A smart grid substation is a type of substation that uses advanced digital technology to improve the efficiency and reliability of the electricity grid. Smart grid substations are equipped with sensors, communications systems, and other devices that allow them to collect data about the grid and its operation. This data can be used to optimize the grid’s performance, improve power quality, and provide other benefits.
SMART GRID / GRID SUBSTATION
As the demand for electricity increases, so does the need for a smarter, more efficient grid. The Smart Grid Substation is one way utilities are meeting this challenge. By automating monitoring and controls, the substation can help reduce energy consumption and improve reliability.
The substation is equipped with sensors that monitor conditions such as voltage, current, and temperature. This data is then transmitted to a control center where it can be analyzed to identify potential problems. For example, if the sensors detect an abnormal voltage spike, the control center can take action to prevent damage to equipment or disruption of service.
In addition to improving efficiency, the Smart Grid Substation can also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the need for backup generation during peak demand periods. By providing real-time data on conditions at the substation, utilities can make informed decisions about when and how to use scarce resources like natural gas-fired power plants.
Substation Automation
Substation automation is the process of using technology to automate the operation and management of substations. This can include automating tasks such as monitoring equipment, diagnosing problems, and controlling the flow of electricity. Automation can help improve safety and efficiency while reducing costs.
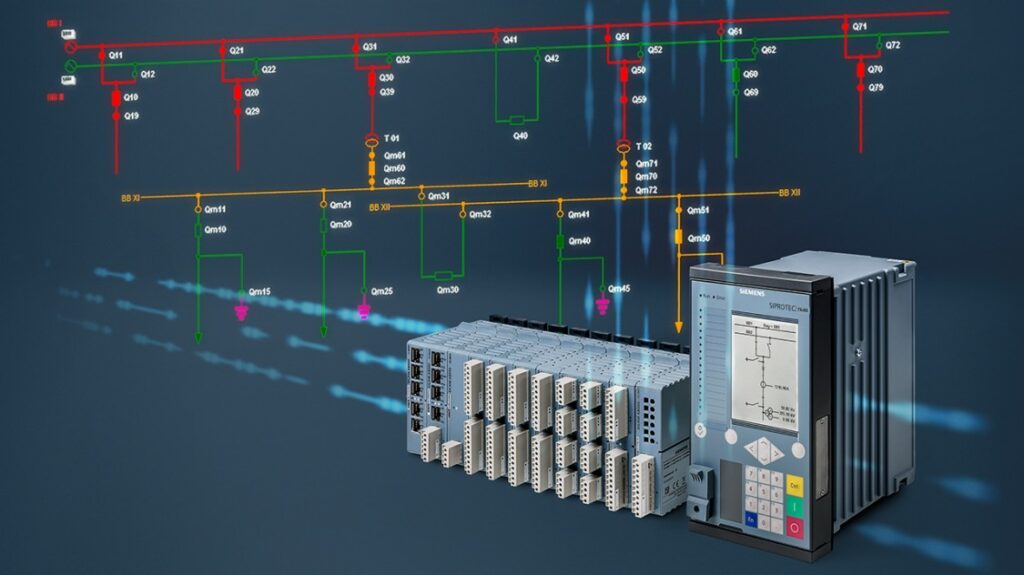
Capgemini Smart Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electricity grid, providing a link between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. A smart substation takes this one step further, adding advanced monitoring and control capabilities that can help improve grid efficiency and resilience.
Capgemini’s Smart Substation solution helps utilities to take advantage of these benefits by providing a complete suite of hardware, software, and services.
The solution includes an Intelligent Electronic Device (IED) for each substation asset, along with a central management system that provides real-time visibility into substation operations. Capgemini’s team of experts can also help with installation, commissioning, and ongoing support.
The benefits of deploying a smart substation are numerous:
• Increased Efficiency: By monitoring asset performance in real time, utilities can identify problems early and take corrective action to avoid outages or other disruptions. This improved visibility also allows for more proactive maintenance planning, which can lead to reduced downtime and increased efficiency overall.
• Improved Resilience: Smart substations are equipped with sensors that can detect faults before they cause an outage.
This information can be used to reroute power around the problem area and minimize the impact of an event on the grid as a whole. Additionally, should an outage occur, smart substations can provide critical data that can help restore service more quickly.
