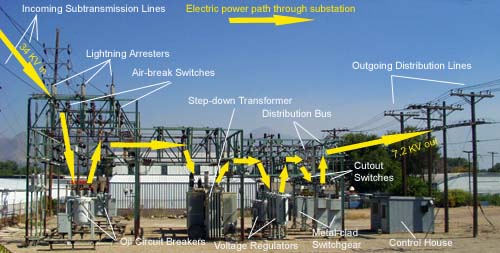
A substation is a crucial part of an electrical grid. It steps up or steps down the voltage of electricity, making it safe for homes and businesses to use. A substation has four main components: transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and control panels.
Transformers increase or decrease the voltage of electricity passing through them. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when there are spikes or other problems. Busbars connect all of the different parts of the substation together.
Control panels help operators keep track of what is happening in the substation and make sure that everything is working properly.
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. It serves as a link between different parts of the grid, and helps to regulate the flow of electricity. A substation typically consists of several key components, which work together to ensure the smooth operation of the grid.
The first component is the transformer. The transformer helps to step up or step down the voltage of electricity, depending on where it is needed. This ensures that electricity can flow smoothly between different parts of the grid.
The second component is the switchgear. The switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation, and ensures that power is directed where it is needed. Without switchgear, electricity would be unable to flow properly through a substation.
The third component is the control room. The control room houses all of the equipment necessary to monitor and control the substation. This includes things like circuit breakers, monitoring equipment, and more.
Without a control room, operators would not be able to effectively manage a substation.
These are just some of the main components that make up a typical substation.
Components of a Substation
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a crucial link in the power supply chain. It steps down high-voltage transmission line voltages to the lower voltages used by distribution circuits and end-use equipment. Substations also switch circuits, isolate faults, and protect against overloads.
The heart of every substation is its switchgear—the devices that control, regulate, and monitor the flow of electricity.
The three main types of switchgear are air-insulated (AIS), gas-insulated (GIS), and vacuum insulated (VIS). AIS uses air as an insulator between live parts, GIS uses an inert gas like sulfur hexafluoride, and VIS uses a vacuum.
AIS switchgear is the most common type in use today because it is less expensive than GIS or VIS and has a smaller footprint.
While each type of switchgear has its own advantages and disadvantages, all share certain common features:
• A bus bar system to conduct electricity
• Switching devices like circuit breakers or disconnect switches to open or close circuits
• Protective relays to sense abnormal conditions on the network
• Instrument transformers to measure voltage or current levels
Substation Components And Their Functions Ppt
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a junction point where two or more circuits connect, and it plays a vital role in regulating voltage and ensuring the smooth flow of electricity. There are several key components to a substation, each with its own important function.
The first component is the transformer. The transformer steps up or steps down the voltage of an electric circuit, depending on whether it is being used in a generation or transmission substation. This ensures that electricity can flow safely and efficiently through different parts of the grid.
Another key component is the switchgear. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity by opening and closing circuits as needed. This helps prevent overloads and maintain safe levels of current throughout the substation.
Finally, protective relays are used to monitor conditions within the substation and automatically shut off power if there is an abnormal condition detected. These relays help prevent damage to equipment and ensure public safety.
Substation Equipment List
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, providing a link between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in all shapes and sizes, but all contain several key pieces of equipment.
Here is a list of some common substation equipment:
Transformer: A transformer helps to step down voltage from high-voltage transmission lines to a level that can be used by lower-voltage distribution lines. Transformers also help to isolate different parts of the electrical grid from each other.
Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker helps to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or faults in the electrical system.
Circuit breakers can automatically disconnect parts of the system that are not functioning properly.
capacitor bank: A capacitor bank helps to improve power quality by compensating for reactive power loads on the system. Capacitor banks are often used in conjunction with other devices, such as transformers and reactors, to provide an overall solution for power quality issues.
voltmeter and ammeter : These devices are used to measure voltage and current levels in the substation. This information is important for monitoring equipment performance and diagnosing problems with the electrical system.
gas-insulated switchgear (GIS): GIS is specialized equipment that helps to increase safety and reliability in substations by reducing the amount of space required for electrical components.
Components of Substation And Their Functions
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. It is a collection of equipment that receives power from the generating station, transforms it to a higher voltage, and then distributes it to consumers. The main components of a substation are:
* Transformers – these raise or lower the voltage of the electricity passing through them. * Circuit breakers – these protect equipment from damage by automatically disconnecting the circuit when there is an overload. * Capacitors – these store electrical energy and help stabilize voltages.
