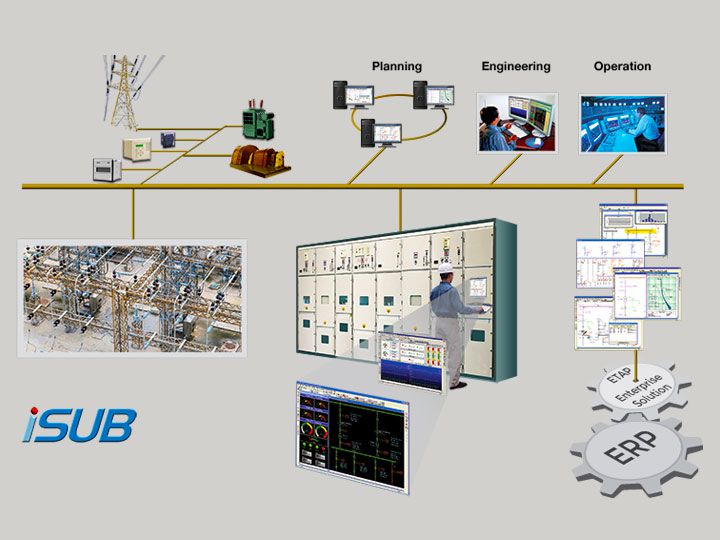
A substation automation system is a computer-based system that automates the operations and controls of equipment at an electric power substation. The system typically includes hardware and software components that are integrated to perform specific functions such as monitoring, control, protection, and communication.
Functions of Substation Automation System || Introduction to Smart Grid ||
Substation automation system is a system that helps to automate the process of monitoring and controlling substations. It helps in reducing the time and effort required for managing substations manually. This system can be used for both small and large scale substations.
Substation Automation System Pdf
Substation Automation System Pdf
The substation automation system (SAS) is a distributed control system that monitors, controls and automates the electrical equipment and processes in a substation. It is used to manage the substation assets, protect the personnel and equipment, ensure the quality of power supply, and improve the efficiency and reliability of power grid operation.
A typical SAS includes three parts:
1) Process Control System: for monitoring and controlling the key parameters of electrical equipment such as voltage, current, frequency, temperature, pressure, etc.
2) Protection System: for detecting faults in electrical equipment and circuits, and automatically isolating them from the rest of the system to prevent further damage.
3) Communication System: for transmitting data and commands between different parts of the SAS and between the SAS and other systems.
Substation Automation System Tutorial
Substation Automation System (SAS) is a comprehensive and integrated solution that helps manage, monitor and control substations remotely. It offers various benefits like reducing operational cost, improving availability and efficiency of power system assets and enhancing grid security.
A substation automation system typically consists of three main parts:
1. Sensors and actuators for monitoring and controlling the equipment in the substation
2. A communication network to connect the devices in the substation with a central control room
3. A centralized control system that monitors and controls the equipment in the substation from the remote location
The sensors and actuators are installed on all major electrical equipment like circuit breakers, transformers, buses, etc. They continuously monitor various parameters like voltage, current, temperature, pressure, oil level, etc. The data collected by these sensors is transmitted to the control room through the communication network.
The centralized control system uses this data to generate real-time status reports of all equipment in the substation. Based on these reports, operators can take necessary actions to maintain or improve the performance of power system assets.
SAS provides many benefits over traditional methods of substation monitoring and control.
One key advantage is its ability to provide real-time information about equipment condition which helps operators make informed decisions about preventive maintenance activities. SAS also offers improved grid security by detecting faults early and preventing outages before they happen.
Substation Automation System Ppt
Substation automation system ppt is a presentation created by experts in the field of substation automation. It provides detailed information about substation automation systems, their components, and how they work. This presentation is perfect for those who want to learn more about substation automation or for those who are looking for specific information about a certain component of a substation automation system.
Substation Automation System Siemens
A substation automation system from Siemens helps make your power distribution more reliable, efficient, and secure. It can be used to monitor and control all aspects of your substation, from the high-voltage equipment to the low-voltage switchgear. The system is designed to work with any type of substation, whether it’s AC or DC.
The benefits of using a substation automation system include:
Improved reliability: By monitoring all aspects of the substation, potential problems can be identified and addressed before they cause an outage. Additionally, automated controls can help reduce human error.
Increased efficiency: Automated systems can provide real-time data on power usage and demand, allowing you to make adjustments to improve efficiency. Additionally, by automating routine tasks such as equipment maintenance, you can free up staff for other tasks.
Enhanced security: Substation automation systems can help improve security by providing remote access capabilities and intrusion detection features.
Additionally, the data collected by the system can be used to improve overall security planning.
