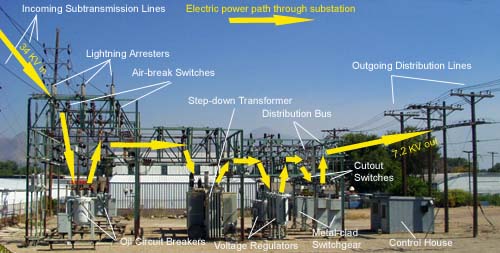
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then transformed to extra high voltage for long distance transmission. Inside the substation, there are many large devices such as transformers, breakers, and switches that control the flow of electricity.
A substation is a junction point on an electrical grid where high-voltage transmission lines connect with lower-voltage distribution lines. A substation may also include transformers to step down the voltage for use in household or commercial applications.
How Do Substations Work?
Types of Substation
There are two types of substations: primary and secondary. A primary substation is the first point at which electricity is brought into a system from the generating source. The secondary substation is the last point before distribution to consumers.
Each type of substation has a unique function, and both are critical to ensuring reliable power delivery.
A primary substation takes high-voltage power from the generating source and steps it down to a lower voltage that can be fed into the secondary substation. The transformers in a primary substation are usually much larger than those in a secondary substation because they have to handle more voltage.
The secondary substation then steps the voltage down again for distribution to consumers. Because the voltages involved are lower, the transformers in a secondary substation are smaller than those in a primary station.
Both types of substations must have adequate ventilation to dissipate heat generated by the transformer coils.
If not properly cooled, transformers can overheat and fail, causing blackouts.
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electricity grid. It is a junction point where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines and transformers change the voltage so that it can be used by consumers.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have one common goal: to provide a safe and reliable place to connect different parts of the electrical grid.
In order to do this, they must have several key components.
The first component is the switchgear, which includes circuit breakers and other devices that control the flow of electricity. The second component is the transformer, which changes the voltage of electricity so that it can be used by consumers.
The third component is the busbar, which distributes power to different parts of the substation. And finally, there are various monitoring and control systems that help make sure everything is running smoothly.
Electrical substations play a vital role in our everyday lives – we rely on them for everything from powering our homes to keeping our lights on at night.
Without them, we would be living in a very different world indeed!
Substation Pdf
Substations are an important part of the electrical grid. They help to ensure that power flows smoothly and efficiently from generation sources to load centers. A substation typically includes a transformer that steps down the voltage from the high-voltage transmission system to a lower voltage that is more suitable for distribution to consumers.
Substations also may include devices such as circuit breakers and capacitors that help to regulate power flow and protect equipment from damage due to faults or other abnormal conditions.
In order for a substation to function properly, it must be designed according to specific criteria and standards. The first step in designing a substation is to identify the purpose of the substation and the loads it will serve.
This information will determine the size, type, and number of transformers needed as well as the required voltages and capacities. The next step is to develop a layout that minimizes risk while maximizing efficiency and reliability. Once the layout is complete, engineers select equipment based on its ability to meet the specific needs of the substation.
The construction phase of a substation project is critical because it involves working with high-voltage electricity. Safety is paramount during construction, so workers must be properly trained and follow all safety protocols. After construction is complete, substations must be regularly maintained in order to continue functioning properly.
Transmission Substation
A transmission substation is a type of power plant that is used to transmit electricity from one place to another. It is usually located at a point where two or more power grids meet. The substation transforms the high-voltage electricity from the power plant into lower voltages that are suitable for distribution to homes and businesses.
The first step in the process is to generate electricity at a power plant. The electricity is then sent through large transformers that increase the voltage. From there, the electricity travels through transmission lines to the substation.
At the substation, the voltage is lowered so it can be sent out on distribution lines to customers.
Transmission substations play an important role in ensuring that electricity flows smoothly and efficiently from its point of origin to its final destination. Without these vital components, our modern world would come to a halt.
Indoor Substation
An indoor substation is a type of electrical substation that is typically located inside a building. This type of substation is usually used for distribution purposes, and it may be located at the end of a power line or in an industrial area. Indoor substations can be either air-cooled or water-cooled, and they typically have a variety of safety features to protect both workers and equipment.
Function of Substation
A substation is a vital part of the electrical grid. It acts as a hub, where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines. The substation transforms the electricity so it can be sent safely to businesses and homes.
Substations come in all shapes and sizes. Some are as small as a garage, while others are larger than a football field. They can be located underground, above ground, or even floating on water.