* Reactors – these limit the flow of current in a circuit.
Primary Substation
A primary substation is a type of electrical substation that transforms medium voltage (MV) into low voltage (LV) using transformers. The MV to LV transformation can be done either by step-down or step-up transformers. A primary substation is typically located at the edge of an electrical grid and distributes electricity to a secondary substation or directly to consumers.
A primary substation consists of three main components:
1. Transformers – Transformers are used to change the voltage level of electricity passing through them. In a primary substation, either step-down or step-up transformers are used to convert MV to LV.
2. Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or faults in the electrical system.
3. Metering devices – Metering devices are used to measure various parameters such as voltage, current, power, etc., in an electric circuit.
Classification of Substation
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes. They may be as simple as a metal pole with a few circuit breakers or they may be large, multi-story buildings. But regardless of their size or complexity, all substations serve the same purpose – to provide a safe place to connect and disconnect electrical equipment.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and service. Transmission substations step down high-voltage electricity from the transmission system to the lower voltages used by the distribution system. Distribution substations take this lower voltage electricity and make any necessary adjustments before sending it out to homes and businesses through power lines.
Service substations provide power directly to customers who have their own generators or other special needs.
Within each of these categories, there are further classifications based on the specific type of equipment used. For example, air-insulated switchgear (AIS) is typically used in transmission substations while gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) is more common in distribution substations.
Other factors such as climate and terrain can also influence the type of equipment chosen for a particular location.
No matter what classification a substation falls into, its ultimate goal is to ensure that electricity flows safely and smoothly from one point to another.
Substation Transformer
A substation transformer is a device that transforms high-voltage electricity from transmission lines into the low-voltage electricity used by local distribution systems. The substation transformer also steps down the voltage so that it can be used by customers. Substations are usually located near population centers where there is a demand for electricity.
The first step in power generation is to transform raw energy into electrical energy. This process begins at a power plant, where large turbines spin generators to produce electricity. The electricity produced at the power plant is extremely high voltage – on the order of hundreds of thousands of volts.
This high voltage electricity travels through transmission lines to substations, where the voltage is transformed to a lower level using a substation transformer. From the substation, this lower voltage electricity flows through distribution lines to homes and businesses, where it powers lights, appliances, and other devices.
Substation transformers play an important role in ensuring that electrical power can flow safely and efficiently from its point of generation all the way to end users.
Distribution Substation Components
As a homeowner, you may not think about the substation that provides electricity to your neighborhood very often. But if you’re curious about how it works, this blog post is for you! We’ll cover the basics of distribution substations and the different components that make them up.
A distribution substation takes the high-voltage electricity from the power plant and “steps it down” to a lower voltage that can be used in homes and businesses. This process is done by transformers, which are one of the key components in a substation.
Other important components include circuit breakers, which protect the transformer from damage if there is an electrical surge; capacitors, which help regulate voltage; and disconnect switches, which allow crews to safely work on the equipment.
Distribution substations come in all shapes and sizes, but they all serve the same purpose: to provide safe and reliable electricity to our homes and businesses.

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
A unit substation is a type of electrical substation that is typically used in an industrial or commercial setting. The three main components of a unit substation are the transformer, switchgear, and metering equipment.
The transformer is the heart of the unit substation, and its purpose is to convert voltage from one level to another.
For example, a common use for a transformer in a unit substation is to take high-voltage power from the utility grid and transform it into lower-voltage power that can be used by machinery or other equipment.
The switchgear is responsible for controlling the flow of electricity within the substation. It consists of various switches, circuit breakers, and other devices that allow electricians to safely control the flow of electricity.
The metering equipment is used to measure various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, and power factor. This information is important for both monitoring and troubleshooting purposes.
What is the Most Important Thing in a Substation?
There are many important things in a substation, but if we had to choose one, the most important thing would be the equipment. This includes the transformers, breakers, and switches that make up the substation. Without this equipment, the substation would not be able to function.
Conclusion
The main components of a substation are the power transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and grounding equipment. The power transformers step down the voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by distribution circuits. Circuit breakers are used to open and close electrical circuits.
Disconnect switches allow for maintenance on individual components without affecting the rest of the substation. Grounding equipment protects against electrical shocks.