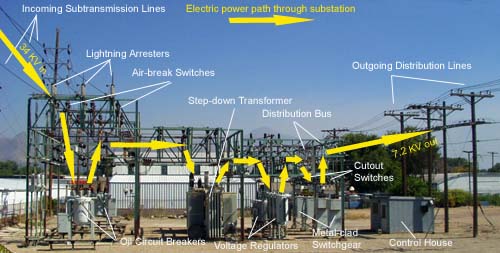
A substation is an electrical installation where high voltage switchgear and transformers are used to drop the voltage to a safe level so that it can be distributed to consumers. The main components of a substation are:
-Transformers: Used to change the voltage levels of alternating current (AC).
-Circuit breakers: Used to open and close circuits.
-Busbars: Used as a connection point for multiple circuit breakers and other equipment.
-Isolators: Used to isolate sections of the substation for maintenance or repair.
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid, and it’s important to understand the different components and their functions. The main components of a substation are the transformer, switchgear, circuit breakers, and ground grid.
The transformer is responsible for changing the voltage of electricity coming from the power plant so that it can be used by homes and businesses.
The switchgear regulates the flow of electricity going to different parts of the substation. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when there’s a problem. And finally, the ground grid helps dissipate any excess electricity so that it doesn’t damage equipment or cause injuries.
Each of these components plays an important role in keeping the electrical grid running smoothly. Without a properly functioning substation, blackouts could occur more frequently and last longer. So next time you see a substation, take a moment to appreciate all its hard work!
Substation Components And Their Functions Ppt
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, providing a link between generating stations and distribution networks. Substations come in a variety of sizes and designs, but all share a common set of components that perform essential functions.
The first component of a substation is the transformer.
The transformer increases or decreases the voltage of electricity passing through it, allowing for safe and efficient transmission over long distances. Transformers also help to regulate the flow of electricity by isolating different parts of the grid.
The second key component is the switchgear.
Switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation and protects equipment from damage due to sudden changes in voltage or current. Circuit breakers are an important type of switchgear that can quickly shut off power in the event of an emergency.
Other important components include busbars, which distribute power to different parts of the substation; instrument transformers, which measure voltage and current; and capacitors and reactors, which help to stabilize voltages.
Substation Components And Their Functions Pdf
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines and where electricity is transformed to a lower voltage for use in homes and businesses. A substation includes several key components, each with a specific function.
The first component is the transformer. The transformer steps down the high voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be used on the distribution line. It also serves to isolate the transmission line from the rest of the substation equipment.
The second key component is the switchgear. The switchgear controls the flow of electricity through the substation and protects equipment from damage due to overloads or faults in the system. It consists of circuit breakers, switches, and other devices that can open or close circuits as needed.
The third key component is the capacitor bank. The capacitor bank stores energy that can be used to help stabilize voltage levels in the event of a sudden drop in demand or an unexpected surge in power consumption. This helps prevent blackouts and brownouts by providing a buffer against fluctuations in power supply and demand.
Substations also typically include control buildings, outdoor lighting, fencing, and other features necessary for safe operation and maintenance of equipment.
Indoor Substation Components
An indoor substation is a type of substation that is typically located indoors, usually in a building. Indoor substations are used to distribute electricity within a facility or campus. Indoor substations are typically used in locations where space is limited, such as in downtown areas.
Indoor substations typically have three main components: the transformer, the switchgear, and the busbar system. The transformer converts high-voltage electricity from the utility company into lower voltages that can be used by the facility. The switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the indoor substation.
The busbar system distributes electricity throughout the facility.
Indoor substations are typically more expensive than outdoor substations because they require more specialized equipment to operate safely indoors. However, indoor substations offer several advantages over outdoor substations, including reduced noise pollution and improved security against weather and vandalism.
Components of Substation
A substation is a crucial part of the electric power grid. It transforms voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and can also isolate different parts of the grid for maintenance. The three main components inside a substation are:
1. Transformers: A transformer changes the voltage of an electric current. In a substation, transformers are used to change high voltages from transmission lines into lower voltages that can be used by consumers.
2. Circuit Breakers: A circuit breaker is used to protect equipment in the event of an electrical fault.
When a fault occurs, circuit breakers open to interrupt the flow of electricity and prevent damage to equipment.