• Greater Sustainability: Reducing energy losses through improved monitoring and control helps utility companies meet their sustainability goals by reducing emissions from power generation.
Types of Smart Grid
There are many different types of smart grid technologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here is a rundown of some of the most popular smart grid technologies:
1. Distributed generation – This type of smart grid technology involves generating electricity at or near the point of use, instead of at a central power plant.
This can help to improve efficiency and reduce transmission losses.
2. Smart meters – Smart meters are used to track electricity consumption in real-time, allowing utilities to better manage demand and avoid peak demand charges. They can also provide customers with information about their energy usage, so they can make more informed choices about how to conserve energy.
3. Renewable energy integration – Smart grids can help to integrate renewable energy sources such as wind and solar into the electrical grid. This can help to increase the amount of clean, renewable energy that is available on the grid, and ultimately help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Demand response – This type of smart grid technology allows utilities to manage demand by providing incentives for customers to use less electricity during times of high demand.
This can help to avoid blackouts and brownouts, and ultimately save money for both utilities and consumers.
Smart Grid Software
The smart grid is an electricity network that uses digital technology to deliver electricity more efficiently and reliably. Smart grid software is the computer programs and applications that enable the smart grid to function.
Smart grid software includes applications for monitoring and managing the flow of electricity, as well as for providing information to consumers about their energy usage.
The software also helps utilities detect and respond to power outages and other problems on the grid.
One of the key benefits of the smart grid is its ability to handle two-way communication between utilities and consumers. This allows consumers to see real-time data on their energy use, so they can make informed decisions about how to conserve energy.
It also enables utilities to send alerts to customers about power outages or other disruptions on the grid.
The smart grid is still in its early stages of development, but it has already shown great promise in improving the efficiency and reliability of our electrical system.
Features of Smart Grid
The Smart Grid is a term used to describe a new electrical grid that incorporates advanced digital technology to monitor, protect and optimize the delivery of electricity. The Smart Grid will allow utilities and consumers to use less energy, reduce costs and improve the reliability of the electrical grid.
Some of the key features of the Smart Grid include:
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI refers to the network of devices that are used to measure electricity consumption at homes and businesses. This data is then transmitted back to the utility so they can manage power demand more efficiently. AMI also allows customers to see their own energy usage data, which can help them save money on their electric bills.
Demand Response (DR): DR programs give customers financial incentives to conserve electricity during times of peak demand. This helps utilities avoid having to build additional power generation capacity, which saves money and reduces environmental impact.
Distributed Energy Resources (DER): DER refers to small-scale power generation sources like solar panels or wind turbines that are located close to where the power is needed.
Using DER can help reduce transmission losses and improve system efficiency.
Intelligent Devices: Intelligent devices are equipped with sensors and communication capabilities that allow them to automatically detect problems on the grid and take corrective action without human intervention. This can help prevent outages, improve system reliability and even self-heal after an outage occurs.
Smart Grid Project
The Smart Grid Project is an initiative of the Department of Energy (DOE) to modernize America’s electricity grid. The project will help to create a more efficient, reliable, and secure electric grid by integrating new technologies such as smart meters, advanced sensors, and two-way communication between utilities and consumers. These new technologies will allow for better management of electricity demand, improved grid operations and maintenance, and enhanced security against threats such as cyberattacks.
In addition, the Smart Grid Project will also help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by enabling greater use of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Smart Grid Company
The Smart Grid Company is a leading provider of smart grid technology and services. The company offers a suite of products and services that enable utilities and other customers to modernize their electricity grids. The company’s products and services include advanced metering, demand response, distribution automation, energy storage, and software and analytics.
The company has more than 1,000 employees and serves customers in more than 30 countries.
Smart Grid Introduction
Smart Grid is a digital upgrade of the traditional electrical grid. The Smart Grid uses two-way communications and computerized controls to manage electricity demand and supply in real time. This helps to improve grid reliability, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
The goal of the Smart Grid is to modernize the electric power system so that it can meet the challenges posed by increasing electricity demand, climate change, and the need for more renewable energy sources.
The benefits of the Smart Grid include:
-Improved grid reliability: With two-way communication and automated controls, the Smart Grid can quickly identify and isolate problems so that they can be fixed more quickly.
This reduces the frequency and duration of power outages.
-Increased grid efficiency: By managing electricity demand and supply in real time, the Smart Grid can reduce overall energy use. This saves money and reduces pollution.
