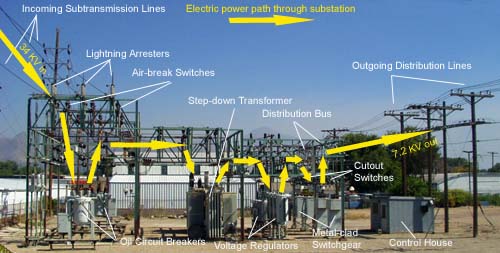
In a substation, the main components are the power transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, busbars, and ground grids. The power transformers raise or lower the voltage of the electricity passing through them so that it can be used by consumers. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage due to electrical faults.
Disconnect switches allow for the isolation of equipment for maintenance or repair. Busbars are used to connect different pieces of equipment within a substation. Ground grids provide a safe path for excess current to flow in case of an electrical fault.
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It serves as a junction point for high-voltage transmission lines and low-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but all have certain key components.
The most important component of a substation is the transformer. The transformer changes the voltage of the electricity passing through it, either stepping it up or down. This is necessary because different parts of the grid operate at different voltages.
For example, transmission lines carry electricity at very high voltages, while distribution lines carry it at lower voltages suitable for household use.
Another important component is the switchgear. This equipment controls the flow of electricity into and out of the substation, and can be used to isolate sections of the grid for maintenance or repair work.
Circuit breakers are also used to protect equipment from damage due to faults or overloads.
Other key components include transformers (for changing voltage levels), capacitors (for storing electrical energy), inductors (for filtering out unwanted frequencies), and relays (for controlling electrically actuated switches). Together, these components make up a substation that plays a vital role in keeping the electric power grid running smoothly.
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electric power grid. It consists of high-voltage equipment that transforms electricity from one voltage level to another. Substations are also responsible for switching electricity between different parts of the grid.
There are four main types of substations: transmission, distribution, converter, and transformer. Transmission substations are located at the highest voltage levels in the power grid and are responsible for moving electricity over long distances. Distribution substations step down the voltage so that it can be used by homes and businesses.
Converter substations change alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), while transformer substations simply transform voltages from one level to another.
Within each type of substation, there are several key components that make up the overall facility. These include switchgear, transformers, circuit breakers, capacitor banks, and more.
Switchgear is used to safely disconnect and connect different parts of the electrical system. Transformers convert voltages so that electricity can flow through different parts of the grid without damaging equipment. Circuit breakers protect equipment by automatically breaking an electrical circuit if there is too much current flowing through it.
Capacitor banks store energy so that it can be released when needed to help regulate voltage levels in the system.
Substation Components And Their Functions Ppt
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, and there are several different types of substations that serve different purposes. The most common type of substation is the transmission substation, which takes high-voltage electricity from power plants and steps it down to a lower voltage so that it can be transported across long distances on transmission lines. Distribution substations then step down the voltage again so that it can be used by homes and businesses.
There are several key components in a typical substation, including transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, and busbars. The transformer is the most important component as it changes the voltage of the electricity passing through it. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation, while circuit breakers protect equipment from damage caused by excessive currents.
Busbars connect all of the components together so that they can work in harmony.
Distribution Substation Components
A distribution substation is a collection of components that distribute electricity from the high-voltage transmission system to the lower voltage distribution system. The main components of a distribution substation are:
1. Transformers – Transformers change the voltage of the electricity so it can be used by homes and businesses.
2. Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers help protect the electrical system by breaking circuits when there is an overload of electricity.
3. Capacitors – Capacitors store electrical energy and help improve power quality by compensating for voltage fluctuations.
4. Disconnect switches – Disconnect switches provide a way to safely disconnect parts of the electrical system for maintenance or repair.
5. Grounding – Grounding helps protect people and equipment from electric shocks and provides a path for electrical current to flow in case of a short circuit or other problem with the system.
Substation Components And Their Functions
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where high-voltage electricity from power plants is transformed to lower voltages for distribution to customers. A substation consists of several key components:
Transformers – Transformers are used to change the voltage of the electricity passing through them. This is done by coiling and uncoiling the wires inside the transformer, which increases or decreases the magnetic field and thus the voltage.
Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment and prevent fires by interrupting the flow of electricity in the event of a fault or overload.
Capacitors – Capacitors store electrical energy and help regulate voltage levels in a substation.
