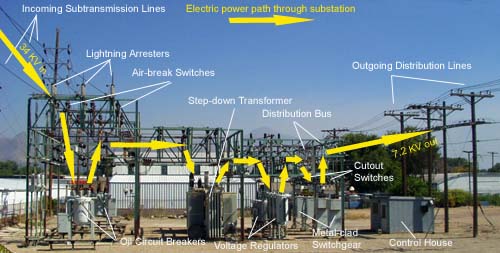
In a substation, power is distributed from the high-voltage side of the transformer to the low-voltage side. The distribution board then distributes power to the loads.
Substations are an important part of our power distribution system. They help to distribute electricity from the power plant to our homes and businesses. Without substations, we would not have the reliable electricity that we depend on every day.
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a critical link in the power grid. It is where electricity from the generating plant is transformed to a higher voltage for transmission on the high-voltage power lines. The substation also steps down the voltage for distribution to consumers.
A typical substation includes:
• transformers that raise or lower voltages
• circuit breakers and switches that isolate equipment and circuits for repair
• metering devices that measure flow, pressure, current, voltage, and power
• protective relays that detect faults and clear them quickly to minimize damage
Substations may be located indoors or outdoors.
Indoor substations are typically found in urban areas where land is expensive. Outdoor substations are usually located in rural areas where land is less expensive.
Substation Equipment
Substation equipment is critical to the functioning of an electric power system. A substation transforms voltage from high to low, or the reverse, and also connects different parts of the system. The primary piece of equipment in a substation is the transformer.
A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer’s coils. A varying current in one coil creates a varying magnetic flux in the other coil(s). This varying magnetic field at the secondary winding induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or “voltage” across it.
The secondary winding can be connected to a load, which draws current from the secondary winding and so reduces or increases the power flowing through it, depending on whether its impedance is lower or higher than that of the primary winding.
If we consider an ideal transformer, then we can say that there is no loss of energy during transformation; all of the input energy appears either as output mechanical work done by forces acting on cores and windings, heating losses within those cores and windings due to resistances present (Joule heating), or magnetic field losses within any air gaps present (hysteresis losses). However, non-ideal transformers do exist in practice, and may exhibit any combination of core loss (magnetic hysteresis) and copper loss (resistive heating).
These factors limit both a transformer’s maximum efficiency as well as its ability to function accurately at very high voltages and currents where dielectric breakdown effects inside insulation materials become significant problems requiring special design considerations for real-world systems.
Substation Pdf
Substations are an important part of the electrical grid. They provide a place where power can be transformed from one voltage to another, and where circuits can be isolated from each other. Substations also house equipment that protects against faults on the electrical system.
A substation typically contains high-voltage equipment, including transformers, circuit breakers, and disconnect switches. The high voltages present in a substation can pose a serious hazard to workers and the public, so safety is a top priority when designing and operating a substation.
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
An electrical substation is a critical piece of infrastructure that helps to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the electric grid. While each substation is unique, there are certain components that are essential for most substations. This blog post will provide an overview of some of the key components of an electrical substation.
One of the most important components of an electrical substation is the transformer. The transformer helps to step up or step down the voltage of electricity as it moves through the substation. This is important in order to maintain optimal power levels and prevent damage to equipment.
Another key component of an electrical substation is the switchgear. The switchgear helps to control the flow of electricity through the substation and can be used to isolate equipment in case of problems. Circuit breakers are also typically included in switchgear assemblies.
Protective relays are another important type of equipment often found in electrical substations. Protective relays help to monitor conditions within the substation and can automatically take corrective action if necessary to protect equipment from damage.
Last but not least, another key part of most electrical substations is communication systems.
Communication systems allow operators to remotely monitor and control operations at the substation. They can also be used for troubleshooting and coordination with other parts of the electric grid.
Power Substation near Me
If you’re looking for a power substation near you, there are a few things to keep in mind. First, power substations are usually located near major population centers or along major transportation routes. Second, they’re typically owned and operated by utilities companies.
And third, they generally don’t allow public access.
That said, if you know where to look, you can usually find a power substation near you. One good place to start is your local utility company’s website.
