The main difference between a high voltage (HV) substation and a low voltage (LV) substation is the voltages they are designed to handle. HV substations take in power at high voltages – usually 132 kV or higher – and use transformers to step this down to lower, more manageable voltages for distribution. LV substations, on the other hand, receive power at much lower voltages – typically below 1 kV – and distribute it without the need for transformers.
LV substations are used for distributing electricity at low voltages (typically 230 V or 400 V) to consumers. HV substations are used for stepping down high voltage from the transmission system to a level suitable for local distribution. The main difference between the two types of substations is in the voltages they use.
How Do Substations Work?
Difference between Lv And Mv Switchgear
The difference between low voltage (LV) and medium voltage (MV) switchgear is the voltage at which they are designed to operate. Low voltage switchgear is typically used for voltages up to 1,000 volts, while medium voltage switchgear is designed for voltages up to 38,000 volts.
The main difference between LV and MV switchgear lies in the amount of insulation required to protect against electrical shock.
LV switchgear uses air as an insulator, while MVswitchgear uses oil or gas. This means that MVswitchgear is more expensive and requires more maintenance than LVswitchgear.
Another difference between LV and MVswitchgear is the way in which they are operated.
LVswitchgear can be manually operated, while MVswitchgear must be automated due to the high voltages involved.
Finally, LV and MVswitchgear differ in terms of the applications they are used for. Low voltage switchgears are typically used in residential and commercial applications, while medium voltage switchgears are used in industrial settings such as power plants and substations.
Difference between Lv And Hv
There are two key types of voltage: low voltage (LV) and high voltage (HV). The main difference between LV and HV is the potential risk they pose. Low voltage is safe to the touch, while high voltage can be dangerous.
That’s why it’s important to know which type of voltage you’re dealing with before attempting any electrical work.
In general, LV systems operate at voltages below 1 kV, while HV systems run at voltages above 1 kV. However, the specific cutoff point can vary depending on the context.
For example, in Europe, the limit for LV systems is 1 kV AC or 0.415 kV DC; in North America, it’s 600 V AC or 300 V DC.
The main reason HV is more dangerous than LV is that it requires heavier insulation to prevent electrical leakage across its surface. This reduces the risk of electrocution if someone comes into contact with an HV conductor.
However, this also means that HV cables are more expensive and difficult to install than LV cables.
Lv, Mv Hv Voltage Ranges
Different types of equipment and appliances require different voltages to operate. The most common voltage ranges are 110-120 volts (known as low voltage or LV), 220-240 volts (known as medium voltage or MV), and 440-480 volts (known as high voltage or HV).
110-120 volt appliances include most small household items such as lamps, computers, printers, and chargers.
220-240 volt appliances include large household items such as clothes dryers, stoves, ovens, water heaters, and air conditioners. 440-480 volt appliances are mostly industrial and include items such as motors, generators, and welding machines.
The difference in voltage is due to the amount of current that each type of appliance requires to operate.
Low voltage appliances require less current than medium or high voltage ones because they have smaller heating elements or use less power overall.
Difference between Hv And Lv Motors
There are many types of motors available on the market, each with its own specific set of features and benefits. When it comes to HV and LV motors, there are some key differences that set them apart. Here’s a look at the main differences between these two types of motors:
HV Motors:
– Higher voltage rating than LV motors
– Can handle more power than LV motors
– More expensive than LV motors
LV Motors:
– Lower voltage rating than HV motor
– Cannot handle as much power as an HV motor
As you can see, there are some key differences between HV and LV motors. If you’re unsure which type of motor is right for your application, be sure to speak with an expert to get guidance.
Mv/Lv Electrical
Mv/Lv Electrical is a specialized form of electrical work that involves the installation, repair and maintenance of medium voltage and low voltage electrical systems. These systems are typically found in commercial and industrial settings, and can include anything from office buildings to factories. Mv/Lv Electricians are trained to work with both AC and DC power, and must be able to safely install, repair and maintain electrical systems of all sizes.
Hv Switchgear Components
HV Switchgear Components
The basic components of HV switchgear are: circuit breakers, disconnectors, earthing switches, and voltage transformers. The function of each is as follows:
Circuit breakers: Used to open and close electrical circuits. Disconnectors: Used to physically disconnect parts of the switchgear. Earthing switches: Used to connect or disconnect the earth (ground) connection.
Voltage transformers: Used to change the voltage level in a circuit.
Hv Mv/Lv Switchgear
High voltage (HV) and medium voltage (MV) switchgear are two types of electrical equipment that are used to control the flow of electricity in a power system. HV switchgear is designed for voltages above 72.5 kV, while MV switchgear is designed for voltages below 72.5 kV.
Both types of switchgear play an important role in ensuring the safe and reliable operation of a power system.
HV switchgear is typically used to connect high-voltage circuits, while MV switchgear is used to connect medium-voltage circuits.
The main difference between HV and MVswitchgear lies in their respective voltage ratings. HVswitchgear is designed to withstand higher voltages than MVswitchgear.
This means that HVswitchgear must be able to safely interrupt higher currents, which requires heavier and more expensive components.
Another key difference between these two types of switchgear is their size. HVswitchgear is typically much larger than MVswitchGear due to the increased strength required to withstand higher voltages .
This can make it difficult to install HVs witch gear in some locations .
High Voltage Switchgear
High Voltage Switchgear
In electrical engineering, high voltage switchgear is equipment used for controlling, protecting and isolating electrical equipment operated at high voltages. The main types of high voltage switchgear are air-insulated switchgear (AIS), gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) and solid dielectric insulated switchgear (SDIS).