Grounding devices – Grounding devices provide a safe path for excess current to travel in the event of a fault, preventing damage to equipment and minimizing fire risk.
Substation Equipment List
Substation Equipment List
The following is a list of equipment typically found in a substation:
-Circuit breakers
-Capacitors
-Transformers
-Busbars
-Isolators
-Current transformers
Indoor Substation Components
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, or distributed. Indoor substations are more common in urban areas where space is limited. These substations are usually located in buildings or underground vaults.
The three main components of an indoor substation are the transformer, switchgear, and busbar system.
The transformer increases or decreases the voltage of alternating current (AC). The switchgear controls the flow of electricity by opening and closing circuits.
The busbar system distributes power to different parts of the substation.
Indoor substations must be designed to withstand extreme weather conditions and seismic activity. They must also be able to protect equipment from fire, explosion, and chemical fumes.
Transmission Substation Components
Transmission substations are an important part of the electricity grid. They receive power from generators at high voltages and then distribute it to load centers at lower voltages. Substations usually have transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment that help to regulate the flow of electricity.

Credit: www.critterguard.org
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
Substations are an integral part of any electrical grid, and their main purpose is to convert voltage from high to low, or vice versa. A typical substation will have three main components: a transformer, switchgear, and circuit breakers.
The transformer is the heart of the substation, and its job is to change the voltage of the electricity passing through it.
This is done by using coils of wire to create a magnetic field, which can either increase or decrease the voltage.
Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within the substation. It consists of a variety of switches, fuses, and other devices that can be used to direct power where it needs to go.
Circuit breakers are used as a safety measure to prevent damage if there is an overload of electricity flowing through the substation. They work by quickly interrupting the flow of power when needed, and then automatically resetting once the problem has been resolved.
Which Equipment are Used in Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electric power delivery system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and perform other important functions. Without substations, it would not be possible to deliver electricity over long distances or connect different parts of the power grid together.
Substations are made up of a variety of different types of equipment, all working together to help deliver electricity safely and efficiently. Some of the most important pieces of equipment found in a substation include:
-Transformers: Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity travelling through the substation.
This is necessary because electricity produced at a power plant has a very high voltage (tens of thousands of volts), but this needs to be reduced before it can be sent out over power lines to homes and businesses (typically around 240 volts).
-Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are used as a safety measure to protect equipment in the substation (and beyond) from damage due to electrical faults. When an electrical fault occurs, circuit breakers quickly open up, stopping the flow of electricity and preventing damage.
-Capacitors: Capacitors store energy temporarily and help regulate voltage levels in the substation by providing quick bursts of energy when needed.
-Protective relays: Protective relays are specialised devices that monitor conditions in the substation constantly and act automatically if an abnormal condition is detected that could lead to an electrical fault.
-Busbars: Busbars are thick metal bars that conduct electricity within the substation – they provide a low resistance path for current flowing between various pieces of equipment inside the substation.
What are the Components of Substation Switchgear?
A substation is an assembly of equipment for transforming, switching, and controlling electric power in an electric power system. A substation switchgear is the part of the substation that contains the electrical disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to de-energize equipment so work can be safely performed on it.
The three primary components of a substation switchgear are:
1) Circuit breakers – these are used to open and close circuits by interrupting the flow of electricity. The two main types of circuit breakers are air-break and oil-immersed.
2) Disconnect switches – these provide a way to quickly and safely disconnect circuits without having to shut down the entire substation.
3) Fuses – these protect equipment from damage by breaking the circuit when too much current flows through it.
Components of a Substation
Conclusion
Components of a Substations and their Functionality
A substation is a crucial part of the electricity network. It transforms voltage from high to low or the reverse, as well as regulates frequency.
A substation consists of several components that work together to carry out these important functions.
The first component is the power transformer. The power transformer steps down the voltage from the high-voltage transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used in the distribution system.
The second component is the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker protects equipment in the substation by automatically disconnecting circuits when there is an overload or a fault.
The third component is the bus bar.
The bus bar connects all of the components in the substation together.
The fourth component is the switchgear. The switchgear controls and protects equipment in the substation by automatically opening and closing circuits as needed.
The fifth and finalcomponent isthe control panel. The control panel allows operators to remotely control and monitor equipment in the substation.