A generation substation is a power plant where electricity is produced. The facility usually contains several high-voltage generators that are connected to the electrical grid.
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then distributed to consumers. A generation substation is a type of substation that specifically generates electricity. These types of substations are usually located near power plants or other sources of electrical energy.
The electricity that is generated at a generation substation is then sent through transmission lines to distribution substations, where it is finally sent to consumers.
Power Generation
Function of Substation
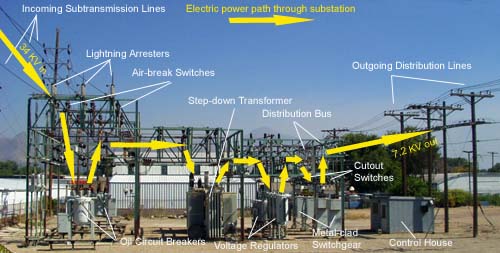
A substation is a crucial piece of the power grid, providing a link between generating plants and distribution systems. Its function is to receive electricity from high-voltage transmission lines and transform it to a lower voltage for distribution to businesses and residences. A substation includes switches,transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment necessary to control the flow of electricity.
The first step in the process is for generators to produce electricity at a very high voltage—on the order of tens of thousands of volts. This electricity is then sent through transmission lines that can span hundreds of miles. When the electricity reaches its destination, it must be transformed to a lower voltage so that it can be safely distributed to customers through smaller power lines.
This transformation takes place at a substation.
Inside the substation, giant transformers reduce the voltage of the incoming electricity so that it can be routed through switchgear—a system of electrical disconnects and fuses used to protect equipment from overloads. From there, circuit breakers cut off the flow of electricity in case of an emergency, such as when a tree falls across power lines and causes them to short-circuit.
Substation Construction
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, distributed and controlled. A substation can be as simple as a transformer to change voltage levels between two points in the distribution system, or it can be a complex multi-functional facility that includes generation, transformation, transmission, distribution and control equipment.
The construction of a substation requires careful planning and execution to ensure safe and reliable operations. The first step is to determine the electrical loads that the substation will need to serve. This information will dictate the size and type of transformers and other equipment that will be required.
The next step is to select a site for the substation. The location must have enough space to accommodate all of the equipment, as well as provide access for maintenance and repair crews. Once the site has been selected, utility easements must be obtained so that power lines can be run to and from the substation.
The next phase of construction involves erecting fences around the perimeter of the site and installing security lighting. Once these items are in place, work can begin on digging trenches for underground cables and setting foundations for above-ground structures. Once all of the concrete has cured, transformers and other large pieces of equipment can be installed inside buildings or metal enclosures called switchgear houses.
Control panels, circuit breakers and other smaller components are installed inside these houses or buildings as well. Finally, all electrical connections are made between various pieces of equipment and tested before energizing the substation..
Distribution Substation
A distribution substation is a power substation that provides electricity to an electrical grid. A typical distribution substation includes:
* A transformer to increase or decrease the voltage of the electricity
* Circuit breakers and switches to control the flow of electricity
* Metering equipment to measure the amount of electricity flowing through the substation
* Protective devices to prevent damage to equipment in case of faults or other problems
Substation Voltage Levels
A substation is a power station that provides equipment for the distribution and/or switching of electric power. The primary voltages at a substation are either 69 kV or 115 kV. Secondary voltages are either 4.16 kV or 13.2 kV.
The typical secondary voltage levels in a substation are as follows:
4160/2400 volts, three-phase, 60 hertz
13200/7620 volts, three-phase, 60 hertz
23040/13380 volts, three-phase, 60 hertz
34560/19920 volts, three-phase, 60 hertz
A 69kv to 4160v transformer would be used for this application .
The following is a list of some common types of loads that may be served by each type of secondary voltage:
4160 volt circuit: general lighting and small motor loads such as air conditioners units , pumps , office equipment , etc.
13200 volt circuit: large motor loads such as elevators , compressors , large air conditioning units , etc.
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the power grid. It is a collection of equipment that transforms high-voltage electricity from the transmission system to lower voltages that are safe for use in homes and businesses. Substations also help to regulate voltage and improve the quality of power.
While substations come in all shapes and sizes, they typically have three main components: transformers, switchgear, and protection devices. The transformer steps down the high voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used on the distribution line. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation and provides isolation between different parts of the substation.
Protection devices monitor conditions within the substation and automatically disconnect circuits if there is a problem.
