There are many different types of substations and the training to become a substation operator varies depending on the company, type of substation, and location. However, there are some commonalities among all operators. All operators must be able to understand basic electricity, have strong communication skills, and be able to work well under pressure.
Are you looking for substation training? There are many different types of substation training available, depending on your needs. Whether you’re a new employee or an experienced veteran, there’s a course out there for you.
Here are just a few examples of the kinds of substation training that might be available:
– Basic electricity and safety training: This kind of course is perfect for those who are new to working with electricity. You’ll learn about the dangers of electricity and how to stay safe while working around it.
– Equipment operation and maintenance: If you’ll be responsible for operating or maintaining any of the equipment in a substation, this type of training will teach you everything you need to know. You’ll learn about the different types of equipment, how to use them properly, and how to keep them in good condition.
– Emergency response procedures: In the event of an emergency at a substation, it’s important that everyone knows what to do.
This type of training will teach you how to respond to various types of emergencies, so that everyone stays safe.
Substation Technician Training
As a substation technician, you will be responsible for the installation, maintenance, and repair of electrical equipment used in power generation and distribution. You will need to have a strong understanding of electrical theory and principles in order to perform your job safely and effectively. There are a number of ways that you can receive training to become a substation technician.
One option is to complete an apprenticeship program. Apprenticeship programs typically last four years and combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction. Many electric utilities offer apprenticeship programs, so this may be a good option if you are already employed by an electric utility company.
Another option is to attend a technical school or community college that offers training in electricity or power technology. These programs usually take two years to complete and will provide you with the necessary knowledge and skills to begin working as a substation technician.
Once you have completed your training, it is important to stay up-to-date on changes in the industry by attending continuing education courses or seminars.
Substation Technician School near Me
There are many schools that offer substation technician training. You can find a school near you by searching online or contacting your local utility company. Many of these programs last for several weeks and cover topics such as safety, equipment operation, and maintenance.
After completing a program, you will be able to work as a substation technician in various industries.
How to Become a Substation Technician
A substation technician is responsible for the installation, maintenance and repair of equipment used in electrical power generation and distribution. substation technicians work with a variety of specialized equipment, including high-voltage transformers, switchgear and circuit breakers.
Most substation technicians have at least a high school diploma or equivalent, although some jobs may require postsecondary education or training.
Many community colleges offer programs in electricity or power technology that can help prepare students for this career. Employers also often provide on-the-job training for new employees.
Substation Technician Test
Substation technicians are responsible for the installation, operation, and maintenance of substation equipment. This equipment includes transformers, breakers, switchgear, and other electrical components. A typical day for a substation technician may involve performing routine maintenance tasks such as checking fluid levels and inspecting equipment for signs of wear or damage.
They may also be called upon to respond to emergencies such as power outages or transformer failures.
The job of a substation technician requires a high level of technical knowledge and skills. Many employers require candidates for this position to possess an associate’s degree in electrical engineering or a related field.
Some positions may also require certification from the National Institute for Certification in Engineering Technologies (NICET).
Ibew Substation Technician Apprenticeship
The International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers offers a substation technician apprenticeship program that can give you the skills and training you need to become a qualified substation technician. This four-year program includes on-the-job training as well as classroom instruction, and can give you the chance to earn journeyman status.
As a substation technician apprentice, you’ll learn how to install, maintain, and repair electrical equipment in substations.
You’ll also gain knowledge about safety procedures, blueprint reading, and basic electricity. Once you complete the program, you’ll be able to work independently as a substation technician.
If you’re interested in becoming a substation technician apprentice, contact your local IBEW union hall for more information.
Substation Technician Salary
As of May 2019, the median annual salary for a substation technician was $62,650, with a range between $54,390 and $72,150. The top 10% of earners made over $79,490 per year. Factors that can affect earnings include experience, geographic location, and type of employer.
Substation technicians are responsible for maintaining and repairing electrical equipment in substations. They install new equipment as needed, perform tests to ensure proper functioning, and troubleshoot problems. In addition to their technical skills, substation technicians must be able to work safely around high-voltage equipment and follow strict safety procedures.
Most substation technicians have an associate’s degree in electrical engineering technology or a related field. Many also complete on-the-job training lasting up to several months. Some states require licensure for workers who maintain high-voltage equipment; requirements vary by state but generally include passing an exam.
Substation Technician Apprenticeship Program
The electric power industry is looking for qualified candidates to fill the role of substation technician. This is a highly technical position that requires a great deal of training and experience. A substation technician apprenticeship program is the perfect way to get your foot in the door and begin a career in this exciting field.
As a substation technician apprentice, you will receive on-the-job training as well as classroom instruction. You will learn how to maintain and repair electrical equipment, read blueprints and schematics, and perform safety checks. Upon completion of the program, you will be prepared to take on the responsibility of keeping our nation’s power grid running smoothly.
