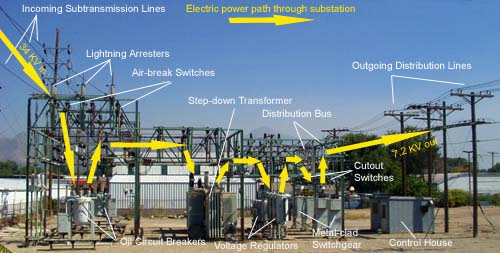
A substation is a critical part of the electricity grid, providing a link between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have three basic components: transformers, circuit breakers, and disconnect switches.
Transformers are used to step down the voltage of high-voltage transmission lines to a level that can be safely handled by lower-voltage distribution lines.
Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to faults or overloads by interrupting the flow of electricity. Disconnect switches are used to isolate equipment for maintenance or repair.
Webinar – Substation The basics of a substation configuration and its components
A substation is a vital component in the electrical power system. Its function is to receive, distribute, and convert electrical energy from one form to another. The most common use of a substation is to convert high-voltage electricity from the transmission system to lower voltages that can be used by consumers.
A substation consists of several key components, each with a specific function:
Transformer: The transformer steps down the voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be used by distribution circuits.
Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage caused by overloads or faults in the circuit.
They are located at both the incoming and outgoing sides of the transformer.
Capacitors: Capacitors store energy and help improve power factor (a measure of how efficiently electricity is being used). They are typically located on the outgoing side of the transformer.
Reactors: Reactors limit current flow and help improve power factor. They are usually located on the incoming side of the transformer.
Substation Components And Their Functions Pdf
A substation is a crucial part of the electricity grid. It takes high-voltage power from the transmission lines and steps it down to a voltage that can be used by consumers. Substations come in all shapes and sizes, but they typically have three main components: transformers, circuit breakers, and disconnects.
Transformers are responsible for stepping down the voltage of the power coming from the transmission lines. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage caused by sudden surges of electricity. Disconnects provide a way to safely shut off power to equipment for maintenance or repair.
Substations play a vital role in keeping the lights on for millions of people around the world. Without them, our modern way of life would not be possible.
Electrical Substation Pdf
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, or distributed. A substation may include one or more transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, voltage regulators, meters, and other equipment. The function of an electrical substation is to receive power from the generating station and transmit it to the distribution system.
A typical substation configuration includes a set of high-voltage transmission lines coming into the facility, where they are connected to one or more transformers. The transformer(s) steps down the voltage so that it can be used by the distribution system. From the transformer(s), lower-voltage distribution lines fan out to serve customers in the area served by the substation.
In some cases, a single substation may serve an entire city or town; in other cases, there may be several substations serving different parts of a large city or rural area.
Underground Substation Ppt
Are you looking for information on underground substations? If so, you’ve come to the right place. This blog post will provide detailed information on this topic, including a description of how underground substations work and the benefits they offer.
An underground substation is a type of electrical substation that is built underground, typically in a trench or tunnel. The purpose of an underground substation is to distribute electricity from a high-voltage transmission line to a lower-voltage distribution system. Underground substations are usually more expensive to build than their above-ground counterparts, but they offer several advantages.
One advantage of an underground substation is that it can be hidden from view. This can be beneficial for aesthetic reasons or because it can help to protect the substation from vandalism or other damage. Another advantage is that an underground location can help to protect the substation against extreme weather conditions like floods or hurricanes.
If you’re considering building an underground substation, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, you’ll need to make sure that the site you choose has enough space for the trench or tunnel that will house the substation. Second, you’ll need to factor in the cost of construction, which can be higher than for an above-ground facility.
Finally, you’ll need to consider whether an above-ground location might be more suitable for your needs.
Electrical Substation Safety Ppt
Working around electrical substations can be dangerous if you don’t take the proper safety precautions. In this blog post, we’ll go over some of the hazards you need to be aware of and how to stay safe while working near or inside an electrical substation.
The first thing to be aware of is the high voltage equipment that is used in substations.
This equipment can cause serious injuries or even death if you come into contact with it. Always make sure that you know where the equipment is located and that you stay clear of it. If you must work near it, always use caution and follow all safety procedures.
Another hazard to be aware of is the possibility of fire. Electrical substations are full of flammable materials, so a fire could quickly spread throughout the entire facility. If a fire does break out, evacuate immediately and do not try to fight it yourself.
Let the professionals handle it.
There are also many chemicals used in electrical substations, so it’s important to be familiar with the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) for these products. These sheets will tell you what precautions need to be taken when handling these substances.
Follow all instructions carefully to avoid exposure or injury.
If you follow these safety tips, you’ll be able to safely work around electrical substations without putting yourself at risk.
Substation Switchgear Components
A substation is a critical part of the electrical power grid. It is a collection of switchgear and equipment that receive electricity from transmission lines and distribute it to lower voltage distribution lines. The substation switchgear components include circuit breakers, transformers, capacitors, and disconnects.
Circuit breakers are one of the most important components in a substation. They protect equipment from damage caused by electrical faults. Circuit breakers can be either air-cooled or oil-cooled.
Air-cooled circuit breakers use compressed air to extinguish the arc when the breaker trips, while oil-cooled circuit breakers use dielectric fluid to cool and extinguish the arc.
Transformers are used to step down the voltage of electricity coming from transmission lines so that it can be used by distribution lines. The two main types of transformers are autotransformers and isolation transformers.
Autotransformers have only one winding, while isolation transformers have two windings that are electrically isolated from each other.
