A busbar is an electrical conductor that carries high current and voltage. It is used to connect electrical equipment in a substation. Busbars are made of copper or aluminum.
They can be flat or tubular.
If you’re looking for busbar images in substation, you’ll find plenty of results with a quick Google search. But what exactly is a busbar? A busbar is simply a conductor that carries electric current within a substation.
Busbars are often made from copper or aluminum, and they can be either bare or insulated. When it comes to substation design, there are many different ways to configure busbars. The most important factor is ensuring that the busbars are properly sized for the amount of current they’ll be carrying.
BUSBAR ARRANGEMENTS IN SUBSTATIONS
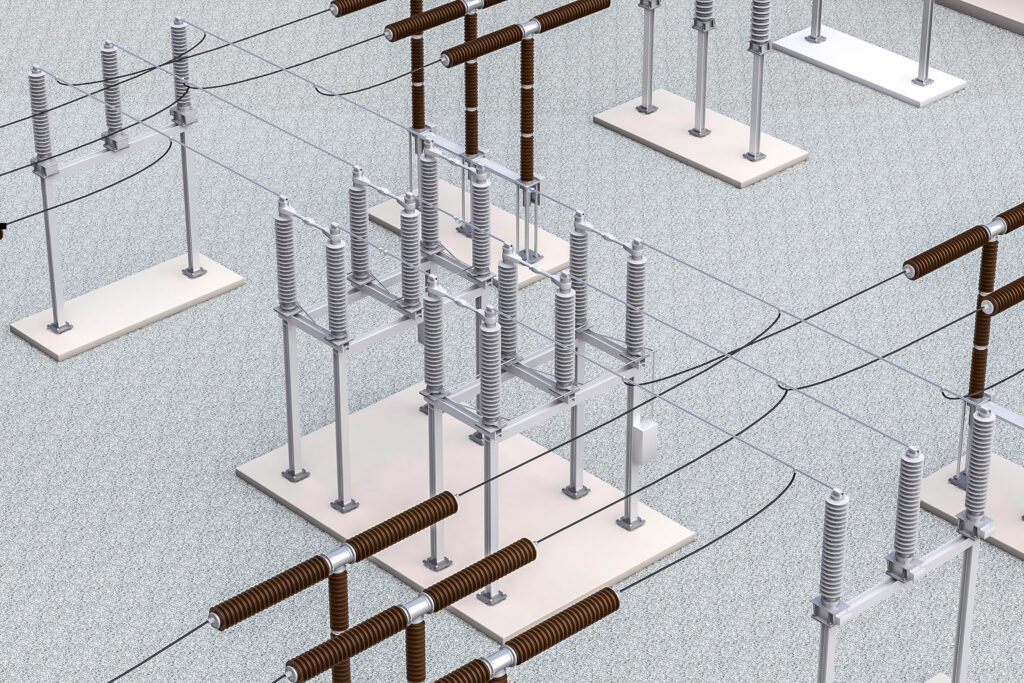
Busbar in Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electricity grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines connect to lower-voltage distribution lines. The substation includes equipment that transforms the voltage of the electricity so that it can be used by homes and businesses.
A key component in a substation is the busbar. The busbar connects all of the electrical components in the substation and allows for the flow of electricity between them. The busbar must be made of materials that are able to withstand high temperatures and pressures, as it carries a large amount of current.
The busbar must be regularly inspected and maintained to ensure that it is in good condition. If there are any problems with the busbar, it can cause serious disruptions to the power supply.
Types of Busbar
A busbar is a type of electrical conductor, typically made of copper or aluminum, that is used to carry high-current electrical power from one point to another. Busbars are often used in industrial and commercial applications, such as switchgear and panelboards, where they are typically bolted or welded to the enclosing equipment.
There are three common types of busbar: flat, rigid, and tubular.
Flat busbars are the most common type and are typically made from sheet metal that has been rolled into a flat strip. Rigid busbars are solid bars that have been extruded or machined from a block of metal. Tubular busbars are hollow tubes that have been formed from sheet metal or drawn through a die.
The size of a busbar is usually expressed in terms of its cross-sectional area; the larger the cross-sectional area, the greater the amount of current it can carry. The width and thickness of a flat busbar are usually equal, while the diameter of a tubular busbar is usually twice its width.
Busbars must be properly sized for the application in order to prevent overheating due to resistance losses.
They must also be installed so that they do not vibrate excessively, which could cause damage to their insulation.
Electrical Bus Bar
An electrical bus bar is a metal strip or bar that conducts electricity within a switchboard, panel board, or other electrical distribution equipment. Bus bars are typically made of copper or aluminum, and they are used to connect outgoing circuit breakers, incoming feeders, and other devices within the distribution equipment.
Bus bars can be either rigid or flexible, and they come in a variety of sizes and shapes depending on the specific application.
They can be either bare or insulated, and the insulation can be either rubber or PVC.
Rigid bus bars are typically used in larger switchboards and panel boards where there is more space for them. These types of bus bars are less likely to vibrate or move around, which makes them ideal for applications where reliability is critical.
