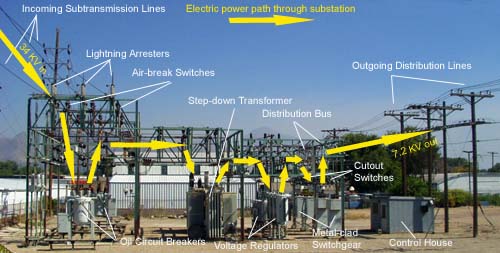
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower-voltage distribution lines and where electricity is transformed from one voltage to another. Substations can be as small as a single transformer or as large as a complex facility with multiple buildings, fences, and switches.
The equipment in a substation performs three essential functions: 1) safety, 2) switching, and
3) power transformation.
The first function of substation equipment is safety. High-voltage transmission lines carry enough electricity to cause serious injury or death if someone comes into contact with them.
Substations have several layers of protection to keep people safe, including physical barriers like fences and signs that warn of the dangers inside; electrical devices like circuit breakers that automatically shut off the flow of electricity if there is a problem; and alarms that sound if someone breaks through the fence or tries to enter the substation without authorization.
The second function of substation equipment is switching. Transmission lines carry electricity at a very high voltage—usually between 115 kilovolts (kV) and 765 kV—and this voltage must be reduced before it can be used by homes and businesses.
This reduction takes place in transformers, which are located inside substations. The transformer changes the voltage so it can be safely sent out on distribution lines, which carry electricity at voltages between 2 kV and 35 kV. Switches are also used in substations to control the flow of electricity on transmission and distribution lines.
The third function of substation equipment is power transformation. Transformers not only reduce voltage; they can also increase it. In some cases, for example, it may be necessary to raise the voltage on a line before sending it over long distances because higher voltages result in less energy loss during transmission.
Introduction to Substation Equipment | Video series Intro | Video #1
A substation is a vital piece of equipment in the power grid. It helps to regulate voltage and distribute electricity from the power plant to homes and businesses. Without a substation, the electricity would be too unstable for safe use.
There are several different types of substations, each with their own specific function. The most common type is the transmission substation, which steps down high-voltage electricity so it can be transported over long distances without losing power. Another type is the distribution substation, which further steps down the voltage so it can be used in homes and businesses.
There are also speciality substations, such as those that generate or store electricity, or that help to regulate frequency.
Substations are usually located away from populated areas due to the risk of fire or explosion. They must also be built to withstand severe weather conditions, as they are often located in remote areas where severe storms can occur.
Substation Equipment Pdf
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Its purpose is to switch or transform voltage levels in order to connect sections of the system at different voltages. A substation equipment pdf typically contains high-voltage equipment such as power transformers and circuit breakers, as well as low-voltage equipment such as control panels and relays.
33/11Kv Substation Equipment Pdf
As the name suggests, a 33/11kV substation is an electrical substation that transforms electricity from 33,000 volts to 11,000 volts. This type of substation is typically used in urban areas to provide power to homes and businesses. The equipment needed for a 33/11kV substation includes:
-A transformer to step down the voltage from 33,000 volts to 11,000 volts
-Circuit breakers to protect the transformer and other equipment from damage caused by overloads or faults in the system
-Disconnect switches to isolate parts of the system for maintenance or repair
-Grounding devices to ensure safety in case of electrical faults
-Lightning protection devices to guard against damage from lightning strikes
The exact configuration of a 33/11kV substation will vary depending on the specific needs of the area it is serving.
However, all of these types of substations share one common goal: providing safe and reliable power to homes and businesses.
Substation Equipment Names
Substation Equipment Names
You may not know what all of the equipment in a substation is called, but each piece plays an important role in delivering electricity to homes and businesses. Here are some common pieces of substation equipment and their functions:
Transformer – A transformer increases or decreases the voltage of an electric current. Transformers are used to step up voltage for long-distance transmission or step down voltage for local distribution.
Circuit breaker – A circuit breaker interrupts the flow of electricity in the event of a fault or overload.
This protects both equipment and people from damage.
Capacitor bank – Capacitors store energy that can be released quickly to meet sudden demands (such as when a large appliance turns on). This helps stabilize voltage and improve power quality.
Reactor – Reactors control the flow of current by introducing inductance (resistance to current flow). This is used to regulate voltage levels in the system.
Function of Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is a place where electricity is converted from high to low voltage or vice versa, and where circuits are switched. The function of a substation is to provide a safe place for these activities to take place.
Substations are usually located near power plants or other large generators of electricity. This proximity allows for easy conversion of the electricity from high to low voltage. Once the electricity reaches the substation, it goes through transformers that lower the voltage.
From there, the electricity can be sent to homes and businesses through distribution lines.
At a substation, circuit breakers are used to open and close circuits as needed. This helps prevent overloads on the system and keeps everyone safe.
Substations also have devices called reclosers that automatically close circuits if they sense an overload. This helps reduce downtime in case of an emergency.
Substations play a vital role in keeping our electrical grid running smoothly.
Without them, we would not be able to use electricity safely or efficiently!
Substation Equipments
Substation equipment includes a variety of devices that are used to control, monitor, and protect substations. These devices include circuit breakers, transformers, voltage regulators, current transformers, capacitor banks, and more.
