A Step down Transformer of a Substation is a transformer that steps down the voltage from the primary side to the secondary side. The primary side is usually the high voltage side, while the secondary side is usually the low voltage side.
A substation is an electrical system that converts high-voltage electricity from transmission lines to the lower voltages used by customers. A step-down transformer is a type of transformer that is used in a substation to convert high-voltage electricity to lower voltages. The primary winding of the transformer has more turns than the secondary winding, which causes the voltage to be reduced when it passes through the transformer.
Disadvantages of Step-Down Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. A step-down transformer is a type of transformer that steps down the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. The disadvantages of using a step-down transformer include power loss, magnetic flux leakage, and core saturation.
Power Loss: Power is lost in a step-down transformer due to resistance in the windings and core losses. The power lost in the windings is known as I²R losses, while the power lost in the core is known as hysteresis and eddy current losses. The I²R losses are proportional to the square of the current flowing through the windings, while the hysteresis and eddy current losses are proportional tothe frequency ofthe AC supply.
Magnetic Flux Leakage: Another disadvantage of using a step-down transformer is that there will be some magnetic flux leakage fromthe primary winding tothe secondary winding due to imperfect coupling betweenthe two windings. This leakage flux results in an additional loss known as magnetizing loss. Core Saturation: When operating at high frequencies, there is also a riskof core saturation occurring ina step-down transformer.
Step down Transformer 220V to 110V
A step down transformer is a device that transforms high-voltage electricity into low-voltage electricity. The most common use for a step down transformer is to convert 220 volts of alternating current (AC) power to 110 volts AC power, which is the standard voltage in North America.
There are many reasons why you might need to use a step down transformer.
Perhaps you’re traveling overseas and need to use your North American appliances, or maybe you want to run some heavy-duty equipment that requires more power than what’s available in your home or office. Whatever the reason, using a step down transformer is relatively simple and straightforward.
Here’s what you need to know about how to use a step down transformer:
First, make sure that the input voltage (the220V side) of the transformer matches the voltage of the outlet you’ll be plugging it into. If it doesn’t, don’t try to force it—this could damage both the outlet and the transformer. Once you’ve found an outlet with matching voltage, plug the transformer into it and then flip the switch on the side of the unit to “on.”
Next, take note of which way the current is flowing through the primary coil (the 220V side). In order for the current to flow properly through your appliance or equipment, this must match up with how they are designed. For example, if your appliance has two prongs that are different sizes (one thicker than the other), make sure thatthe thick prong lines up withthe wide part ofthe primary coil onyourtransformer.
If everything looks good so far, go ahead and plug your appliance into one ofthe outlets onthe secondary coil(110V side)ofyourtransformerandfliptheswitchto “on.”Yourapplianceor equipmentshouldnowbegettingpowerfromthetransformerandbegoodtouse!
Step down Transformer Example
A step-down transformer is a type of transformer that steps down the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. The most common use for a step-down transformer is to convert high voltage, low current electricity from the power plant into low voltage, high current electricity used in homes and businesses.
The first thing to understand about a step-down transformer is how it works.
Transformers work by using two coils of wire (the primary and secondary windings) wrapped around a metal core. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field in the core. This changing magnetic field then induces a current in the secondary winding, which steps down the voltage.
The amount that the voltage is stepped down depends on the ratio of turns between the primary and secondary windings. For example, if there are 100 turns in the primary winding and 50 turns in the secondary winding, then the voltage will be stepped down by half. In general, you can calculate this as follows:
Step-Down Transformer Working Principle
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. A varying current in one coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux, which, in turn, induces a voltage across a second coil wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between the two coils, without any direct electrical connection between them.
The primary winding is connected to an AC source and the secondary winding is connected to load resistance RL. The current flowing through the primary winding creates flux φ which links with both windings and produces EMF E2 in the secondary winding by mutual induction. The ratio of number of turns per volt (N/V) for both windings is equal to the transformation ratio (K), therefore;
E2/E1= N2/N1= K ……….
Types of Step-Up Transformer
There are many types of step-up transformers, each with different features and applications. The most common type is the air-core transformer, which uses a magnetic field to convert AC voltage from one level to another. Other types include the ferrite-core transformer, pulse transformer, and auto-transformer.
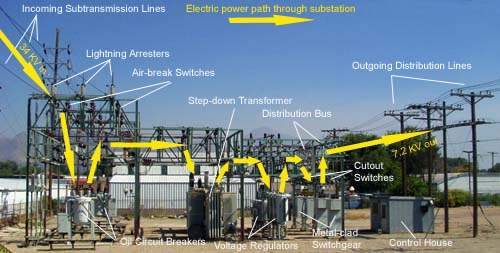
Credit: www.osha.gov
What is the Purpose of a Step down Transformer?
A step down transformer is an electrical device that transforms alternating current (AC) from a higher voltage to a lower voltage. It is commonly used to convert the high voltage of a power line down to a safe level for use in homes and businesses. Transformers are also used to change the voltage of an AC signal for compatibility with devices that run on different voltages.
For example, a 110-volt TV can be plugged into a 220-volt outlet by using a step down transformer.
What is Step down Transformer in Simple Words?
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. A varying current in one coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux, which, in turn, induces a voltage across a second coil wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between the two coils, without using any moving parts.
In simple words, a step down transformer is a type of transformer that transforms high-voltage electricity into low-voltage electricity. The primary winding (input) has more turns than the secondary winding (output), so the output voltage will be lower than the input voltage.
What is the Difference between Step down And Step Up Transformer?
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Transformers can be used to step up or step down the voltage in an electrical circuit. The difference between a step up and step down transformer lies in the direction of the flow of current.
In a step up transformer, the current flows from the primary winding to the secondary winding, while in a step down transformer, the current flows from the secondary winding to the primary winding.
The most common type of transformer is the AC power transformer, which is used to transfer alternating current (AC) from one circuit to another. AC power transformers are classified by their turns ratio; that is, the ratio of the number of turns on the primary winding to the number of turns on the secondary winding.
A turn is simply one loop of wire around either side of a magnetic core. The primary purpose of an AC power transformer is to change (transform) voltage levels.
There are two types of voltage transformation that can be achieved by an AC power transformer: stepping-up and stepping-down voltages.
Stepping-up voltages is accomplished by having more turns on the secondary coil than on the primary coil; less volts are induced into each turn on secondary than was supplied to each turn on primary but since there are more turns, overall voltage output is higher than input voltage. Stepping-down voltages occurs when there are fewer turns onsecondary coil thanprimary coil; this causes each turn onthe secondaryto receivea greater volts inducement thaneachturnonprimarybutsincefewerturnsonsecondarythanonprimary ,theoverallvoltage outputhastobelessthaninputvoltage .
How does a Transformer work – Working Principle electrical engineering
Conclusion
In a substation, the voltage is stepped down by a transformer before it is sent out to consumers. The transformer steps down the voltage so that it can be used safely.



