An HV substation is a high voltage electrical substation that changes the voltage of an electric power system. An LV substation is a low voltage electrical substation that changes the voltage of an electric power system.
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform other important functions. between generating stations and customers’ premises.
The word substation comes from the days when electricity was generated at central stations and then distributed to customers.
A high-voltage (HV) substation steps down the voltage from the transmission line to a level that can be used by consumers. A typical HV substation might have voltages of 138 kV or 115 kV entering it from the transmission grid, with transformer(s) inside the substation changing (or “transforming”) this voltage to a lower “distribution” voltage such as 46 kV for further distribution around an urban area.
The outgoing distribution lines from an HV substation are not usually considered part of the substation itself, but may be close by on land owned or leased by the power company for that purpose. These lines carry electricity at relatively low voltages (around 1kv) but over long distances (from several kilometres up to hundreds of kilometres). Low-voltage (LV) sub-stations step down these voltages even further for use within buildings.
[1]
In very simple terms, a high voltage sub station is one where high tension cables bring in electric power which is transformed into lower voltages before being sent out again on lower tension cables.
How Do Substations Work?
Lv, Mv Hv Voltage Ranges
There are three different voltage ranges that are typically used in electrical systems: low voltage (LV), medium voltage (MV), and high voltage (HV). Each of these voltage ranges has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to choose the right one for your application.
LV systems are typically used for smaller applications where power needs are lower.
This makes them more affordable and easier to install. However, they can’t handle as much power as MV or HV systems.
MV systems are a good middle ground between LV and HV.
They’re more powerful than LV systems, but not as expensive or difficult to install as HV systems.
HV systems are the most powerful option, but they’re also the most expensive and difficult to install. They’re typically only used for large-scale applications where very high levels of power are needed.
Difference between Lv And Mv Switchgear
Almost all industrial and commercial facilities have some type of switchgear to supply electricity to their operations. The two most common types of switchgear are low voltage (LV) and medium voltage (MV). Both LV and MV switchgear have their own advantages and disadvantages, so the best type for a particular facility depends on the specific needs of that facility.
Advantages of Low Voltage Switchgear:
– Less expensive than MV switchgear
– Smaller and lighter weight, so it is easier to install
– Can be used with smaller conductors which results in lower installation costs
– Safer to work on since voltages are lower
– More energy efficient because losses are lower at lower voltages
Disadvantages of Low Voltage Switchgear:
– Not suitable for very high power applications (> 5 MVA or 6,000 amps) where higher voltages are required to minimize losses.
– Requires more frequent maintenance due to the greater number of components
Advantages of Medium Voltage Switchgear:
– Higher voltages result in less I^2R losses, so they are more energy efficient for high power applications.
– Fewer components than LV switchgear, so they require less maintenance.
Hv Switchgear Components
HV switchgear components are used in a variety of industries, including the power generation, transmission and distribution, and manufacturing sectors. They are designed to provide safe, reliable and efficient operation of electrical equipment. HV switchgear is an important part of the electrical infrastructure and its proper functioning is essential to the safe and reliable operation of the power system.
The main components of HV switchgear include circuit breakers, contactors, fuses, disconnectors, transformers and voltage regulators. Circuit breakers are used to interrupt the flow of electricity in case of an overload or fault. Contactors are used to connect or disconnect electrical equipment from the power supply.
Fuses protect electrical circuits from excessive currents by breaking the circuit when required. Disconnectors allow for safe isolation of electrical equipment from the power supply. Transformers change the voltage level of electricity while voltage regulators maintain a constant voltage level despite changes in load conditions.
HV switchgear must be carefully selected to match the specific application requirements. It is important to consider factors such as system voltages, short-circuit levels, environmental conditions and future expansion plans when selecting HV switchgear components.
Mv/Lv Electrical
Mv/Lv Electrical is a family owned and operated business that has been servicing the Greater Toronto Area for over 25 years. We are a team of highly trained and experienced electricians that are dedicated to providing our customers with the highest quality of service possible. We offer a wide range of electrical services including: residential, commercial, industrial, and emergency.
No matter what your electrical needs may be, we have the experience and knowledge to get the job done right.
As a family owned and operated business, we understand the importance of customer satisfaction. That’s why we go above and beyond to ensure that each and every one of our clients is 100% satisfied with our work.
We take pride in our workmanship and stand behind everything we do. If for any reason you are not completely satisfied with our work, please contact us so that we can make it right.
If you’re in need of an electrician in the Greater Toronto Area, look no further than Mv/Lv Electrical.
Contact us today to schedule a free consultation!
Extra High Voltage Substation
An extra high voltage (EHV) substation is a type of electrical substation that uses equipment with voltages above 100 kV. These substations are used in the electric power industry for the transmission and distribution of electricity. EHV substations are typically located at strategic points along the electric power grid, such as where different parts of the grid meet or where long-distance transmission lines connect to local distribution networks.
EHV substations play a vital role in ensuring the reliable operation of the electric power grid. They help to ensure that electricity can be transmitted and distributed efficiently and safely, while also providing a measure of protection against system failures. The use of EHV equipment allows for higher voltages and thus higher capacities for electrical transmission, which results in lower line losses over long distances.
