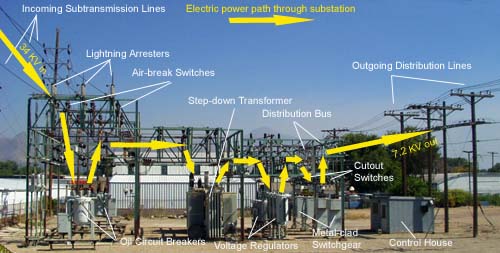
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform other important functions. An electrical substation consists of equipment for switching or transforming electric power circuits, voltages, and wave forms.
This equipment is needed to set up a sub station:
-Transformers
-Circuit breakers
-Switches
-Capacitors
How Do Substations Work?
If you’re considering setting up a substation, there are a few key pieces of information you’ll need to get started. First, you’ll need to know the voltage and amperage of the line or lines that will be feeding into the substation. You’ll also need to know the desired output voltage of the substation – this is typically lower than the input voltage, since the substation’s purpose is to step down (or transform) high-voltage electricity into a lower voltage that can be used safely by homes and businesses.
Finally, you’ll need to have an idea of the size and layout of your substation. This will help determine things like how many transformers you’ll need, where they should be placed, and what type of switchgear will be required. With this basic information in hand, you can begin planning your substation project.
What is Substation
A substation is an electrical installation where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. It may also be used for switching purposes, such as connecting and disconnecting parts of a network. Substations are usually located near power plants or large consumers of electricity.
The word “substation” can also refer to the actual building housing the equipment, especially in American English.
In addition to transforming voltage, a substation may include devices such as circuit breakers and transformers to change the current or frequency. These devices may be necessary because different parts of a power system use different voltages and frequencies.
For example, domestic appliances in most countries operate on alternating current (AC) at a frequency of 50 hertz (Hz), but some industrial equipment needs direct current (DC) at 400 Hz or even higher frequencies. Similarly, while the standard voltage in Europe is 230 volts AC single phase or 400 volts AC three phase, some equipment requires much higher voltages—up to 800 kV DC in HVDC transmission systems.
Substation Standards
In the U.S., substation standards are set by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA). These standards ensure that substations are designed and built to safely deliver electricity to homes and businesses.
The IEEE sets the standards for electrical equipment, including substations.
The NFPA sets the standards for fire safety in substations. Both organizations work together to ensure that substations are safe for workers and the public.
Substation design must meet several criteria, including fire safety, reliability, security, and environmental impact.
Fire safety is a critical concern in substation design. Substations must be designed to prevent fires from starting and spreading. They must also have adequate ventilation to prevent smoke buildup in case of a fire.
Reliability is another important consideration in substation design. Substations must be able to withstand extreme weather conditions, such as high winds, ice storms, and earthquakes. They must also be able to operate during power outages caused by severe weather or other events.
Security is another key concern in substation design. Substations must be designed to protect against physical intrusions, vandalism, and terrorist attacks. Physical security measures may include fencing, lighting, cameras, and guards.
Electronic security measures may include intrusion detection systems and access control systems.
Substation Pdf
Substations are an important part of the electrical grid. They help to ensure that electricity is delivered safely and reliably to homes and businesses. A substation transforms high-voltage electricity from the power plant into lower voltages that are safe for households and businesses to use.
There are two types of substations: transmission and distribution. Transmission substations step down voltage from higher levels so it can be transported over long distances through high-voltage transmission lines. Distribution substations then step down the voltage again so it can be distributed to local neighborhoods through medium-voltage distribution lines.
Most substations are above ground, but some may be built underground or even underwater if necessary. They typically include a variety of equipment, such as transformers, circuit breakers, disconnect switches, and other devices. This equipment helps to protect the system from faults and improve its reliability.
Operators must carefully monitor conditions at all times to ensure that the system is operating safely and efficiently. They use a variety of tools, including computers, sensors, and communication systems, to do this. In the event of a problem, they can take corrective action quickly to minimize any disruption to service.
How Does a Substation Work
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where electricity is transformed from high voltage to lower voltage so that it can be safely delivered to homes and businesses. without a substation, the electrical grid would not be able to function.
Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but they all have three basic components: transformers, switches, and Busbars. The transformer is the most important component of a substation because it transforms high-voltage electricity into lower voltages. Switches are used to connect or disconnect parts of the substation, and busbars are used to conduct electricity from one transformer to another.
In order for a substation to work properly, it must be designed with careful consideration for safety, reliability, and efficiency. Safety is paramount in any electrical system, but it is especially important in a substation because of the high voltages involved. A well-designed substation will have multiple redundancies built in so that if one component fails, there are backup systems in place that can take over.
Reliability is also key because an interruption in power can cause major disruptions for businesses and homeowners alike.
Substation Construction Guidelines Pdf
If you’re in the process of planning or constructing a substation, there are a few key guidelines you’ll need to follow to ensure a successful outcome. This blog post provides an overview of those guidelines, with a focus on the PDF document that outlines them.
The first step is to create a site plan, which will show the location of the proposed substation and all associated facilities.
The next step is to obtain all necessary permits and approvals from local authorities. Once that’s done, you can begin construction.
There are a number of important considerations during construction, including foundation type, building materials, equipment layout, and safety features.
The PDF document goes into detail on each of these topics. Following these guidelines will help ensure that your substation is built safely and efficiently.
Types of Substation Pdf
Substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions.
Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltages. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages.
They are also used as switching stations where circuits are switched on or off.
Substations do not usually generate electricity themselves but they are vital in ensuring that electricity can be directed to where it is needed most effectively.
There are three main types of substation:
1) Transmission Substation
2) Distribution Substation
3) Generator Substation
4) Industrial Substation
1) Transmission Substations: A transmission substation takes power from the generating station and transforms it into a higher voltage so that it can be sent across long distances through high-voltage power lines to another substation. The voltage is then transformed back down to a lower level before being distributed to consumers. These types of substations are usually owned and operated by utility companies.
2) Distribution Substations: A distribution substation receives power from a transmission substation and further transforms it into a lower voltage so that it can be distributed to local businesses and residences through medium-voltage power lines. These types of substations are typically owned by utility companies but sometimes they may be owned by large industrial customers who have their own internal generation and distribution systems. 3) Generator Substations: A generator substation connects a generator to the electrical grid so that the electricity produced by the generator can be fed into the system for use by consumers.
Substation Voltage Levels
In the U.S., the most common voltages for electric power systems are: 120/240 volts (single phase), 240/480 volts (three phase), and 69,000 volts. The highest voltage used in North America is 765,000 volts.
The voltage at which electricity is delivered to customers is called the secondary voltage.
This voltage is transformed from a higher primary voltage at a substation. The type of transformer used and the primary-to-secondary turns ratio determine the secondary voltage.
The first step in selecting an appropriate transformer for a particular application is to identify the system voltages:primary, secondary, and tertiary.
For example, if you were looking at a 3-phase system with transformers that have 240 V primary windings and 24,000 V secondary windings, the tertiary winding would be at 6,600 V.
Electrical Substation Design Calculations Pdf
An electrical substation is a vital part of the electricity supply system. It is used to step down high voltage transmission lines to a lower voltage level, making it safe for distribution to homes and businesses. A substation also monitors and controls the flow of electricity, providing protection against power surges.
There are many factors that must be considered when designing an electrical substation, including the type of equipment to be used, the layout of the facility, and the locations of transformers, switchgear, and other components. Calculations must be made to determine the size and capacity of each piece of equipment, as well as the clearances between them. The goal is to create a safe environment that will minimize the risk of fire or electric shock.
In addition to meeting safety requirements, an electrical substation must also be designed for efficiency and reliability. The distribution system must be able to meet demands at all times, without overloading any part of the system. This requires careful planning and coordination among all those involved in operating and maintaining the substation.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
How Do I Set Up a Substation?
Assuming you would like a blog post discussing how to set up an electrical substation, here are some tips:
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the power grid. Without substations, electricity couldn’t be efficiently distributed throughout a city or region.
But what exactly is an electrical substation? What components does it have? How do you go about setting one up?
This guide will answer all those questions and more.
First, let’s start with the basics: an electrical substation is simply a facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or vice versa. In order for electricity to flow through transmission lines, it first needs to be “stepped down” to a lower voltage at a substation.
From there, it can be safely distributed to homes and businesses before being “stepped up” again at another substation closer to the power plant.
There are three main components of every electrical substation:
1) Transformers – transformers are responsible for changing the voltage levels in electric circuits.
At a typical substation, you’ll find several large transformers that can step voltages down from as high as 345 kilovolts (kV) all the way down to 12 kV or even lower depending on the needs of the local distribution network.
2) Circuit breakers – circuit breakers provide protection against faults (short-circuits) in the system by automatically disconnecting equipment when needed.
3) Capacitors/Reactors – capacitors and reactors help regulate voltage levels in electric circuits by either storing energy temporarily or absorbing excess current respectively.
In addition to these three main components, most substations also have other equipment such as surge arrestors (to protect against lightning strikes), metering devices, and control panels.
Now that we know what an electrical substation is and what its basic components are, let’s take a look at how they’re typically set up…
How Much Land is Needed for a Substation?
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but they all need a large amount of land to function properly. The exact amount of land needed depends on the size and type of substation, but it is typically several acres. Substations must have enough space for all of their equipment, as well as room to expand if necessary.
They also need to be located near power lines and other utility infrastructure. In some cases, substations may need to be built on elevated platforms or mounds to protect them from flooding.
What are the Factors to Be Considered While Designing And Erecting a Substation?
While there are many factors to be considered while designing and erecting a substation, some of the key considerations include:
The type of equipment to be used in the substation – this will dictate the size, layout and configuration of the substation.
The voltage level of the substation – this will determine the size and type of transformers to be used, as well as the required clearances between equipment.
The amount of power to be handled by the substation – this affects everything from the size of conductors to be used, to the number and type of circuit breakers required.
The environment in which the substation is located – this includes both climatic conditions (which can affect things like insulation) and also any hazards that may be present (such as flooding or earthquakes).
What is the Main Components of Sub Station?
A substation is a part of an electrical grid. Its main components are transformers, switchgear, and circuit breakers. Substations transfer electricity from one voltage to another, or from one network to another.
They also help to regulate voltage and improve power quality.
Conclusion
To set up a substation, you will need the following information:
1. The location of the substation.
2. The type of substation equipment that is required for your application.
3. The voltage and current ratings of the equipment.
4. The power rating of the equipment in watts or VA.
5. The impedance of the equipment in ohms or percent reactance.
6. The number of phases required by the equipment (single-phase, three-phase).