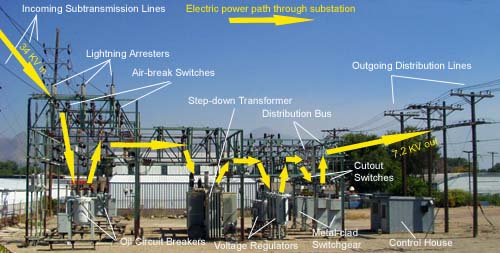
An electric substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, distributed and controlled. Substations are typically located near power plants, but may also be located away from them to provide power to remote areas. The electrical equipment in a substation includes transformers, switches, circuit breakers and other devices.
An electronic substation is a substation that uses electronic equipment for the generation, transmission, distribution and control of electric power. The first large-scale application of electronic equipment in a substation was the installation of static var compensators (SVCs) in the 1970s. Static VAR compensation is a reactive power control technique used to improve power system stability and voltage regulation by creating a controllable impedance in the power system.
Electricity Substation Next to House
If you live in a house that’s next to an electricity substation, you may have some concerns about the safety of the substation and its potential impact on your health. Here’s what you need to know about living next to an electricity substation.
First, it’s important to understand that electricity substations are safe.
The transformer at the substation converts high-voltage electricity from the power lines into lower-voltage electricity that is sent to homes and businesses. The transformer is surrounded by a fence that keeps people and animals away from the equipment.
Second, there is no evidence that living near an electricity substation poses any health risks.
Some people believe that electromagnetic fields (EMFs) emitted by substations can cause cancer, but there is no scientific evidence to support this claim. In fact, studies have found that EMFs at levels typically found around substations are not harmful to human health.
If you’re concerned about living next to an electricity substation, there are some things you can do to reduce your exposure to EMFs.
For example, you can keep windows and doors closed when the substation is in use, and stay inside when the transformer is being serviced or replaced. You can also talk to your utility company about installing EMF-reducing devices on your home’s electrical system.
What is Substation
A substation is an electrical facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. Substations may also be used to change the voltage from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or vice versa. The process of voltage transformation at a substation is known as power transformation.
Electrical Substation near Me
If you live in or near a city, chances are good that there is an electrical substation somewhere nearby. But what exactly is an electrical substation? And what do they do?
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed to consumers. Substations transform high-voltage electricity from transmission lines into the lower voltages used by businesses and households. They also help regulate voltage levels and improve power quality.
Most substations are owned and operated by electric utilities. Some larger industrial facilities also have their own on-site substations. A typical substation contains several pieces of equipment, including:
* Transformers – These devices increase or decrease the voltage of electricity passing through them. * Circuit breakers – These devices automatically shut off the flow of electricity if there is a problem on the line. * Capacitors – These devices store energy so that it can be released when needed to help maintain proper voltage levels.
* Disconnect switches – These devices provide a way to safely disconnect equipment from the power supply for maintenance or other purposes.
Substation Building
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is where voltage is transformed from high to low, or vice versa, in order to keep the power flowing to homes and businesses. The building that houses a substation is just as important as the equipment inside.
Substation buildings must be designed to protect workers and equipment from severe weather conditions, while also providing adequate ventilation and access for maintenance. The buildings must also be strong enough to withstand potential hazards, such as earthquakes or floods.
While the design of substation buildings may vary depending on the location and climate, there are some common features that all substations should have.
These include:
– A control room where operators can monitor and control the flow of electricity
– Switchgear rooms where circuit breakers and other equipment are stored
– Transformer rooms where transformers convert voltage levels
– Cable rooms where power cables are stored and terminated
Types of Substation
There are three types of substations: distribution, transmission, and generation. A distribution substation connects two or more conductor paths with switches so that electricity can be sent to specific locations. A transmission substation increases the voltage so that electricity can travel long distances over power lines before being reduced in voltage at a distribution substation.
A generation substation changes mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Electrical Substation Components
In an electrical substation, there are several different types of components that work together to provide power to a specific area. The main components of an electrical substation are:
-Transformers: Transformers convert high-voltage electricity into lower voltages or vice versa.
This is done by using coils of wire to change the magnetic field in a piece of iron, which then changes the voltage.
-Circuit breakers: Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. When there is too much current flowing through a circuit, the circuit breaker will trip and open the circuit, stopping the flow of electricity.
-Capacitors: Capacitors store electric charge and can be used to stabilize voltage levels in a circuit. They are often used in conjunction with transformers.
-Reactors: Reactors are used to control the flow of current in a circuit by creating inductance.