Many of them have maps that show the locations of their substations. Another option is to use an online mapping service like Google Maps or Bing Maps. Just zoom in on the area where you live or work and look for the telltale signs of a substation: high-voltage transmission lines, large transformers, and fenced-in areas with restricted access.
Keep in mind that even though substations are typically well-marked and easy to find, they’re still dangerous places. High-voltage electricity flows through them 24 hours a day, so it’s important to stay away from them unless you’re authorized to be there. If you see someone trespassing in a substation, call the police or your local utility company immediately.
Grid Substation
A grid substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is where high-voltage transmission lines meet lower voltage distribution lines and transform the electricity so it can be used by consumers.
A grid substation typically contains three main components: transformers, switchgear, and protection devices.
The transformer steps down the high voltage from the transmission line to a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses. The switchgear controls the flow of electricity within the substation. And finally, protection devices help prevent damage to equipment in case of an electrical fault.
Grid substations play a vital role in providing reliable electricity to consumers. Without them, our modern society would not be able to function.
Types of Substation
A substation is a vital part of the electrical grid. They come in many different shapes and sizes, but their main purpose is to take electricity from one place and send it to another. There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and generation.
Transmission substations are used to move electricity long distances. They step up the voltage so that it can travel great distances with little loss. These substations are usually located near power plants where the electricity is generated.
From there, it goes through a series of transformers until it reaches its destination.
Distribution substations are found near population centers. Here, the voltage is stepped down so that it can be used by homes and businesses.
This type of substation also includes circuit breakers and other equipment to help keep the flow of electricity running smoothly.
Generation substations are similar to transmission substations in that they take electricity from one place and send it somewhere else. However, these stations are usually located near hydroelectric dams or other sources of renewable energy.
The electricity generated here is then sent out to the grid where it can be used by consumers.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
What are the 3 Types of Power Distribution?
There are three types of power distribution: direct current (DC), alternating current (AC), and high voltage direct current (HVDC).
Direct current is the flow of electrical charge in one direction only. It is produced by batteries and solar panels, and can be converted to AC using a rectifier.
The main advantage of DC is that it can be transmitted over long distances with minimal loss.
Alternating current reverses direction periodically, typically at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz. It is produced by generators and can be transmitted more efficiently than DC over long distances.
The main disadvantage of AC is that it cannot be stored in batteries.
High voltage direct current uses voltages above 1000 volts and can transmit power over very long distances with minimal losses. However, HVDC systems are expensive to build and maintain, so they are typically used only for large-scale projects such as transcontinental power lines.
What is the Difference between Power Substation And Distribution Substation?
A substation is an electrical installation that forms part of an electricity supply system. Substations may be associated with generation, transmission, distribution and end user applications. A power substation is a type of substation that converts high-voltage, long-distance electric power into the form used by local consumers.
A distribution substation serves as a local transformer, connecting secondary circuits to the primary grid.
The main difference between a power substation and a distribution substation is the voltage level at which they operate. Power substations convert high-voltage electricity from the transmission grid into lower voltages used by local distribution systems.
Distribution substations take electricity from the lower voltage distribution system and convert it into higher voltages for use in secondary circuits.
Where Do Substations Get Power From?
Most substations in the United States get their power from the grid – the system of high-voltage power lines that crisscrosses the country. The grid is made up of a network of transmission and distribution lines, which connect electricity generators to consumers. Substations are typically located at key points along this network, where power can be transformed from one voltage level to another.
In some cases, substations may also be powered by on-site generators or renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines. This is often seen in remote locations or areas where thegrid infrastructure is not well developed.
What are the Three Main Parts of a Substation?
A substation is a power plant where electricity is generated and distributed to consumers. It consists of three main parts: the generator, the transformer, and the distribution system. The generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The transformer increases or decreases the voltage of the electricity. The distribution system distributes the electricity to consumers.
How Do Substations Work?
Conclusion
The article discusses the power distribution in substations. It explains how the electricity is distributed from the substation to different parts of the city. The article also provides a detailed diagram of how the power is distributed in a substation.