If you are interested in a challenging and rewarding career, consider applying for a substation technician apprenticeship program today!
Substation Protection And Control Training
A substation is a vital part of the electrical power system. It is where voltage is transformed from high to low or the reverse, making it an important place for regulation and distribution. The first step in protecting a substation is understanding how it works and what its components are.
This article will provide an overview of substation protection and control training.
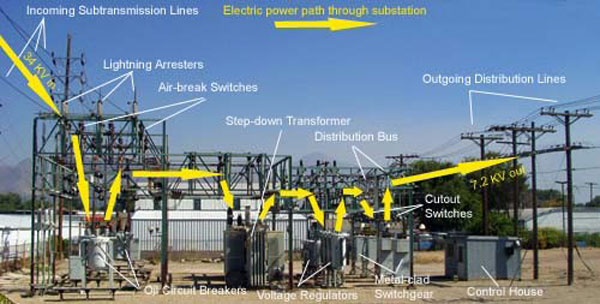
Substation Components
The key components of a substation are the transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and meters.
The transformer changes the voltage from high to low or vice versa, while the circuit breaker protects the system by disconnecting circuits when there is an overload. The busbar carries the current from one part of the substation to another, and the meters measure various parameters such as voltage, current, and power factor.
Protection System Basics
The protection system ensures that the equipment in a substation does not get damaged during faults or abnormal conditions. It consists of three main parts: sensing devices, relays, and trip units. Sensing devices detect any abnormalities such as overcurrents or overvoltages.
Relays receive these signals and activate the appropriate trip units to isolate any faulty equipment from the rest of the system.
Trip units are electrically operated switches that open circuits automatically under abnormal conditions to protect equipment from damage.
Credit: www.electricityforum.com
What is Substation Training?
Substation training is a process and program used to prepare individuals to work safely and effectively in or near substations. The goal of substation training is to provide workers with the knowledge and skills necessary to identify, assess and control hazards when working in or near substations.
Substation training programs typically include classroom instruction on topics such as electrical safety, hazard identification and control, PPE selection and use, work site set-up and management, incident response and more.
In addition to classroom instruction, most substation training programs also include hands-on practical exercises designed to give workers the opportunity to apply what they’ve learned in a safe environment.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
A substation is an electrical installation where high-voltage transmission lines connect to lower-voltage distribution lines. Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all typically have three types of components: incoming circuits, outgoing circuits, and transformers.
Incoming circuits are the high-voltage transmission lines that bring electricity into the substation.
These circuits are sometimes called “primary circuits.” The electricity coming into the substation through these primary circuits is then routed to outgoing circuit breakers.
Outgoing circuits are the lower-voltage distribution lines that carry electricity away from the substation.
Like incoming primarycircuits, outgoing secondarycircuits are also protected by circuit breakers. The voltage on these secondarycircuits is much lower than on primarycircuits because it has been reduced (or “transformed”) by one or more transformers.
Transformers are devices that change (or “transform”) the voltage of an alternating current (AC).
In a substation, transformers step down (lower) the voltage on incoming high-voltage primarycircuits so it can be used on outgoing secondarycircuits for local distribution. Transformers also step up (raise) the voltage on secondarycircuits before it goes back out onto primarytransmission lines.
What are the Requirements of a Substation?
A substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid, providing a link between high-voltage transmission lines and lower-voltage distribution lines. Without substations, the electricity generated at power plants would be unable to flow to homes and businesses.
Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but all contain three essential components: transformers, switches and circuit breakers.
Transformers convert high-voltage electricity into a lower voltage that can be used by consumers. Switches connect or disconnect sections of the electrical grid. Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when there is an overload or short circuit.
What is Substation Basic Knowledge?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where electricity is transformed from one voltage to another, or distributed to homes and businesses. A substation can be as simple as a single transformer, or it can be a complex facility with multiple transformers, switchgear, and other equipment.
The primary purpose of a substation is to deliver electricity at the correct voltage for safe and efficient operation of customer equipment. A secondary purpose is to provide switching capabilities so that circuits can be isolated for maintenance or repair.
Substations are typically located near large loads such as factories or power plants, or at key points in the distribution system where circuits branch off in different directions.
They may also be located near generation sources such as hydroelectric dams.
Substations: Basic Principles | Circuit Breakers | Disconnectors | Relays | CTs & VTs | Arresters
Conclusion
In the electrical industry, a substation is a critical link in the power grid. Without proper training, workers could be seriously injured or even killed.
Substation training is essential for anyone who works with or around substations.
The first step is to understand the basics of electricity and how it works. Next, workers need to learn about the different types of equipment found in a substation and how to safely work with it. Finally, workers should be familiar with the procedures for responding to an emergency situation at a substation.
Substation training can be completed online or in person. There are many resources available to help workers learn about this important topic. With the right training, workers can stay safe and keep the power grid running smoothly.