Substation Automation System Protocol
Substation automation systems are used to remotely monitor and control substations. These systems typically use a variety of protocols to communicate with devices in the substation, such as Modbus, DNP3, IEC 60870-5-101/103/104, and proprietary protocols.
In this blog post, we’ll take a look at some of the most common substation automation system protocols and how they work.
Modbus is a popular protocol for industrial applications. It is used to connect devices such as PLCs, RTUs, and meters. Modbus uses a simple ASCII or RTU framing and provides basic function codes for read/write operations.
DNP3 is commonly used in SCADA systems. It uses TCP/IP or UDP/IP for transport and has extensive security features. DNP3 also supports encrypted communications using SSL/TLS.
IEC 60870-5-101/103/104 is an international standard for substation automation systems. It defines communication protocols for electric power utilities. IEC 60870-5-101 defines the physical layer specifications, while IEC 60870-5-103 defines the data link layer specifications.
IEC 60870-5-104 defines the application layer specifications.
Proprietary protocols are custom protocols developed by manufacturers for their own products. They are typically not compatible with other vendor’s products.
Substation Automation System Course
Substation automation system (SAS) is a comprehensive and integrated solution that helps you manage your substation operations more effectively. The course provides an overview of the key components of SAS and how they work together to provide a complete solution for substation management.
Components of Substation Automation System
Substation automation system (SAS) is a comprehensive and integrated solution for automating the substation operations. It includes various hardware and software components that work together to provide automated control, protection, monitoring, and data management for the substation equipment.
The main components of SAS are:
1. Sensors: These are installed at various locations in the substation to monitor the status of the equipment. The data collected by the sensors is used by the SAS to take appropriate actions.
2. Communication network: This connects all the devices in the substation with each other as well as with external systems.
The communication network uses different technologies like fiber optics, Ethernet, power line carrier (PLC), etc.
3. Intelligent electronic devices (IEDs): IEDs are installed both inside and outside of equipment cabinets. They perform functions such as protection, measurement, control, etc.
IEDs communicate with each other using protocols such as DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol 3), IEC 61850, Modbus, etc.
4. Human-machine interface (HMI): HMIs are used by operators to interact with SAS for monitoring purposes or for changing settings/configurations when required. HMIs can be either local or remote depending on the requirements.
5 .
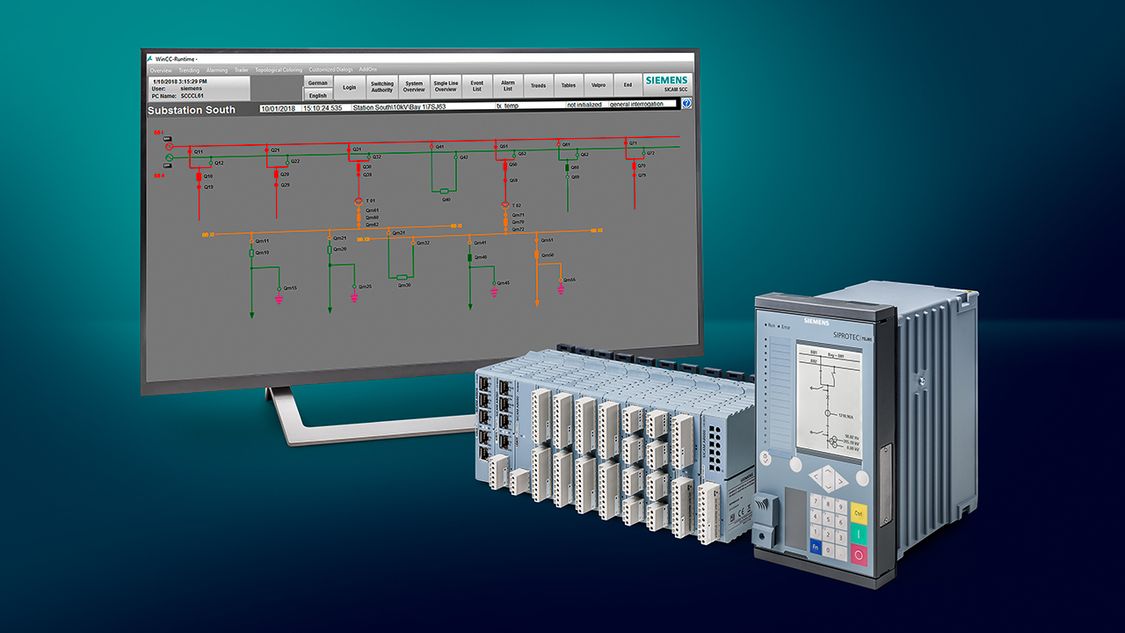
Credit: new.siemens.com
How Does Substation Automation Work?