Capacitors are used in substations to improve power factor by storing energy until it is needed. They are usually installed between phases or between a phase and ground.
Capacitors can be either fixed or variable depending on their intended application. Disconnects provide an easy way to open or close circuits without having to de-energize the entire substation.
Substation Bus Schemes Ppt
A substation bus scheme is a power system in which all of the equipment in the substation is connected to one or more buses. The buses may be either ac or dc, but they are usually ac. The advantage of a substation bus scheme is that it simplifies the wiring in the substation by eliminating the need for many individual conductors between the various pieces of equipment.
The disadvantage of a substation bus scheme is that if any one piece of equipment fails, the entire system can go down. In addition, if there is a short circuit on one of the buses, all of the equipment on that bus will be affected.
There are three basic types of substation bus schemes: radial, looped, and meshed.
In a radial bus scheme, each piece of equipment is connected directly to the main bus. If there is more than one main bus, each piece of equipment must be connected to all of them. This type of scheme is used when reliability is not as important as simplicity and cost.
In a looped bus scheme, each piece of equipment is connected to two other pieces of equipment so that there are no dead ends in the system. This typeof scheme provides better reliability than a radialbus scheme because if one pieceof equipmentshould fail, current can still flow throughthe systembygoing aroundthe failedequipment . However , this typeof schemecanbesomewhatmorecomplexandexpensivethanaradialbus schema .
A meshedbus schema has both featuresofradialand loopedsubstationbusschemesso thatifone pathshouldfailthereisanotherpaththatcanbeusedtocarrycurrent . Thisprovidesforthehighestdegreeofreliabilitybutatacostwhichmaybereducedbysizing someoftheconductorsforcarrying lesscurrentthanwouldbethecaseinamorefullymeshedsystem .
33Kv Substation Layout
A 33kv substation is a high voltage electrical substation that uses 33,000 volt (33 kV) AC electricity. They are typically used to distribute electricity to large commercial and industrial customers. A 33kv substation layout usually consists of a number of key components, including power transformers, circuit breakers, and switchgear.
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at each of these components and how they work together to keep your business or facility running smoothly.
Power transformers are one of the most important components in a 33kv substation layout. These devices step down the high voltage from the transmission lines into a lower voltage that can be safely used by customer loads.
Circuit breakers are another critical component, as they provide protection for both the transformer and the customer’s equipment in case of an overload or short circuit. Finally, switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within the substation and between different parts of the distribution system.
When designing a new 33kv substation layout, it’s important to work with experienced professionals who understand all of the factors that need to be considered.
At Utility Systems Engineering, we have over 30 years of experience helping utilities plan and design efficient substations that meet their specific needs.
What is Substation
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then transmitted to an electrical grid. The first substations were built in the late 1800s, and they revolutionized the way electricity was produced and distributed. Today, substations are an essential part of the electrical grid, and they play a vital role in ensuring that power is delivered safely and efficiently to homes and businesses.
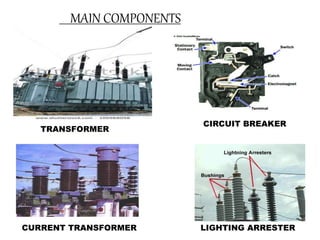
Credit: www.slideshare.net
What are the Parts And Its Function of Substation?
A substation is an assembly of equipment for electric power transmission and distribution. Its primary purpose is to step down the high voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be used by consumers. A substation also serves as a switchyard where various circuits are interconnected and switched.
The function of each part in a substation is briefly described below:
Switchgear: The switchgear contains all the necessary equipment for controlling, protecting and isolating electrical equipment. This includes circuit breakers, switches, fuses and transformers.
Voltage Regulators: Voltage regulators are used to control the voltage in the system by either stepping it up or down as required.
Capacitors: Capacitors are used to store electric charge and help improve power factor by providing reactive power to the system.
Reactors: Reactors are inductive devices that help regulate voltage by absorbing or releasing energy as required.
What are the Main Components of Electrical Substation?
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, distributed and delivered to end users. The main components of an electrical substation are:
-Generators: Generators are used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
-Transformers: Transformers are used to increase or decrease the voltage of an alternating current.
-Busbars: Busbars are used to conduct electricity from one circuit to another.
-Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or short circuits.
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
A unit substation is a three-phase, medium-voltage electrical substation that contains equipment for transforming voltage from the distribution system to the utilization voltage. The three main components of a unit substation are:
#1.
Primary Equipment – This includes the transformer(s), circuit breakers, and associated hardware required to connect the substation to the distribution system.
#2. Secondary Equipment – This refers to the devices used to provide service connections and secondary protection for the primary equipment.
Common secondary equipment includes switchgear, fuses, and metering devices.
#3. Tertiary Equipment – The tertiary or ancillary equipment provides additional functionality and/or safety features for the unit substation as a whole.
What is the Most Important Thing in a Substation?
There are many important things in a substation, but if we had to choose just one, it would be the transformer. The transformer is responsible for stepping down the high voltage from the transmission lines to a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses. Without a transformer, substations would not be able to provide power to their customers.
Conclusion
A substation is a critical part of the power grid. It is where electricity is transformed from high to low voltage or vice versa, and it also serves as a switchyard where power can be routed to different parts of the grid. Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have three basic components: transformers, circuit breakers, and disconnects.
Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity passing through them. The primary winding of a transformer is connected to the high-voltage side of the substation, while the secondary winding is connected to the low-voltage side. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to overloads or faults in the system.
They work by automatically opening and closing circuits as needed. Disconnects are used to isolate equipment for maintenance or repair.