The main equipment used in a substation are:
-Transformers
-Circuit breakers
-Disconnect switches
-Busbars
-Capacitors
-Instrument transformers.
Substation is an important part of the power system. It is a medium voltage (MV) or high voltage (HV) electrical installation consisting of switchgear, transformers, and other equipment used to regulate the flow of electricity.
The main equipments and accessories used in substation are:
-Switchgear: This is used to control, protect and isolate electrical equipment. It consists of circuit breakers, fuses, contactors, relays, etc.
-Transformers: These are used to change the voltage level of alternating current (AC).
-Cables: Cables are used to connect different parts of the substation.
-Busbars: Busbars are made of copper or aluminum and carry large amounts of current. They are often used in place of cables.
-Grounding system: This is used to provide a safe path for electric current in case of faults or accidents.
Transformer Equipment List
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. A varying current in one coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux, which, in turn, induces a voltage across a second coil wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between the two coils, without electrical connection between them.
Faraday’s law of induction states that: The induced EMF in any circuit is proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage with respect to time.
Transformers are used to increase or decrease the alternating voltages in electric power applications. While transformers are used extensively throughout the world of electricity generation, transmission and distribution; they are also utilized in electronic devices such as radios and televisions to convert household voltage (110 V or 220 V) into a much lower voltage required by most electronic devices (5 V or 12 V).
The first commercial application for polyphase AC was an arc lighting system installed by inventor Thomas Edison in 1882 to light Broadway in New York City.[1] Transformers were later used extensively in radio broadcasting. Early transmitters used high-voltage direct current (DC), which could not be effectively transmitted over long distances without costly resistors and capacitors;[2] therefore low-frequency alternated currents were generated instead and transformed up to very high voltages for efficient long-distance transmission.
Large DC generators were built at central power stations and connected directly to local grids via very thick cables; however these systems were difficult and expensive to expand.[3] With increasing loads on central generating plants due to electrification, it became apparent that distributing electricity at high voltages was more efficient than lower voltages.[4][5]
The terms “low frequency” and “high voltage” refer specifically to early 20th century technology; modern equipment uses different frequencies (50/60 Hz) but similar principles.
Equipment Used in Substation
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid, where high-voltage power lines are connected to lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all contain some key pieces of equipment that perform essential functions.
Transformers are perhaps the most important piece of equipment in a substation.
They step down the voltage of incoming power lines so that it can be distributed to homes and businesses at a safe level. Transformers also help to regulate the flow of electricity, keeping it consistent even as demand fluctuates.
Circuit breakers are another essential piece of equipment in a substation.
These devices protect transformers and other equipment from damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when there is an overload or short circuit. Circuit breakers can be manually operated or automated, and they play a vital role in keeping the electrical grid running smoothly.
Other important pieces of equipment found in many substations include disconnect switches, capacitor banks, and grounding systems.
These components work together to ensure that electricity flows safely and efficiently through the substation – and ultimately to your home or business!
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a critical component of the electric power grid. It is a collection of equipment that transforms high-voltage electricity from transmission lines into lower voltages that are safe for distribution to homes and businesses. A substation also typically includes devices to protect equipment and personnel from electrical faults.
A typical substation includes a transformer to convert voltages, circuit breakers and switches to control the flow of electricity, and busbars to conduct electricity within the substation. Other components may include capacitors, reactors, ground grids, and metering equipment.
Substations are often located near power plants or along major transmission lines.
They come in a variety of sizes, from small units that serve only a few customers on a single circuit to large complexes that handle hundreds of thousands of volts on multiple circuits.
Substation Equipment Names
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It houses high-voltage equipment that transforms electricity from one voltage to another. This equipment includes transformers, circuit breakers, and other electrical devices.
The term “substation” can refer to the entire facility, or just the equipment inside it. The word “equipment” is used more often when referring to the latter. Here are some common names for substation equipment:
Transformer: A device that changes the voltage of an electric current. Transformers are used to step up or step down voltages.
Circuit Breaker: A device that interrupts the flow of electricity in an electrical circuit.
Circuit breakers are used to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits.
Busbar: A metal bar that conducts electricity between two or more objects (such as circuit breakers or transformers).
11Kv Substation Equipment
An 11Kv substation is a power station that provides electricity to homes and businesses in an area. The substation equipment includes transformers, switchgear, and other electrical devices. The 11Kv voltage is high enough to cause serious injury or death if not properly handled, so it is important to be familiar with the proper safety procedures before working on or near this type of substation.
33/11Kv Substation Equipment Pdf
A 33/11kv substation is a power supply system that provides electricity to homes and businesses. It consists of a transformer, switchgear, and associated equipment. The transformer steps down the voltage from the primary distribution line to the secondary distribution line.
The switchgear controls the flow of electricity between the primary and secondary distribution lines. The associated equipment includes meters, relays, and circuit breakers.