3. Capacitors and Reactors: Capacitors store energy while reactors help control the flow of electricity. Together, these two components help regulate voltage levels in the electric power grid.
Substation Transformer
A substation transformer is a type of power transformer that is used to step down the voltage in an electrical grid. The substation transformer is typically located at the boundary between two different voltage levels in the grid, and its function is to transform the high-voltage electricity from one level to a lower voltage so that it can be used by consumers.
The substation transformer consists of three main parts: the primary winding, the secondary winding, and the core.
The primary winding is connected to the high-voltage side of the circuit, while the secondary winding is connected to the low-voltage side. The core provides a path for magnetic flux created by the flow of current through the windings.
Substation transformers are designed to have a high degree of reliability and safety.
They are typically built with multiple layers of protection, including fuses, circuit breakers, and ground fault protection devices.
Distribution Substation Components
A distribution substation is a power substation that distributes electricity to end users. It generally steps down the voltage from higher voltages used in transmission lines to the lower voltages used in distribution lines. A typical distribution substation contains a transformer, circuit breakers, and metering equipment.
The transformer steps down the voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be safely used in distribution lines. The circuit breaker protects the transformer from damage due to overloads or faults in the system. The metering equipment monitors the flow of electricity and records data for billing purposes.
Distribution substations are typically owned and operated by utilities companies. They are located near population centers so that they can distribute electricity to as many people as possible.
Function of Substation
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and distributed to consumers. It includes equipment for generating, transmitting, and distributing electric power. A substation can also be an assembly of electrical components that regulate the voltage in an electric system.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
A unit substation is a substation that consists of three main components: a transformer, a switchgear, and a control panel. The transformer is responsible for converting the voltage from the high-voltage side to the low-voltage side. The switchgear is responsible for controlling the flow of electricity between the two sides.
The control panel is responsible for monitoring and regulating the operation of the unit substation.
What are the Different Equipment Used in a Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and perform other important functions. Without substations, the electric power grid wouldn’t be able to function.
There are several different types of equipment used in a substation:
Transformers – Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity passing through them. This is necessary because different parts of the grid operate at different voltages.
For example, transmission lines carry electricity at very high voltages (hundreds of thousands of volts), while distribution lines carry electricity at lower voltages (tens of thousands of volts). By using transformers to change the voltage, electrical energy can be efficiently transported across long distances without being lost due to resistance.
Circuit breakers – Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment in the substation from damage caused by excessive currents.
They work by automatically interrupting the flow of electricity when they detect a problem. This prevents damage to equipment and helps prevent blackouts by keeping too much current from flowing through sensitive electrical components.
Capacitors – Capacitors are used to store electrical energy and release it when needed.
They help regulate voltage levels in the substation by providing a “buffer” against fluctuations. This helps maintain a consistent voltage level for customers served by that particular substation.
Some capacitors are also used for power factor correction, which helps improve efficiency by reducing losses due to resistive loads on the system.
Busbars – Busbars are thick metal bars that conduct electricity between various pieces of equipment inside the substation . They provide a low-resistance pathway for current flow and help distribute electricity evenly throughout the substation .
Isolators and disconnectors – Isolators and disconnectors allow certain parts of the substation to be isolated from others so that maintenance can be performed without shutting down the entire facility .
These devices also provide protection against accidental contact with energized equipment .
What are Substation Functions?
Substations are an integral part of the electric power system. They play a vital role in the safe and reliable operation of the electric grid. Substations receive electricity from generating stations and then step down the voltage to a level that can be used by consumers.
They also regulate the voltage and protect equipment from power fluctuations.
What is the Most Important Thing in a Substation?
There are many important factors to consider when designing or operating a substation. However, if we had to choose one most important factor, it would be safety. A substation typically contains high-voltage equipment and components, which can pose serious risks to workers and the public if not properly managed.
Therefore, safety must be the top priority when planning and executing substation projects.
Components of a Substation
Conclusion
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a collection of electrical equipment that transforms high-voltage electricity from transmission lines into the lower voltages used by consumers. Substations also play an important role in voltage regulation and power quality.
There are four main components of a substation: transformers, circuit breakers, switchgear, and ground grids. Transformers raise or lower voltages to meet customer demand or match line voltages. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage due to faults in the system.
Switchgear controls the flow of electricity through the substation. Ground grids provide a safe path for excess current to flow to earth in case of a fault.