Circuit breakers are one of the most important pieces of equipment in a substation.
They are used to open and close circuits in order to prevent damage to equipment or interruptions in service. The type of circuit breaker that is used depends on the voltage level of the substation.
Transformers are another critical piece of equipment in a substation.
They are used to step up or step down voltages in order to match the voltage level of the electricity being supplied to the load. Voltage levels in a substation can range from 12 kV to 345 kV.
Voltage regulators are used to maintain a constant voltage level within a substation.
They do this by automatically adjusting transformer tap settings or by shunt capacitors or inductors into or out of the circuit.
Current transformers are used for metering and protection purposes within a substation. They provide an accurate measurement of current flow and can also be used as secondary windings in protective relays.
Capacitor banks are installed at certain points within a power system in order to improve power factor. Power factor is a measure of how efficiently electricity is being utilized and is affected by the inductance of loads such as motors andtransformers .
Substation Components And Their Functions Ppt
A substation is a vital part of the electric power grid. It is where electricity from generating plants is transformed to a voltage that is suitable for distribution to consumers. The three main components of a substation are transformers, switchgear, and control equipment.
Transformers increase or decrease the voltage of electricity passing through them. This is done by using coils of wire to change the magnetic field around the conductor carrying the current. The primary winding has more turns of wire than the secondary winding, which results in a higher voltage on the secondary side.
A typical transformer used in a substation has a primary voltage of 115,000 volts and a secondary voltage of 23,000 volts.
Switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation and includes circuit breakers and switches. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to excessive currents by automatically opening up circuits when predetermined threshold levels are exceeded.
Switches provide manual control over circuits and can be used to isolate sections of equipment for maintenance or repair.
Control equipment monitors conditions within the substation and initiates actions as needed to maintain normal operation. This includes devices such as relays that sense abnormal conditions and initiate corrective action, such as opening up circuit breakers or closing switches.

Credit: electrical-engineering-portal.com
What are the Equipments in a Substation?
In a substation, there are several pieces of equipment that work together to provide power to an electric grid. These include transformers, circuit breakers, and switchgear.
The transformer is the most important piece of equipment in a substation.
It steps up or steps down the voltage of electricity coming into the substation from the power plant. The amount of voltage that a transformer can step up or down is determined by its capacity, which is measured in megavolt-amperes (MVA).
Circuit breakers are used to protect the transformers and other equipment in the substation from damage caused by electrical faults.
A fault is when too much current flows through a conductor, such as a wire. When this happens, the circuit breaker interrupts the flow of current so that it does not cause any damage.
Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within the substation.
It consists of switches, fuses, and relays that allow operators to turn circuits on and off and to isolate sections of the substation for maintenance purposes.
What are Substation Functions?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. Its function is to take the high-voltage electricity from the transmission lines and step it down to a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses. The substation also includes equipment to help protect the grid from surges and other problems.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and then transformed for use in homes and businesses. There are three types of substations: generating, transmission, and distribution.
Generating stations transform mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The most common type of generating station is a hydroelectric dam, which uses the force of moving water to turn turbines connected to generators. Other types of generating stations include nuclear power plants, coal-fired power plants, and solar photovoltaic arrays.
Transmission substations step up the voltage of electricity so that it can be sent over long distances through high-voltage transmission lines.
The voltages used in transmission systems range from 115 kilovolts (kV) to 765 kV. Transmission substations typically have several transformer banks that convert the electricity to different voltages for different parts of the grid.
Distribution substations step down the voltage so that it can be distributed to homes and businesses through lower-voltage distribution lines.
The voltages used in distribution systems are usually between 2 kV and 35 kV. Distribution substations typically have only one or two transformer banks since the electricity needs to be converted to only one voltage for distribution within a small area.
What are the Three Main Components of a Unit Substation?
A substation is an electrical installation consisting of transformers and other equipment for changing the voltage of electric power. They are typically used to connect high-voltage transmission lines to lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations can also be used to connect two different voltages together, such as connecting a 115 kV line to a 13.8 kV distribution system.
The three main components of a substation are the transformer, switchgear, and cabling.
The transformer is the most important component in a substation, as its function is to change the voltage of the electricity passing through it. The transformer has two coils of wire wrapped around an iron core; the primary coil is connected to the high-voltage input, while the secondary coil is connected to the low-voltage output.
When electricity flows through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field that induces a current in the secondary coil. This process increases or decreases the voltage depending on whether the primary and secondary coils are wound in opposite directions (step-up transformer) or in the same direction (step-down transformer).
Switchgear is another critical component in a substation as it controls how electricity flows throughtoutthe facility.
The switchgear includes circuit breakers, which are devices that open or close an electrical circuit automatically when there is too much current flowing through it; disconnect switches, which manually open or close circuits; and ground fault detectors, which monitor currents and sound an alarm if there is excessive current flow due to a ground fault.
Cabling carries electricity from one part of the substation to another and must be properly sized so that it can handle both normal loads and short circuit conditions without overheating.
Conclusion
A substation is a type of power plant that is used to step down the voltage of an electrical system. The equipment inside a substation includes transformers, circuit breakers, and busbars. The transformers are used to change the voltage of the system, while the circuit breakers are used to protect the system from overloads.
The busbars are used to connect the different parts of the substation together.