Distribution Substation Components
A substation is a vital part of the electricity distribution system. It is where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, and also where currents can be split into separate circuits. The main components of a substation are:
Transformers: These convert voltages from high to low, or the reverse, by inductively coupling two or more windings.
Circuit breakers: These protect equipment and conductors by automatically opening and closing circuits in response to abnormal conditions such as ground faults or excessive current.
Capacitors and reactors: Capacitors store energy in an electric field, while reactors consume energy by creating a magnetic field.
Both are used to regulate voltage and current levels in a circuit.
Busbars: These are made of copper or aluminum and carry large currents between circuit components.
Isolators and disconnectors: These provide an electrically safe way to connect or disconnect parts of the substation without having to shut down the entire facility.
Indoor Substation Components
An indoor substation is a type of substation that houses all or most of its electrical equipment inside a buildings or other structures. This kind of substation is typically used in urban areas where land is expensive, and it can be more aesthetically pleasing than an outdoor substation. Indoor substations can range from small, single-bay facilities to large, multi-story buildings housing hundreds of pieces of equipment.
The main components of an indoor substation are the same as those for an outdoor substation: transformers, switchgear, busbars, and cables. The differences lie in how these components are arranged and protected from the elements.
Transformers in an indoor substation are usually located on the ground floor, with switchgear and busbars above them on mezzanines or upper floors.
This arrangement helps to keep the weight of the transformer close to the ground and minimizes the length of conductor runs between it and the switchgear. Cables are also routed through ducts or conduit to protect them from damage.
Indoor substations have several advantages over their outdoor counterparts.
They’re less likely to suffer from weather-related problems like flooding or ice buildup, and they offer better security against vandalism and theft.
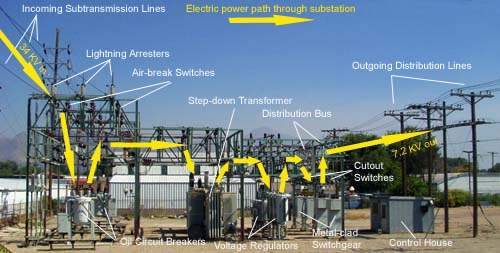
Credit: www.osha.gov
What are the Equipments in a Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, providing a safe and reliable connection between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but all contain key components that perform essential functions.
The following are some of the most important pieces of equipment found in a substation:
1. Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers are used to safely disconnect parts of the electrical system for maintenance or repair. They can also be used to protect against faults, such as power surges, by automatically opening up and interrupting the flow of electricity.
2. Transformers – Transformers are used to raise or lower the voltage level of electricity passing through them.
This is necessary because different parts of the grid operate at different voltage levels – for example, transmission lines typically carry electricity at much higher voltages than distribution lines.
3. Capacitors and reactors – Capacitors and reactors are devices that store or release energy into the system to help regulate voltage levels and improve power quality.
4. Measurement devices – A variety of measurement devices are used in substations to monitor various aspects of the electrical system, including voltage, current, power factor, and frequency levels.
5 .Protective relays – Protective relays are installed throughout the grid to detect abnormal conditions and automatically take corrective action if needed (such as opening circuit breakers). This helps ensure system stability and prevent damage to equipment or outages.
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
A unit substation is a type of electrical substation that is used to change voltage levels between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. The three main components of a unit substation are the transformer, circuit breaker, and disconnect switch.
The transformer is the most important component of the unit substation as it changes the voltage level from the high-voltage transmission line to the lower-voltage distribution line.
The secondary winding of the transformer is connected to the lower-voltage distribution line while the primary winding is connected to the higher-voltage transmission line.
The circuit breaker is used to protect the transformer from overloads by breaking the circuit if there is too much current flowing through it. The disconnect switch is used to isolate the unit substation from both the high-voltage transmission line and low-voltage distribution line so that maintenance can be carried out safely.
What are the Elements Or Main Parts of a Substation *?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines and where electricity is transformed to a lower voltage for use in homes and businesses.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have three basic components: transformers, switchgear, and controls.
Transformers are used to step down the voltage of the transmission line to a level that can be used by distribution lines. Switchgear is used to connect and disconnect equipment from the power supply. Controls help regulate the flow of electricity through the substation.
Which is the First Equipment Installed in Substation?
The first equipment installed in a substation is the switchgear. The switchgear includes the circuit breakers, disconnects, and other necessary components that allow for the safe and efficient operation of the substation.
Introduction to Substation Equipment | Video series Intro | Video #1
Conclusion
Substations are an important part of the electrical grid, and there are a variety of equipments and accessories used in these facilities. The main equipment used in substations includes transformers, circuit breakers, voltage regulators, and surge protectors. These devices work together to ensure that electricity flows smoothly and safely through the substation.
In addition to this essential equipment, substations also use a variety of tools and accessories to help with maintenance and operations. Some of these items include cranes, ladders, cable trays, and switchgear. With all of these equipments and accessories working together, substations are able to provide a safe and reliable source of electricity for homes and businesses.