Flexible bus bars are often used in smaller enclosures where space is limited. They offer the advantage of being able to fit into tighter spaces, but they may not be as reliable as rigid bus bars due to their potential for movement.
The size of a bus bar is typically determined by the amount of current it needs to carry.
For example, a typical home circuit breaker panel may use 40-amp breakers with #6-gauge wire (which has a capacity of 65 amps). This means that the bus bar connecting these breakers must have a capacity of at least 65 amps in order to safely handle the maximum amount of current that could flow through it.
When choosing a bus bar for your application, it’s important to select one that has sufficient capacity for the amount of current you expect it to carry.
You should also consider the environment in which the bus bar will be installed – if it will be exposed to moisture or corrosive fumes, for example – and select an appropriate material accordingly.
Bus Coupler Diagram
A bus coupler is a device that allows two buses to be connected together. It can be used to connect two different types of buses, or to connect two buses of the same type. A bus coupler typically has a connector on one side that connects to one bus, and another connector on the other side that connects to the other bus.
There are many different types of bus couplers, and they vary in size, shape, and features. Some bus couplers are very simple and only allow two buses to be connected together. Others are more complex and may provide additional features such as routing, filtering, or translation between the two buses.
Bus couplers can be used for many different purposes. For example, they can be used to connect two different types of devices together, or to connect two devices that use different protocols. They can also be used to extend the length of a bus orto create a daisy-chain topology.
Bus Bar Box
A bus bar box is an essential component in any electrical system. It is used to distribute power among various circuits and devices. The box provides a safe, convenient way to connect multiple wires and cables.
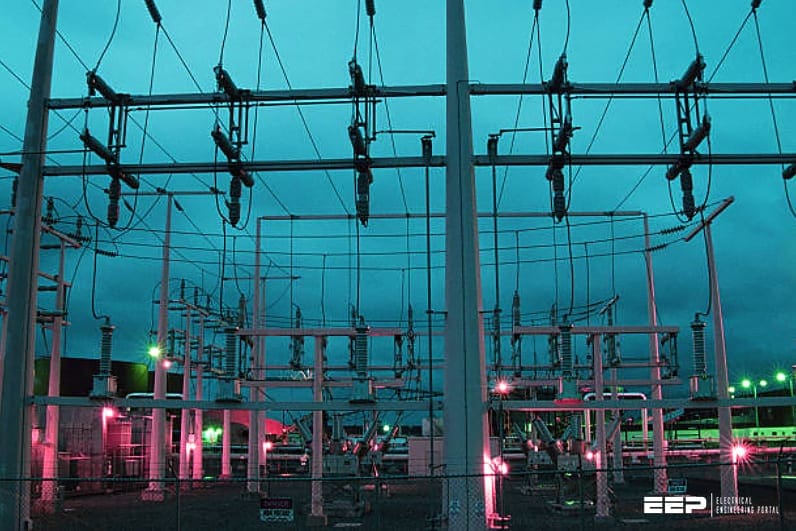

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
What is Busbar in Substation?
Busbar is an electrical conductor that carries current between two or more devices in a substation. It is also used to connect equipment within a substation. Busbars are made of copper or aluminum and can be either solid or hollow.
How Does a Busbar Work?
A busbar is a metal strip or bar used to conduct electricity within an enclosure. Busbars are typically made of copper or aluminum, and they can be either flat or round in shape. The cross-sectional area of a busbar is important for determining its amperage capacity.
Busbars are used to connect electrical components within switchgear, distribution boards, and other electrical equipment. They provide a convenient way to consolidate multiple circuits into a single location. This allows for easy maintenance and repairs, as well as improved safety by reducing the number of live exposed wires.
In many cases, busbars are used in lieu of cables because they have lower resistance and thus can carry more current. They also tend to be less expensive than cables with comparable amperage capacities. However, busbars must be properly sized and installed in order to work effectively and safely.
What are the Different Types of Busbar Arrangement Used in Substation?
A busbar is an electrical conductor that connects two or more circuit elements. Busbars are used to distribute power in substations, switchgear, and other electrical systems. There are several types of busbar arrangements used in substations, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common type of busbar arrangement is the double-busbar system. In this system, two parallel busbars are used to carry the full load of the substation. The advantage of this system is that it can be easily expanded by adding additional busbars.
The disadvantage is that if one busbar fails, the entire system will fail.
Another type of busbar arrangement is the single-busbar system. In this system, only one busbar is used to carry the full load of the substation.
The advantage of this system is that it is simpler than the double-busbar system and therefore less expensive to maintain. The disadvantage is that if the single busbar fails, the entire system will fail.
Where is Busbar Located?
A busbar is a strip of metal or other conductor that is used to provide a low-resistance path for electric current. Busbars are often used to connect multiple electrical devices together, such as in a circuit breaker panel. They can also be used as standalone conductors, such as in high-voltage transmission lines.
Conclusion
The post discusses different images of busbars in a substation. A busbar is an electrical conductor that connects multiple circuits together. They are typically made of copper or aluminum and are used in high-current applications.
The post goes on to discuss the different types of busbars, such as single-pole, double-pole, and multi-pole busbars. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of each type.