No matter the size or location, all substations have three basic components: transformers, switchgear, and protection devices.
Transformers change the voltage of electricity so it can be used by businesses and households. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity through the substation.
Protection devices keep people and equipment safe from harmful electrical currents.
Substations play a critical role in keeping our lights on and our appliances running.
Substation Voltage Levels
A substation is a power plant where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. The first substations were built in the 1830s and they are an essential part of the modern electric grid.
There are three main types of substations:
– Transmission substations: These are located between generating stations and distribution substations. The voltages at transmission substations are usually very high – up to 765 kV.
– Distribution substations: These supply electricity to the customer.
The voltages at distribution substations are lower than those at transmission substations, typically around 240/415 V for single-phase lines or 600/1000 V for three-phase lines.
– Industrial Substations: These provide service for a particular factory or group of factories. The voltages used here depend on the equipment being served but will usually be lower than those at transmission and distribution substations.
Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a type of electrical substation that transforms voltage from high to low, or the reverse. It is also used to change the current from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), or vice versa. The transformer substation is one of the most important types of substations, as it plays a vital role in the distribution of electricity.

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
What is Contained in a Substation?
A substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, or switched. The word “substation” can refer to either the buildings and equipment that house these functions or the actual land area where the facility is located. Substations are usually located near power plants or large transmission lines.
The three main types of substations are: generation, transmission, and distribution. Each type has a different purpose and contains different equipment.
Generation substations take electricity from power plants and raise the voltage so it can be sent on high-voltage transmission lines.
These substations typically have few if any transformers and do not change the frequency of the electricity.
Transmission substations step up or step down voltage for long-distance electric power transmission. Most use transformers to change voltages because it is more efficient than using generators to produce different voltages.
Transmission substations also may convert between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC).
Distribution substations deliver electricity from transmission lines to local businesses and residences. They generally have several transformers that step down voltage for use in homes and office buildings.
What is the Most Important Thing in a Substation?
There are many important things in a substation, but if we had to narrow it down to one, we would say the most important thing is safety. A substation is an electrical facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or vice versa. This process happens through large transformers and other equipment, which means there is a potential for danger if something goes wrong.
That’s why safety is always the top priority in a substation. Everything from the layout of the facility to the training of employees focuses on keeping everyone safe.
What is the Difference between a Substation And a Transformer?
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed to consumers. A transformer is a device that changes the voltage of an alternating current (AC).
How Does a Substation Work?
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electricity grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower voltage distribution lines and transformers step down the voltage to be used by homes and businesses. Substations come in all shapes and sizes, but their basic purpose remains the same – to ensure that electricity can flow safely and efficiently from power plants to consumers.
The first step in understanding how a substation works is to understand the different types of electrical equipment that are used within one. These include:
* Transformers – which reduce or increase the voltage of electricity passing through them.
* Circuit breakers – which protect equipment from damage caused by faults or overloads. * Capacitors – which store energy and help regulate voltage levels. * Disconnect switches – which provide a safe way to isolate equipment for maintenance purposes.
Each piece of equipment plays an important role in ensuring that electricity flows smoothly through the substation. For example, when demand for electricity is high, transformers will step up the voltage so that it can be transported over long distances without losing any power. Conversely, when demand is low, they will step down the voltage so that it can be used safely by homes and businesses.
Circuit breakers are another important piece of safety equipment. They detect faults in the system and quickly shut off the flow of electricity to prevent damage from occurring. This protection is crucial, as even a small amount of electrical current can cause serious damage or even start a fire if it isn’t managed properly.
Capacitors play a vital role in regulating voltage levels within the substation (and beyond). When voltages get too high, capacitors release stored energy into the system to bring levels back down again. This helps avoid problems like blackouts, which can occur when voltages fluctuate wildly out of control.
Disconnect switches provide another layer of safety by allowing workers to safely isolate parts of the system for maintenance purposes without having to completely shut down operations . Substation Automation Modern substations make use of automatic devices and systems to improve efficiency , including:
* Sensors – Which monitor conditions within the substation such as temperature , pressure , humidity , etc . * Communication systems – Which allow remote monitoring and control of substation equipment . * SCADA systems – Which provide real-time data on operational conditions within the substation .
Conclusion
In a substation, there are many different types of equipment. These include:
-Transformers
-Circuit breakers
-Capacitors
-Reactors