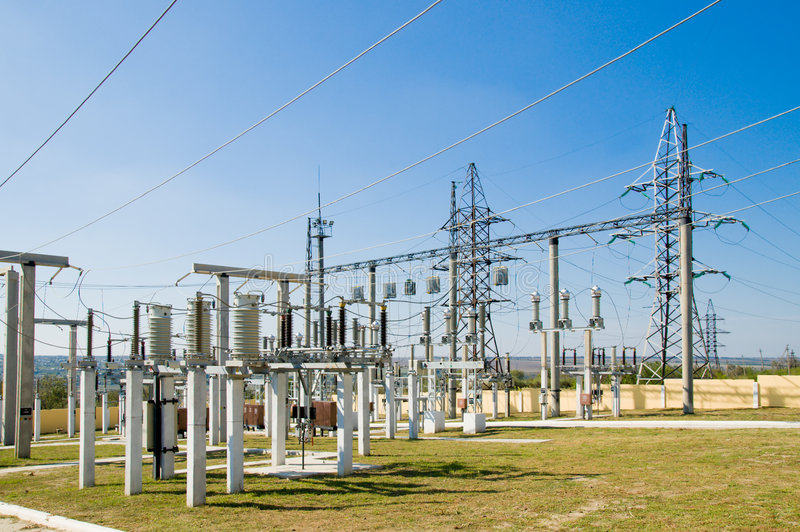
A Switching Substation is a type of power plant that is used to convert between different types of electrical energy. This can include converting between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), or between different voltages. A switching substation may also be known as a converter station, transformation station, or transposition station.
A switching substation is a type of power substation that switches, or changes, the voltage of an electric power grid. The most common use for a switching substation is to change the voltage of electricity coming from a generating station so that it can be fed into the high-voltage transmission system.
Switching substations are also used to change the voltage of electricity coming from one part of the transmission system to another, or to connect two parts of the grid together.
For example, a switching substation might be used to connect a wind farm in one state to the rest of the grid in another state.
Switching substations usually have several transformers that can be switched on or off as needed. They also have devices called circuit breakers that can quickly disconnect part of the grid if there is a problem, such as an equipment failure or severe weather conditions.
ES ( Earthing Switch) Operating in Grid Substation
Switching Station Vs Substation
When it comes to electric power, there are two main types of facilities used to switch and distribute the electricity – switching stations and substations. Both play an important role in getting electricity from the power plant to your home or business, but they each have their own unique purpose. Here’s a closer look at the difference between switching stations and substations:
Switching Stations
A switching station is a facility where electricity is converted from high-voltage transmission lines to lower-voltage distribution lines. The high-voltage transmission lines come directly from the power plant, while the lower-voltage distribution lines are what ultimately deliver electricity to homes and businesses.
Switching stations typically have large transformers that step down the voltage so it can be used on the distribution lines.
Substations
A substation is a facility where electricity is switched from one set of transmission lines to another.
This enables electricity to flow through different routes as needed. Substations also have transformers that convert high-voltage transmission line voltages to lower voltages for use on distribution lines. In addition, many substations also include devices called reclosers, which automatically close off sections of damaged line so that repairs can be made without affecting the rest of the system.
Switching Substation is Used to
A substation is an electrical installation where equipment for generating, transmitting and distributing electric power is present. A switching substation changes the voltage of alternating current (AC) in a power system. This type of substation can also be used to change the frequency or phase of current.
In order to ensure uninterrupted supply of electricity, multiple substations are connected together to form a grid.
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a junction point where electricity from multiple generating sources comes together and is then distributed to consumers. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, as needed.
They also regulate voltage and improve power quality.
As the load on the electric grid continues to grow, utilities are increasingly looking to upgrade existing substations and build new ones. This is because substations play a vital role in ensuring that electricity flows safely and reliably to homes and businesses.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and generation. Transmission substations take electricity from high-voltage power lines and step it down to a lower voltage for distribution over shorter distances. Distribution substations receive electricity from transmission lines and further reduce the voltage so that it can be delivered directly to customers through medium-voltage circuits.
Generation substations connect generators to the electric power grid.
Substations come in many different shapes and sizes, but they all have one thing in common: they contain equipment that must be operated and maintained by qualified personnel. This equipment includes circuit breakers, transformers, capacitors, relays, protection devices, monitoring equipment, communication systems, etc.
Transmission Substation
A transmission substation is a type of electrical substation that is used for switching or transforming high-voltage electricity from one voltage to another. These types of substations are typically used in power plants, hydroelectric dams, and other large generation facilities where there is a need to step down the voltage of the electricity before it is sent out on the power grid. Transmission substations can also be used to connect two different parts of the grid together or to isolate sections of the grid for maintenance.
Electrical Switching Station
An electrical switching station is a facility where electricity is generated and distributed to consumers. The equipment in a switching station includes generators, transformers, switchgear, and other devices. Switching stations are typically located near sources of electric power, such as hydroelectric dams or thermal power plants.
A typical hydroelectric dam has a powerhouse that contains one or more turbines connected to generators. The turbine blades rotate when water flows through the dam and spins the generator shafts. This motion produces electricity that is carried by transmission lines to a nearby switching station.
The electricity generated at the dam may be used to power homes and businesses in the local area or it may be sent to distant cities via the electrical grid.
Thermal power plants also have a powerhouse containing turbines connected to generators. In a coal-fired power plant, steam produced by burning coal turns the turbine blades.
In a nuclear power plant, heat from nuclear reactions turns water into steam that powers the turbines. The electricity produced by thermal power plants is also sent to a switching station for distribution.
The equipment in an electrical switching station transforms high-voltage electricity into lower voltages that are safe for home use.