This is done by winding coils of wire around a core made of iron or another magnetically conductive material.
Function of Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It is a junction point where two or more circuits meet, and it plays an important role in regulating voltage and managing power flow. Without substations, the electrical grid would not be able to function properly.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have the same basic purpose: to take electricity from one place and deliver it to another. Substations are usually located near major load centers, such as cities, factories, or mines. This allows them to effectively manage power demand by connecting and disconnecting different parts of the grid as needed.
Inside a substation, there are several key components that work together to carry out its functions. These include transformers, circuit breakers, busbars, and switchgear. Each component has a specific purpose that contributes to the overall operation of the substation.
Transformers are used to step up or step down voltages as needed. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage due to excessive currents. Busbars are used to connect different parts of the electrical system together.
Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within the substation.
The exact layout of a substation will vary depending on its location and purpose, but all substations share these common components and functions. Without substations, the electrical grid would not be able operate effectively or efficiently.
Distribution Substation
A distribution substation transfers voltage from the distribution grid to the customer’s service drop. The substation steps down the voltage with transformers for customer safety and to minimize line losses in power delivery.
The first piece of equipment in a distribution substation is the busbar.
The busbar connects all of the outgoing circuit breakers and incoming lines together. Circuit breakers are then used to connect individual loads or feeders to the busbar.
The next component in a distribution substation is the transformer.
The transformer steps down the voltage from the grid to a level that is safe for customers and reduces energy losses in transmission.
After the transformer, there is typically a meter bank that monitors electricity flow into each individual load or feeder. These meters allow utilities to billing purposes and can provide valuable data about power usage patterns over time.
The final component of most distribution substations is the switchgear. Switchgear protects against faults on the system by automatically opening circuits when necessary. This helps to prevent damage to equipment and keeps people safe by preventing electrocution hazards.
Distribution substations play an important role in ensuring reliable power delivery to customers connected to the electric grid. By understanding how these facilities work, utilities can better manage their operations and provide quality service that meets customer expectations.
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
What Does an Electric Substation Do?
An electric substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. It is a collection of equipment that transforms high-voltage electricity from the transmission system to lower voltages that are safe for distribution to homes and businesses. Substations also help regulate voltage and improve power quality.
A typical substation includes a transformer that steps down the voltage, circuit breakers or switches that isolate parts of the system for maintenance, and various devices for monitoring and controlling the flow of electricity. Some substations also have generators that can provide backup power if there is an outage on the grid.
Electric substations play a vital role in keeping our lights on and our appliances running.
Without them, we would be living in a very different world.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
A substation is an electrical installation where equipment for generating, transmitting, or distributing electric power is located. The three types of substations are generation substations, transmission substations, and distribution substations.
Generation substations are connected to one or more generators and transform the voltage from the generator(s) to a higher voltage that is then transmitted to a transmission substation.
Transmission substations step up the voltage even further so that it can be transmitted over long distances without significant loss of power. Distribution substations step down the voltage so that it can be used safely by customers.
Substations may also include devices such as switchgear, circuit breakers, transformers, and disconnects.
These devices help to protect equipment and ensure safe and reliable operation of the electrical system.
Can You Live Next to a Substation?
Yes, you can live next to a substation. In fact, many people do. Substations are an integral part of the electric grid and are necessary for providing power to homes and businesses.
While they may not be the most aesthetically pleasing structures, they are typically well-maintained and pose no health or safety risks to those living nearby.
What is the Difference between a Substation And a Transformer?
In the U.S., the terms substation and transformer are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference between the two. A substation is a juncture point in an electrical system where voltage is transformed from high to low, or vice versa. A transformer is a device that changes voltage levels in an electric circuit without changing the frequency.
A typical substation contains one or more transformers, switches, circuit breakers, and other equipment necessary to control the flow of electricity. The primary function of a substation is to switch power from one transmission line to another while maintaining voltage levels constant; however, modern substations can also monitor and record data on the electricity flowing through them.
Transformers are found in both substations and power plants.
In either case, their purpose is to change voltages in order to improve efficiency or connect different parts of the system together. For example, at a hydroelectric dam water spinning turbines generate very high-voltage electricity; this needs to be reduced before it can be sent along power lines to cities—that’s where transformers come in.
How Do Substations Work?
Conclusion
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. Without substations, electricity would have to be generated at a central location and then transmitted across long distances to reach consumers. Substations step down the high voltage of the transmission system to a lower voltage that can be used by businesses and homes.
They also help regulate the flow of electricity and protect equipment from power surges.