A substation automation system is a computer-based system that automates the controls and monitoring of equipment in an electrical substation. The system typically includes sensors, control logic, communication networks, and human-machine interfaces that allow operators to monitor and control the substation equipment.
SA-102 l Substation Automation Introduction v1
Substation automation system is a computer based system that helps to monitor and control the electrical equipment in a substation. This system can be used for various purposes such as monitoring the equipment status, controlling the equipment, managing substation data, etc.
Substation Automation System Ppt
Substation automation system is a term used for various types of equipment installed at an electrical substation to monitor and control the substation equipment and devices. The primary goals of substation automation are to improve the reliability, security and efficiency of the power grid.
A substation typically contains high-voltage equipment that can be dangerous to humans, so automated systems help to reduce the need for personnel to enter the substation.
Automated systems also provide real-time monitoring and control of substation equipment, which helps improve grid reliability by reducing downtime due to faults or maintenance issues.
Some common components of a substation automation system include:
-Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system: This is a computerized system that monitors and controls all aspects of the substation equipment from a central location.
It typically includes sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs) and other devices. SCADA systems use various communication protocols to exchange data with field devices, such as Modbus or DNP3.
-Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs): These are devices that are connected to the SCADA system and perform specific functions such as sensing, protection, metering or control.
IEDs typically have their own microprocessor and software application that allows them to perform their specific function.
-Communication network: This is the infrastructure that connects all of the devices in the substation automation system together. The communication network can be either wired or wireless, depending on the specific needs of the substATIONry installation -Protocol converters: In some cases, different types of devices in a substation may not be able to communicate directly with each other due TO incompatible protocols being used.
Protocol converters can be used To bridge these gaps and allow different types OF devices TO communicate with each other indirectly through The converter device.
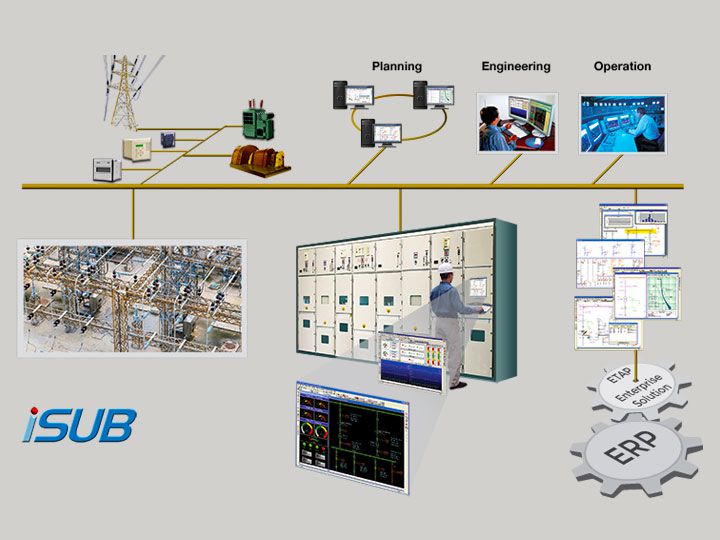
Substation Automation System Architecture
A substation automation system (SAS) is a computer-based system used to remotely monitor and control electrical equipment in a substation. The SAS architecture typically includes three main components: field devices, an intelligent electronic device (IED), and a central management system (CMS).
The field devices are the sensors and actuators that are installed in the substation and connected to the IEDs.
The IEDs are the “brains” of the SAS, containing processing and communication capabilities to interface with the field devices, as well as with the CMS. Finally, the CMS is responsible for monitoring and controlling all of the IEDs in the SAS from a central location.
In addition to these three main components, a fourth component – SCADA systems – is often integrated into SAS architectures.
SCADA systems provide real-time data acquisition and remote control capabilities for electric power systems. By integrating SCADA systems into an SAS architecture, utilities can have a complete picture of what is happening in their substations at all times.
SAS architectures can be designed using different topologies depending on the specific needs of each utility.
The most common topology is called “star” because it resembles a star when viewed from above. In this type of configuration, each IED has its own dedicated communication link to the CMS. This topology provides redundancy in case one of the links fails, but it also requires more cabling than other types of configurations.
Another popular topology is called “ring” because IEDs are configured in a loop around the perimeter of the substation yard. In this type of configuration, each IED has two communication links: one to its immediate neighbor clockwise around the ring, and one to its immediate neighbor counterclockwise around the ring. If one link fails, communications can still be maintained by routing messages through alternate paths aroundthe ring.
Ring configurations generally require less cabling than star configurations because only two links per IED are needed insteadof one link per IED like in stars.

Credit: www.electricity-today.com
What is Substation Automation System?
A substation automation system is a computer-based system that continuously monitors and controls the equipment and processes within an electrical substation. The system includes hardware and software that work together to collect data, process information and control the substation equipment.
The main purpose of a substation automation system is to improve the efficiency and reliability of the power grid.
By automating the monitoring and control of substation equipment, operators can more quickly identify problems and take corrective action. This can help reduce downtime and improve the quality of power delivered to customers.
In addition to improving grid reliability, substation automation systems can also help utilities save money.
For example, by automatically monitoring electricity usage patterns, utilities can make better decisions about when to buy or generate power. And by remotely controlling equipment, utilities can reduce labor costs associated with manual operations.
Substation automation systems are typically designed for specific applications such as transmission or distribution systems.
They may be used in conjunction with other types of automated systems such as SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) or DMS (distribution management system).
What are the Main Three Levels of Substation Automation System?
Substation automation systems are used to control and monitor substations. There are three main levels of substation automation: primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Primary substation automation systems are used to control and monitor the most critical equipment in a substation, such as the transformer, breaker, and busbar.
Secondary substation automation systems are used to control and monitor less critical equipment, such as capacitor banks and reclosers. Tertiary substation automation systems are used to control and monitor non-essential equipment, such as lighting and ventilation.
What is the Difference between Sas And Rtu?
There are a few key differences between SAS and RTU:
SAS is a statistical software package, while RTU is a real-time monitoring system.
SAS can be used for data analysis and predictive modeling, while RTU is mainly used for monitoring purposes.
SAS requires more disk space and memory than RTU.
Which Protocol is Used in Modern Substation Automation System?
In modern substation automation systems, the IEC 60870-5-101 and IEC 60870-5-104 protocols are typically used. These protocols are designed for use in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, and provide communication between substation devices and the control center. IEC 60870-5-101 is used for data exchange between intelligent devices, while IEC 60870-5-104 is used for data exchange between process computers.
Conclusion
Blog post summary:
The blog post discusses the benefits of substation automation systems. The author describes how these systems can improve efficiency and safety while reducing costs.
The post includes a link to a PDF file with more information on substation automation systems.