Transformers step down the voltage so it can be safely routed through secondary networks before being delivered to homes and businesses via low-voltage wires. Switchgear controls the flow of electricity from its source to transformers, distribution lines, and ultimately consumers.
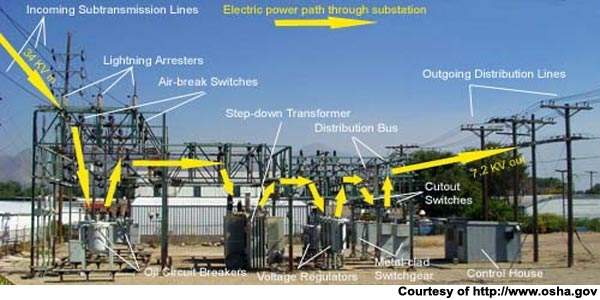
Switching Substation Diagram
A substation is a vital part of the electrical grid. It takes electricity from the transmission lines and distributes it to the local area. A substation diagram is a drawing that shows the components of a substation and how they are interconnected.
The first step in understanding a substation diagram is to identify the different types of components. There are three main types of components: power transformers, circuit breakers, and disconnect switches.
Power transformers change the voltage of the electricity so that it can be used by homes and businesses in the local area.
Circuit breakers protect equipment from damage by automatically shutting off the power if there is an overload or short circuit. Disconnect switches provide a way to manually disconnect equipment from the power supply if necessary.
Once you know what all of the different components are, you can start to understand how they are interconnected.
The easiest way to do this is to follow the flow of electricity through the substation.
Electricity enters the substation through high-voltage transmission lines. These lines connect to power transformers which lower the voltage so that it can be used by homes and businesses in the local area.
From there, circuit breakers protect equipment from damage by automatically shutting off power if there is an overload or short circuit. Finally, disconnect switches provide a way to manually disconnect equipment from power if necessary.
Function of Substation
A substation is an electrical installation where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. The process of transforming the voltage is known as “transformation”. A substation can also be used to change the current form alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), or vice versa.
The devices that are used for these processes are called “transformers”.
The primary function of a substation is to switch electricity between different parts of the power grid in order to balance supply and demand. This switching involves disconnecting and reconnecting circuits very rapidly, which requires specialised equipment known as “switchgear”.
Substations also play an important role in protecting equipment and personnel from electrical faults. When a fault occurs on an electrical circuit, it can cause a large amount of current to flow through the system. If this happens, it can damage equipment or injure people.
To prevent this from happening, substations are equipped with devices that detect when a fault has occurred and automatically disconnect the affected part of the circuit. These devices are known as “protective relays”.
Substation Components
A substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It is a junction point where electricity is received from generating plants and transmitted to distribution networks. A substation also serves as a switchyard where circuits are opened or closed to maintain system stability and reliability.
The key components of a substation include:
*Transformers – Used to step up or step down voltage levels *Circuit breakers – Used to open or close circuits *Capacitors and reactors – Used to regulate voltage and current levels *Protective relays – Used to monitor equipment conditions and isolate problems *Instrument transformers – Used to measure voltage, current, and power levels *Busbars – Conductors that carry large currents between circuit breakers *Cables and conductors – Carry electricity at lower currents than busbars
Operators of substations must have a thorough understanding of the equipment in order to maintain safe, reliable, and efficient operations.
Credit: www.power-technology.com
What are the Three Types of Substations?
A substation is an electrical installation that forms part of the electricity grid. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, as well as perform other important functions. Without substations, the electricity grid would not be able to function.
There are three main types of substations: transmission, distribution, and switching. Transmission substations connect different parts of the high-voltage national grid. They step down the voltage so that it can be used by local distribution networks.
Distribution substations distribute electricity to homes and businesses in a particular area. Switching substations switch electricity between different parts of the network, for example when maintenance needs to be carried out on one section.
Substations are essential for the safe and reliable operation of the electricity grid.
They house a variety of equipment including transformers, switches, circuit breakers, and meters. This equipment is used to control the flow of electricity around the network.
Is Switching the Same As Substation?
No, switching is not the same as substation. A substation is a fixed facility where electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed to consumers. A switchyard is a temporary installation used to connect or disconnect electric circuits.
What is the Purpose of Switching Stations?
In most cases, the purpose of a switching station is to route electricity from a generating station to load centers, which may be sub-stations or customer premises. The type of switchgear used in a particular switching station depends on the voltage level of the circuit and the current carrying capacity required.
A typical large power system will have several thousand volts between its generating stations and load centers.
The current flowing in the conductors is usually quite low, on the order of a few amperes. For this reason, air-insulated switchgear is generally used for these high-voltage applications. This equipment uses air as an insulating medium between live parts, rather than oil or some other dielectric fluid.
What is Switching in Power System?
Switching in power system refers to the process of turning a circuit on or off. This can be done manually, with a switch, or automatically, with a device called a relay. Switches and relays are used to control the flow of electricity in homes, businesses and industrial facilities.
When a switch is open, no current can flow; when it is closed, current can flow freely. A typical light switch is an example of a manually operated switch. The switch has two positions: “on” and “off.”
In the “on” position, the contacts are touching and current can flow; in the “off” position, the contacts are separated and no current can flow.
A relay is an automatically operated switch that can be controlled by an electric signal, magnetism or light. Relays are used extensively in industrial applications such as automated manufacturing lines where they turn machines on or off at specific points in the production process.
Switching devices play an important role in regulating electricity supply and demand throughout power systems. By controlling when and how electrical energy flows through circuits, switching devices help ensure that power is delivered safely and efficiently to homes and businesses across the country every day.
Conclusion
A switching substation is a type of power substation that is used to switch equipment on or off. The most common type of switching substation is the transformer substation, which is used to switch transformers on or off. Other types of switching substations include the circuit breaker substation and the busbar substation.



