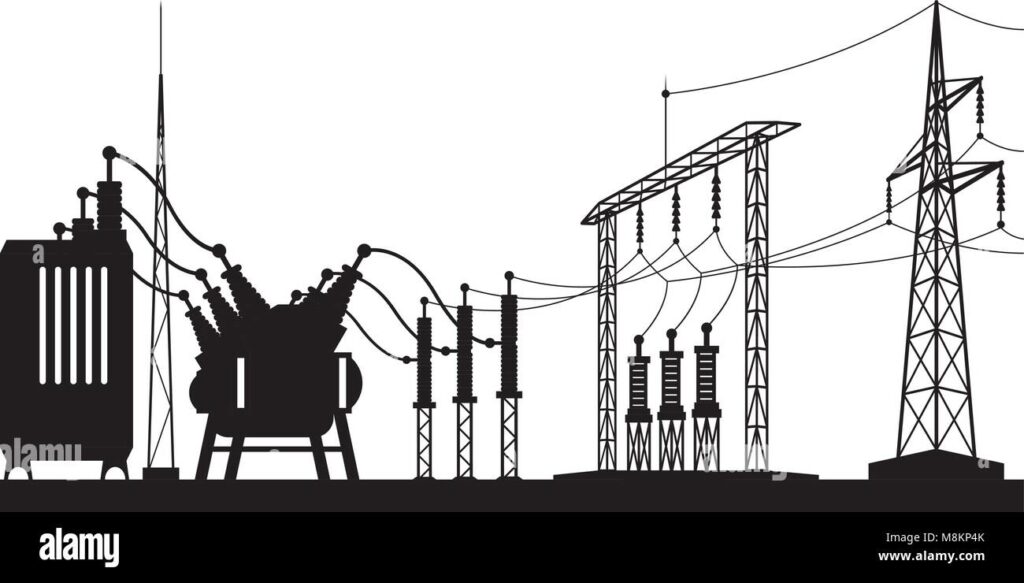
A substation is an electrical facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. Substations may also be used to change the voltage from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), or vice versa. The icon for a substation typically includes a transformer and other equipment enclosed by a fence.
Substation icon is a vital part of any electrical engineer’s toolkit. It is used to represent the various components of an electrical substation, such as transformers, breakers, and busbars. The icon is also used to indicate the direction of power flow within the substation.
14 15 Saving Circuits To An Icon Menu

Credit: www.pixelsquid.com
What are the Three Types of Substations?
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all serve the same purpose: to step down high-voltage electricity to a level that can be used by consumers. There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and power stations.
Transmission substations are typically located near power plants.
The electricity produced at the power plant is transmitted through high-voltage wires to the transmission substation. From there, it is sent through even higher-voltage wires to distribution substations.
Distribution substations take the high-voltage electricity from the transmission lines and step it down even further so that it can be sent out on lower-voltage distribution lines.
These lower voltages are safe for consumers to use in their homes and businesses.
Power stations are different from other substations because they generate electricity rather than just distribute it. Power stations usually burn fossil fuels like coal or natural gas to produce steam, which turns turbines that generate electricity.
What is a Substation Diagram?
An electrical substation is a facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. Substations may be located indoors or outdoors. The former are usually called indoor substations and the latter outdoor substations.
Indoor substations are more expensive to build than outdoor ones, but they require less space and are easier to maintain.
A typical substation includes a power transformer, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, busbars, and grounding equipment. The power transformer changes the voltage of the incoming power so that it can be used by the local distribution system.
Circuit breakers protect the local distribution system from overloads by opening and closing automatically as needed. Disconnect switches allow maintenance crews to safely disconnect parts of the system for repair or replacement. Busbars carry electricity between different parts of the substation.
Grounding equipment keeps the electricity flowing in its intended path by providing a low-resistance path for any stray current that might escape into the air or ground.
Substations must be designed to meet specific safety, reliability, and aesthetic requirements set forth by government agencies and utilities companies. Safety is of paramount importance in any electrical facility; therefore, all substation components must be carefully selected and installed according to strict safety regulations.
Reliability is also critical since an electrical outage can cause significant inconvenience or even danger to nearby residents and businesses.
How Do You Design a Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, providing a link between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all share some common features. This blog post will explain the basics of substation design.
The first step in designing a substation is to determine its function. Substations can serve many different purposes, such as voltage transformation, load shedding, or system protection. Once the substation’s purpose has been determined, its layout can be designed.
Most substations are comprised of three main components: transformers, switchgear, and control equipment. Transformers convert high-voltage electricity into lower voltages that can be used by homes and businesses. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation and includes circuit breakers and switches.
Control equipment monitors and controls the operation of the substation’s components.
Substation designers must take many factors into account when creating a design, including safety, reliability, cost effectiveness, and aesthetics. Safety is always the top priority when working with electrical equipment; all designs must meet strict safety standards set by regulatory agencies.
Reliability is also important; power outages can have major consequences for businesses and households so it is crucial that substations are designed to minimize downtime in the event of an outage. Cost effectiveness must also be considered; while it is important to create a safe and reliable design, it must also be affordable to build and operate over time.
Conclusion
Substation is an important part of the electrical grid. It is a place where electricity is transformed from one voltage to another. This transformation allows for the safe and efficient distribution of electricity to homes and businesses.
A substation icon is a symbol that represents a substation on a map or schematic diagram. The icon helps people understand the function of the substation and its relationship to other parts of the electrical grid.