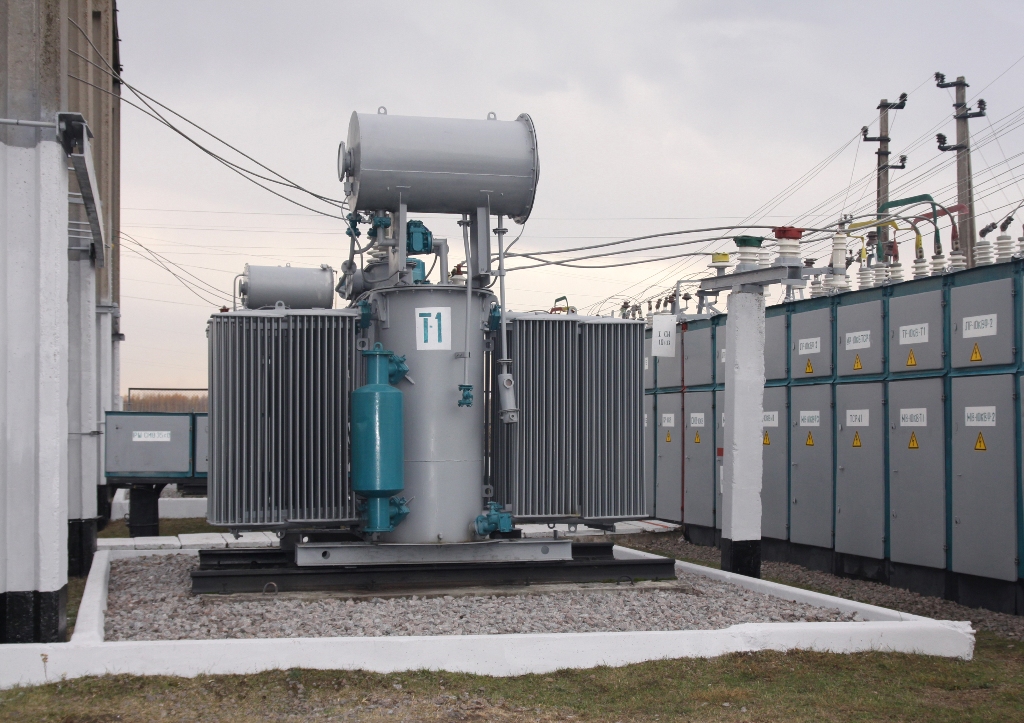
A substation is a part of an electrical grid that transforms voltage from high to low, or the reverse, using transformer(s). A typical substation includes switchgear, busbars, and transformers. The main purpose of a substation is to switch electricity flowing through the power lines.
A substation is an electrical installation that serves as a switchyard where voltage levels are transformed between high voltage transmission lines and lower voltage distribution lines. The substation also serves as a junction where multiple circuits are connected, making it possible to distribute power from a single source to multiple consumers.
What is Substation | Function of Substation | Hindi
What is Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, and/or distributed to consumers. It usually contains several high-voltage transformers and associated equipment for controlling the voltage and flow of electricity. Substations may also contain devices such as circuit breakers and disconnect switches to protect equipment from damage due to faults or overloads.
In an electric power system, a substation transfers power between two or more circuits through transformers. Power stations supply electricity at very high voltages that are not suitable for direct connection to homes or businesses. The first step in reducing the voltage of electricity for end use is accomplished at a substation.
Transformers change the voltage of electric power by magnetic induction between coils wound around opposing cores of iron (or other ferromagnetic materials). The number of turns on the primary coil divided by the number of turns on the secondary coil determines the transformation ratio—for example, a transformer with a primary winding consisting of 500 turns and a secondary winding consisting of 1,000 turns has a transformation ratio of 2:1 (500 ÷ 1,000 = 0.5, or 2:1).
What is Substation
A substation is simply an electrical power switching and/or distribution center. Substations come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but all serve the same purpose: to take in power at high voltages, then switch or distribute that power to lower voltage levels.