-Greater use of renewable energy sources: The Smart Grid makes it possible to integrate large amounts of renewable energy into the electric power system. This helps us move away from fossil fuels and towards a cleaner, more sustainable future.

Credit: teltonika-networks.com
What is a Smart Grid Substation?
A smart grid substation is a type of electrical substation that uses advanced digital technology to improve the efficiency, reliability and safety of the electricity grid. Smart grid substations are equipped with sensors, communication systems and intelligent electronic devices that allow them to monitor and control the flow of electricity on the grid in real-time. This information can be used to prevent or mitigate problems such as power outages, voltage fluctuations and line congestion.
In addition, smart grid substations can provide data that can be used to improve the overall efficiency of the electricity system.
How Does a Smart Substation Work?
A smart substation is a power substation that uses advanced digital technology to monitor, control and optimize the performance of the electrical grid. The term “smart” refers to the ability of the substation to communicate with other parts of the grid, including other substations, generation plants and load centers. The goal of a smart substation is to improve the efficiency, reliability and security of the electric power system.
Smart substations are equipped with sensors that measure various conditions within the substation, such as voltage, current, temperature and oil level. This information is used by algorithms to determine the best way to operate the equipment in order to provide reliable power while minimizing losses. The algorithms are constantly updated as new data is collected and analyzed.
In addition to monitoring and controlling equipment within the substation, smart substations can also be used to manage distributed energy resources (DERs), such as solar panels and wind turbines connected directly to the distribution network. By integrating DERs into a smart grid, utilities can reduce their reliance on centralized generation sources and make better use of renewable energy resources.
What are the 5 Components of a Smart Grid?
The electric grid is a network of power plants, transmission lines, distribution lines and consumers. It is a complex system that must be constantly monitored and maintained to ensure reliability and safety.
The term “smart grid” refers to the use of advanced technologies to improve the efficiency, reliability and safety of the electric grid.
The goal of the smart grid is to create a more resilient and adaptable grid that can better meet the needs of today’s consumers.
There are five key components of the smart grid:
1. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): AMI refers to the use of digital meters that can communicate with the utility company in real-time.
This allows for two-way communication between the customer and utility company, which can help improve customer service and reduce costs. Additionally, AMI provides utilities with valuable data that can be used to improve operations and planning.
2. Distribution Automation (DA): DA refers to the use of technology to automate voltage regulation and other functions on the distribution network.
This helps improve system efficiency and reduces operational costs. Additionally, DA can help reduce outage duration by quickly identifying and isolating problems on the network.
3×16= 3*16=48 3*8=24 3*4=12 3+8+4=15 15/3=5 so 5 is answer what if not?
What is the Smart Grid System?
The grid. It’s something we all take for granted. But what is it, really?
The grid is the network of power lines and equipment that deliver electricity to our homes and businesses. It’s an amazing feat of engineering, and it’s been around for over a hundred years.
But the grid is aging.
It wasn’t designed for the way we use electricity today. And that’s where the smart grid comes in.
The smart grid is a modernized version of the existing power grid that uses digital technology to make it more efficient, reliable, and secure.
Smart grids are already being used around the world, and they’re coming to the United States too. Here’s everything you need to know about this exciting new technology.
What is the smart grid system?
Simply put, the smart grid system is an upgrade to our current electrical infrastructure. By integrating digital technology into every aspect of the power system – from generation to transmission to distribution – we can make it more efficient, reliable, and secure. In other words: a smarter way to power our homes and businesses.
Why do we need a smart grid?
Our current electrical infrastructure was designed over 100 years ago – before most households even had electricity! Today, however, we rely on electricity for just about everything: from powering our lights and appliances to charging our phones and laptops.
And as our dependence on electricity has grown, so have the challenges with our current system: outdated equipment leads to frequent blackouts; overloaded circuits cause widespread power outages; extreme weather damages power lines; and cyberattacks threaten critical infrastructure like hospitals and banks…just to name a few!
Conclusion
A substation is a critical part of the electric grid, and the recent advances in smart grid technology are making them even more important. A substation takes electricity from high-voltage power lines and transforms it to a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses. Smart grid substations are equipped with sensors and other devices that allow utilities to remotely monitor and control the flow of electricity.
This helps to improve efficiency and reliability, while also reducing costs.