Electrical substations play a vital role in delivering electricity safely and efficiently to consumers. Without them, our modern world would not be possible!
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a crucial link in the power grid that supplies electricity to homes and businesses. It consists of high-voltage equipment that transforms electricity from one voltage level to another. This blog post will provide detailed information about the components of an electrical substation.
A typical substation includes a transformer that steps down the voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by consumers. The transformer is usually located atop a steel or concrete platform, which also supports other equipment such as circuit breakers, switches, and busbars.
Circuit breakers are devices that open and close circuits automatically to prevent damage from overloads or faults.
Switches are used to route electricity along different paths, while busbars conduct electricity within the substation.
Other components of an electrical substation include surge protection devices, grounding systems, metering equipment, and control panels. These all work together to ensure safe and efficient operation of the substation.
Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a type of power station that transforms electrical energy from one voltage level to another. These stations are typically used to connect two different electrical grids or to connect a grid to large loads such as factories or pumps. Transformer substations can also be used to step up the voltage of electricity before it is sent long distances through power lines.
The first thing that a transformer substation does is convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This conversion is done using a device called a rectifier, which consists of diodes that allow electricity to flow in only one direction. The DC electricity then flows through an inverter, which converts it back into AC electricity at the desired voltage level.
The inverter also steps up the voltage of the AC electricity if necessary. To do this, it uses magnetic fields to force electrons to flow in one direction through the transformer coils. This increases the amount of energy that each electron carries, and thus the overall voltage of the AC current.
What is a Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It serves as a junction point between different parts of the grid, and also provides a place where electricity can be transformed to meet specific needs. Without substations, the electrical grid would not be able to function.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have one common goal: to take electricity from one place and deliver it to another. Substations are typically located near power plants or other large generators, and they use transformers to step down the high-voltage electricity produced by these plants so that it can be used on the lower-voltage distribution system.
Substations also play an important role in regulating voltage and improving power quality.
By automatically adjusting transformer taps, substations can help ensure that voltage levels remain within acceptable limits even as demand on the system fluctuates throughout the day. This helps prevent blackouts and other disruptions caused by voltage fluctuations.

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
What is a Generating Substation?
A generating substation is a type of power plant where electricity is generated. These plants are usually located near sources of fuel, such as coal mines or natural gas fields, and use this fuel to produce electricity. The electricity produced by a generating substation is then typically fed into the power grid so that it can be used by consumers.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all perform the same basic function: to take electricity from the high-voltage transmission system and lower the voltage so it can be used by local distribution systems. There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and switching.
Transmission substations are located between major power plants and regional grid systems.
They step down the voltage from hundreds of thousands of volts to tens of thousands of volts. From there, the electricity is sent to distribution substations.
Distribution substations take electricity from the transmission system and lower the voltage even further, to around 1,000 volts.
This is the level at which power is delivered to businesses and homes through underground cables or overhead wires.
Switching substations don’t actually generate or transmit electricity; their sole purpose is to switch circuits so that electricity can flow through different parts of the grid as needed.
What are the Three Different Types of Substations And Its Purposes?
A substation is a vital part of the electrical power system. It plays an important role in the safe and reliable operation of the power system. A substation can be classified into three types based on its function: switching, transformation, or both.
Switching substations are used to switch circuits or lines. They provide a means of connecting and disconnecting parts of the power system. Transformation substations are used to increase or decrease the voltage level of the electrical energy.
Both type of substations may have facilities for metering, protection, and control functions.
The purpose of a substation is to bring together all necessary components to supply electricity to end users safely and reliably.
What are Major Types of Substation?
The three most common types of substations are high-voltage, medium-voltage and low-voltage.
High voltage substations take power from the transmission line and lower the voltage to a level that can be used by consumers. These substations are usually located near population centers.
Medium voltage substations step down the voltage from the high voltage levels used in transmission lines to the level used by distribution lines. Low voltage substations provide service to specific customers, such as an industrial complex or a large commercial center.
Conclusion
In a rapidly developing world, the demand for energy is constantly increasing. To meet this demand, new power plants are being built and existing ones are being expanded. Along with these changes, the way in which electricity is generated and distributed is also changing.
Generation substations are one of the key components in this process. They play a vital role in taking the electricity generated at a power plant and distributing it to where it is needed. A generation substation typically consists of high-voltage transformers, switchgear, and other equipment.
The design of generation substations has undergone a number of changes over the years as technology has evolved. One of the most significant changes has been the introduction of digital devices and controls. This has led to a more reliable and efficient operation of generation substations.