Substations may be as small as a cabinet housing a single transformer, or they may be large facilities covering many acres of land.
The size and complexity of a substation depends on the voltages involved, the amount of power to be switched or distributed, and other factors.
At its most basic, a substation consists of one or more transformers to step down the voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be used by local distribution circuits. The transformer(s) are typically housed in an enclosure called a transformer pit.
A typical substation also has devices for switching circuit breakers and disconnects; protection relays; metering equipment; and control circuitry.
Types of Substation
In power engineering, a substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels.
A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different alternating current systems.
These transformers may have taps to change the voltage level slightly if required. Large power users may have private substations.
Some substations are owned by independent grid operators or utilities instead of the company that owns the generators themselves. An example of this is in California where many private generator companies own their own distribution infrastructure but there is only one grid operator: California ISO (CAISO).
Substations can be on ground level, underground, or air-insulated depending on equipment used within it and land availability.
High-voltage equipment is often mounted on steel frames called gantries for site safety reasons. Oil-filled equipment uses pressurized mineral oil as an insulator while SF6 gas has replaced it in some cases due to its superior insulation qualities compared to oil’s especially when it comes to arc flash reduction in medium-voltage switchgear.[1] The site must also be able to protect workers from electrostatic discharges that could occur during work on high-voltage equipment.
[2]
There are five main types of Substations:[3][4]
1) Step up Substation: The primary purpose of a step up substation is increase the voltage from generation source prior feeding into Transmission network .
This type increases voltage by using Transformers .For Instance , Wind farms connected directly with 33KV network , so wind farm will have a Step up Substation which transforms 33KV into 132/220Kv for feeding into Transmission network . From above image you can see , how transformer works inside SUBS .
It has 3 phases Primary winding & 3 phase Secondary winding which are separated by magnetic core inside Transformer tank filled with insulating Oil (Mineral oil / Naphtha ).
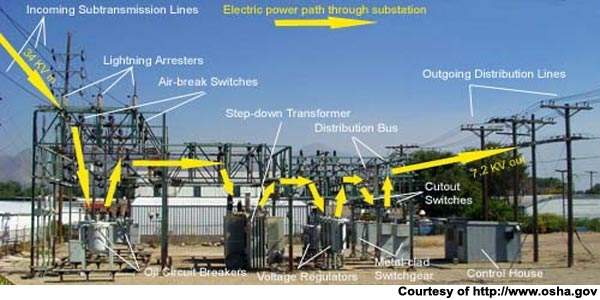
Components of Substation
Substations are an important part of the electrical grid. They provide a place where electricity can be generated, transformed, and distributed. Without substations, the electricity we use every day would not be possible.
There are four main components of a substation: transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, and grounding equipment.Transformers are used to change the voltage of electricity. This is necessary because different parts of the grid need different voltages in order to function properly. For example, homes and businesses use lower voltages than power plants or transmission lines.
Switchgear is used to control the flow of electricity within the substation. It includes devices like switches, fuses, and circuit breakers. Circuit breakers are used to protect equipment from damage by interrupting the flow of electricity when there is a problem.
Grounding equipment ensures that all electrical currents have a safe path to ground if they need to be discharged.
Without these four components, substations would not be able to provide the reliable power we need day-in and day-out!
Transformer Substation
A transformer substation is a type of electrical substation that transforms voltage from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction.
Transformers are used in many applications, including power generation, transmission and distribution, industrial and commercial heating and lighting, automobiles, aircrafts, electronic equipment and consumer electronics.
Substations may also be equipped with tap changers that regulate voltage by slightly altering the turns ratio of the transformers. Circuit breakers and switches are also common features of substations.
The primary function of a transformer substation is to convert voltage from high to low (or vice versa) so that electricity can be transported over long distances without loss.