There are several key components of an EHV substation, including:
* Transformers: Used to step up or step down voltage levels as needed
* Circuit breakers: Used to protect equipment from damage due to faults or overloads
* Capacitors: Used to store energy and improve power quality
* Inductors: Used to smooth out voltage fluctuations
An EHV substation typically contains a variety of specialized equipment that is designed to withstand the high voltages involved.
This equipment includes transformers, circuit breakers, capacitors, and inductors. Each piece of equipment plays an important role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the substation.
Difference between Lv And Hv
There are two types of electrical systems: low voltage (LV) and high voltage (HV). The main difference between these two types is the voltages they use. LV systems use voltages below 1 kV, while HV systems use voltages above 1 kV.
This means that HV systems can transmit electricity over longer distances than LV systems.
High Voltage Substation Components
A high voltage substation is a key component in the electrical grid. It is typically used to connect different parts of the grid, or to provide a connection point for generation and load. A substation may also be used to step down voltages from transmission lines to lower levels suitable for distribution.
The main components of a high voltage substation are:
-Transformers
-Circuit breakers
-Capacitors
-Reactors
Mv Electrical Meaning
Mv electrical meaning is a unit of measurement used to describe the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. The letter “m” stands for milli, or one thousandth, and “v” stands for volt. One mv is equal to one thousandth of a volt.
This unit is often used to measure small potential differences, such as those created by batteries or solar cells.
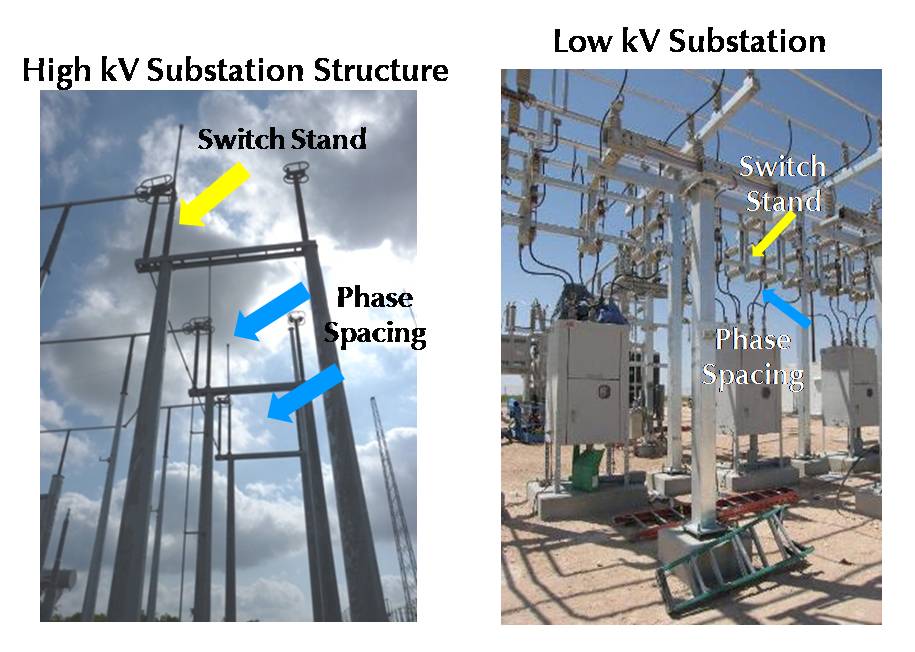
Credit: www.distransteel.com
What is the Difference between Hv And Lv Substation?
A high voltage (HV) substation steps down extra-high voltage transmission lines to the high voltage used by distribution circuits. A low voltage (LV) substation receives power from the distribution system and delivers it to lower voltage customer feeders.
The main differences between HV and LV substations are:
-HV substations use transformers to step down voltages, while LV substations do not.
-HV substations have more equipment than LV substations.
-HV substations require more maintenance than LV substations.
What is Hv And Lv?
HV is high voltage and LV is low voltage. The terms are used to describe electrical circuits, with HV referring to those that carry a higher voltage than LV circuits. The terms are also sometimes used in the context of power supplies, with HV meaning a power supply that outputs a higher voltage than an LV power supply.
What is a Lv Substation?
A low voltage substation is a type of power distribution center that steps down the high voltage from the transmission lines to the level required by local loads. A typical low voltage substation will have a primary voltage rating of between 1 kV and 35 kV. Low voltage substations are typically used in urban areas where there is a high density of load requiring lower voltages for safe operation.
The main components of a low voltage substation include transformers, switchgear, circuit breakers, and metering equipment. The transformer steps down the high voltage from the transmission line to the lower secondary voltages required by local loads. The switchgear controls the flow of electricity through the substation and provides protection against faults on the system.
The circuit breakers are used to isolate sections of the substation in case of an electrical fault. Metering equipment is used to monitor current, voltage, and power flowing through the substation.
Low voltage substations play an important role in ensuring reliable power supply to urban areas.
Without these substations, cities would not be able to function properly as they rely heavily on electricity for many different applications.
What is an Hv Substation?
An HV substation is a high voltage electrical substation. It is used to connect high voltage power lines to lower voltage distribution lines. The substation contains equipment that transforms the high voltage electricity into a lower voltage that can be used by homes and businesses.
Conclusion
A HV substation is a high voltage electrical substation that transforms the voltage from high to low or vice versa. An LV substation is a low voltage electrical substation.