AIS is the most common type of high voltage switchgear and is typically used in medium to large substations. It uses air as an insulating medium, which makes it more economical than GIS or SDIS. However, AIS requires more space than GIS or SDIS, and its performance can be affected by environmental conditions such as humidity and contamination.
GIS uses a gas such as sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) as an insulating medium. SF6 is an excellent insulator and has a very low conductivity, making GIS ideal for use in compact spaces with little or no ventilation. GAS is also less susceptible to environmental conditions than AIS.
However, SF6 is a greenhouse gas that can be damaging to the environment if it leaks into the atmosphere.
SDIS uses a solid dielectric material such as polymers or glass as an insulating medium. SDIS offers several advantages over AICs and GICS, including improved reliability, better resistance to environmental conditions and smaller footprint.
Credit: www.distransteel.com
What is Hv And Lv?
High voltage (HV) is an electrical voltage that is significantly higher than the standard voltages used in most electronic devices and appliances. Low voltage (LV) is an electrical voltage that is significantly lower than the standard voltages used in most electronic devices and appliances. The terms are often used to describe different types of electrical circuits or components, with HV being used to describe circuits or components that operate at high voltages, and LV being used to describe those that operate at low voltages.
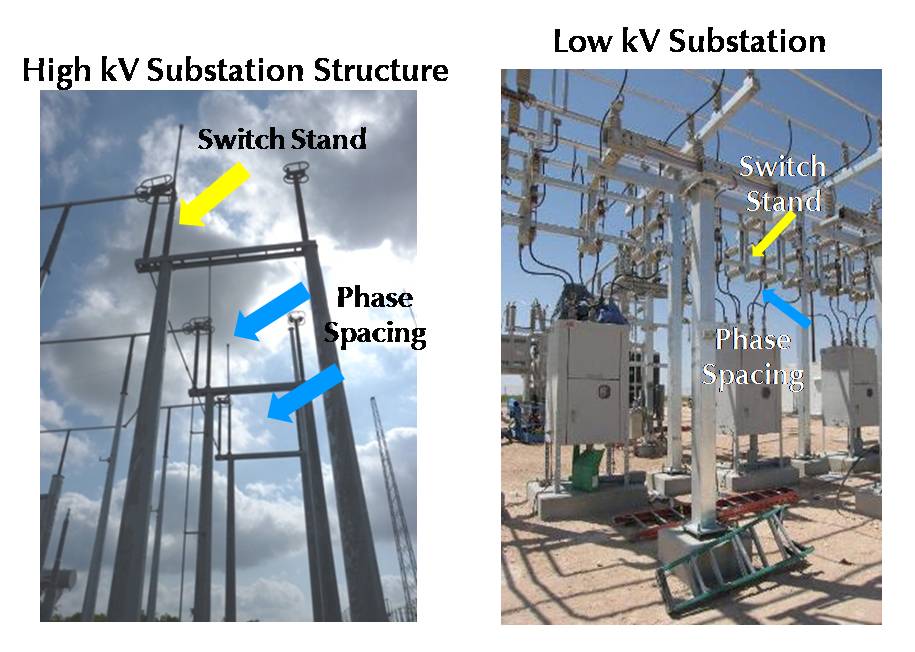
What is an Hv Substation?
An HV substation is a high voltage electrical substation. The main purpose of an HV substation is to step down the high voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by consumers.
HV substations can be either outdoor or indoor, and are typically located near population centers.
Outdoor HV substations are often large and require a lot of space, while indoor HV substations are smaller and can be located in buildings.
The most important component of an HV substation is the transformer. The transformer steps down the high voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by consumers.
Other components of an HV substation include circuit breakers, switchgear, and busbars.
HV substations play an important role in the electricity grid, and without them, electricity would not be able to flow to consumers.
What is Lv Substation?
An LV substation is a low voltage electrical substation. Low voltage refers to the voltages used in domestic and commercial premises, typically between 230 V and 415 V three-phase 50 Hz (in Europe) or 60 Hz (in North America). The main function of an LV substation is to step down the high voltage from the power grid to a level that can be used safely in homes and businesses.
LV substations are usually located at the edge of an electrical distribution network, where the high voltage transmission lines connect to lower voltage distribution lines. The transformer(s) within the substation steps down the voltage so that it can be used by customers on the distribution network.
The secondary winding of the transformer(s) is connected to one or more outgoing low voltage circuits, which distribute power to customers via medium or low voltage cables.
These outgoing circuits are protected by circuit breakers, which isolate faults on the circuit and allow for safe maintenance work to be carried out.
What are the Different Types of High Voltage Substations?
A high voltage substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. These substations take the high voltage electricity from the power plants and step it down to a lower voltage that can be used by businesses and homes. There are several different types of high voltage substations, each with their own unique purpose.
The first type of substation is the transmission substation. This type of substation takes the high voltage electricity from the power plant and steps it down to an even higher voltage for long distance transmission across the country. The second type of substation is called a distribution substation.
This type of substation steps down the voltage even further so that it can be distributed to local businesses and homes.
The third type of substation is called a load center. A load center is typically used by commercial and industrial customers who need a large amount of electricity.
Load centers usually have transformers that step down the voltage to 208 volts, which is standard in North America.
The fourth and final type of high voltage substation is called a generating station. Generating stations are used to produce electricity using turbines that are powered by water, coal, or natural gas.
The electricity produced at these stations is then fed into the grid at high voltages.
Conclusion
HV substations are usually located further away from LV substations since the voltage is higher. The HV substation will have transformers to change the voltage from high to low so that it can be used in the LV substation. The LV substation will then use this lower voltage to power homes and businesses.