They are typically located at either end of an electric power transmission line or circuit – for example at a hydroelectric dam or coal-fired power plant – where they step down the voltage before it enters the distribution system. From there, the electricity flows through secondary stations which further reduce the voltage before it reaches consumers via neighborhood transformers.
Large power users such as factories or office buildings often have their own on-site transformer substations to ensure a reliable supply of electricity.
These types of substations are sometimes called private utility substations (PUS).
Electrical Substation Components Pdf
In an electrical substation, there are several key components that work together to provide power to a particular area. The main component is the transformer, which steps down the high voltage from the main line to a lower voltage that can be used in homes and businesses. There are also circuit breakers and switchgear that help to protect the system from overloads and faults.
Additionally, there may be capacitors and reactors present in order to regulate the flow of current.
Classification of Substation According to Service Requirements
Substation classification is a method of categorizing substations according to their service requirements. The three primary types of substations are transmission, distribution, and switching. Transmission substations step up voltage from lower levels to higher voltages for long-distance power transport.
Distribution substations distribute electricity at the local level, stepping down voltage from transmission levels to meet the needs of residential and commercial customers. Switching substations switch power between different circuits or networks.
Substation Construction
Substation construction is a process by which electrical power plants and substations are built. The first step in substation construction is the site selection. Once a suitable site has been selected, the next step is to prepare the foundation.
The foundation must be able to support the weight of the equipment that will be installed on it. After the foundation has been prepared, the next step is to erect the steel structures that will house the equipment. Once the steel structures have been erected, the next step is to install the equipment.
This includes installing transformers, circuit breakers, and other pieces of equipment. After all of the equipment has been installed, testing can begin.
Credit: www.power-technology.com
What is the Most Important in a Substation?
There are many different factors that contribute to the overall importance of a substation. However, one of the most important aspects is its ability to provide a safe and reliable source of power. Without a reliable power source, a substation would not be able to function properly and could pose a serious safety hazard.
Additionally, a substation must be able to withstand extreme weather conditions and other potential hazards. This means that it must be constructed from high-quality materials and have robust security features in place.
What is a Substation Vs Transformer?
A substation is a power station that provides electricity to an area by boosting the voltage from the generating source and then distributing it to consumers. A transformer is a device that changes or transforms electrical energy from one form to another, usually with different voltages.
Why is a Substation Called a Substation?
A substation is a type of electrical power plant that is used to distribute electricity from the main power grid to local areas. The word “substation” comes from the fact that these plants are typically located near or underneath power lines, which are themselves called “substations”. Substations can also be used to connect two different parts of the grid together, or to provide backup power in case of an outage.
What is the Distribution Substations And What is Its Function?
A distribution substation is a power substation where electricity is transformed from high voltages to the low voltages used by consumers. The function of a distribution substation is to step down the voltage of electricity so that it can be safely used in homes and businesses.
The first step in transforming electricity at a distribution substation is to lower the voltage using a transformer.
The transformer steps down the voltage by using coils of wire to change the electrical current. Once the voltage has been lowered, it passes through circuit breakers which protect against any sudden surges or spikes in the electrical current.
After passing through the circuit breakers, the electricity flows into meters which measure how much electricity is being used.
From there, it flows into Distribution Panels where it is distributed to different parts of the building or home.
The distribution substation plays an important role in delivering safe and reliable power to consumers. Without these substations, homes and businesses would not have access to electricity.
Conclusion
In a substation, various equipment are present for the purpose of switching, controlling and protecting the electrical circuits. The main equipment present in a substation are: Circuit breakers, Transformer, Capacitors, Reactors etc. Let us discuss the function of each of these devices one by one.
A circuit breaker is used to open or close an electrical circuit. It protects the circuit from damage due to overload or short circuit.
A transformer is used to transform the voltage level of an electrical signal.
It can step up or step down the voltage level as required.
Capacitors are used to store electrical energy in the form of electric field. They provide reactive power to the system and improve its power factor.
Reactors are used to limit the current flowing through an electrical circuit. They are mostly used in inductive loads such as motors and generators.



