one section without disrupting power supplies to other areas.
Transmission substations are usually owned and operated by electric utility companies.
Distribution and switching substations are usually owned by actual users like factories or office blocks, who then sell electricity on to smaller businesses or individual households in their area.
Substations come in all shapes and sizes depending on their purpose, but they all have certain common features. Firstly, there will always be a control room where personnel can monitor conditions and make changes if necessary.
This room will contain banks of switches, breakers, and other equipment used to control the flow of electricity passing through the substation – think of it like a giant fuse box! Secondly, there will be a transformer which changes the voltage levels as required – remember AC/DC? Thirdly, there need to be cooling towers or fans present so that heat build-up doesn’t damage equipment or cause fires.
Finally, because electricity is dangerous there will always be a fence around the perimeter with warning signs telling people not to touch anything!

Credit: www.electricaltechnology.org
What is the Purpose of an Electric Substation?
An electric substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. Its purpose is to take the high-voltage electricity from the power plant and step it down to a lower voltage so that it can be used by homes and businesses. The substation also regulates the flow of electricity and keeps it flowing smoothly throughout the grid.
Why Power Transformers are Used in Substation?
A power transformer is a static device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. A varying current in one coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux, which, in turn, induces a voltage across a second coil wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between the two coils without any physical contact between them.
Power transformers are used extensively in high-voltage power systems for the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. They are also used in lower-voltage systems to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), or vice versa. Power transformers come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on their application.
Large units may weigh several hundred tons and have primary voltages exceeding 800 kilovolts.
Why is Dc Supply Used in Substations?
There are many reasons for why DC supply is used in substations. One of the most common reasons is because it can help to reduce line losses. Additionally, DC supply can also provide a steadier current which can be helpful in maintaining voltage levels within the substation.
Another reason why DC might be used instead of AC is because it eliminates the need for reactive power compensation, which can further reduce energy losses. Ultimately, using DC supply in a substation can help to improve its overall efficiency and performance.
How Do Substations Get Power?
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and distribute power around an electrical grid. Without substations, electricity could not be effectively transported long distances or used in most applications.
Substations are typically located where three phases of AC power meet, either at generation plants or where transmission lines connect.
There are three primary types of substations: generation, transmission, and distribution. Generation substations step up voltage from lower voltages used in local distribution systems to the very high voltages needed for long-distance transmission on extra-high-voltage (EHV) lines.
Transmission substations further increase voltage for even longer distance EHV line segments. Distribution substations finally “step down” voltage to the levels required by homes and businesses served by that particular system
Substations must have a source of electricity to operate.
For backup purposes, many also have diesel generators which can provide power if there is an interruption in service from the main grid.
Conclusion
Electricity is used in substations to control the flow of electricity through a power system. By controlling the flow of electricity, substations can regulate the voltage and frequency of the power supplied to customers. Electric substations also help to protect equipment and personnel by providing a safe place to work on electrical equipment.