A substation is an electricity supply station that converts high-voltage electrical transmission lines to lower voltages, or vice versa, for distribution to end users. Substations also regulate voltage and improve power quality. Automation of a substation refers to the use of automatic devices and systems to perform one or more tasks at the substation without direct human intervention.
There are many benefits of automating a substation, including improved reliability, reduced costs, and increased safety. Automated systems can quickly identify and isolate problems, reducing the duration and impact of outages. In addition, automated systems can provide real-time data that helps operators make better decisions about grid operations.
Substation automation generally consists of three main components: intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), communication networks, and control centers. IEDs are devices that measure, monitor, protect, control, or automate various functions within the substation. Communication networks connect the IEDs with each other and with control centers.
Control centers allow operators to remotely monitor and control the substation from a central location.
The most common type of IED used in substation automation is the relay. Relays are used for protection and monitoring purposes; they automatically disconnect equipment when faults are detected in order to prevent damage.
Other types of IEDs include meters, transducers, sensors, actuators, switches, breakers ,and contactors .
Communication networks can be either wired or wireless; both have their advantages and disadvantages. Wired networks are typically more reliable but require more infrastructure investment than wireless networks.
Wireless networks are typically less expensive to implement but may be subject to interference from other radio signals .
There are two main types of control center architectures: distributed and centralized . Distributed architectures place intelligence closer to where it is needed—at individual devices or groups of devices—while centralized architectures place intelligence at a single location .
Both approaches have their advantages and disadvantages; which architecture is best depends on factors such as system size , complexity , application ,and cost .
What is Scada for Substation Automation?
A substation is an electricity supply station that converts high-voltage electric transmission lines to lower voltages for distribution to consumers. A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system is a type of industrial control system that monitors and controls industrial processes through remote devices. In the case of substation automation, SCADA systems are used to remotely monitor and control electrical equipment in substations, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and switchgear.
Substation automation systems typically consist of four main components: sensors, controllers, communication systems, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs). Sensors are used to detect various conditions in the substation, such as voltage levels, current levels, temperatures, etc. The data from these sensors is then sent to controllers which use this information to make automated decisions about how to operate the equipment in the substation.
For example, if a transformer reaches a certain temperature threshold, the controller may automatically open a circuit breaker in order to prevent damage to the transformer.
Communication systems are used to send data between the sensors/controllers and the HMIs. There are many different types of communication protocols that can be used for this purpose (e.g., Modbus, DNP3), but one of the most common protocols used in substation automation is IEC 61850.
This protocol was specifically designed for use in electric power systems and provides several advantages over other protocols (e.g., it supports plug-and-play connectivity between devices).
The HMI is essentially the interface between the SCADA system and operators/engineers. Through the HMI operator can view real-time data from sensors/controllers as well as issue commands to them (e.g., open/close circuit breakers).
Some HMIs also provide historical trending capabilities so that operators can see how equipment has been performing over time.
There are many benefits of using SCADA systems for substation automation including improved safety (due to increased monitoring and automated decision making), reduced costs (through improved efficiency), and improved reliability (due to reduced need for manual intervention).
What are the Main Three Levels of Substation Automation System?
There are three main levels of substation automation system:
1. Basic monitoring and control;
2. Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA); and
3. Distributed energy resources management systems (DERMS).
Each level has different capabilities and features, but all three work together to provide an automated substation solution.
What are the Components of a Substation Automation System?
A substation automation system (SAS) is a collection of electronic devices and software that are used to control, monitor and protect equipment in a substation. The main components of a SAS are:
Substation controllers: These devices act as the brains of the SAS, collecting data from various sensors in the substation and using this information to make decisions about how to operate the equipment.
Substation controllers can be either local or remote.
Communication systems: A communication system is used to send data from the substation controller to other devices in the SAS, such as relays and switches. Communication systems can be either wired or wireless.
Protection devices: Protection devices are used to prevent damage to equipment in the event of an abnormal condition, such as a power surge or loss of power. Common protection devices include circuit breakers and fuses.
Monitoring devices: Monitoring devices are used to collect data about the conditions in the substation, such as temperature, humidity and voltage levels.
This data can be used by operators to troubleshoot problems or identify trends over time.
Conclusion
The substation automation system is designed to improve the efficiency of power distribution. It automates the process of monitoring and controlling the distribution of electricity, making it possible to remotely control all aspects of power distribution. The system can be used to monitor voltage, current, and temperature in real time, as well as to automatically control switches, breakers, and other equipment.
The substation automation system is an important part of the smart grid infrastructure and has the potential to significantly improve the efficiency of power distribution.