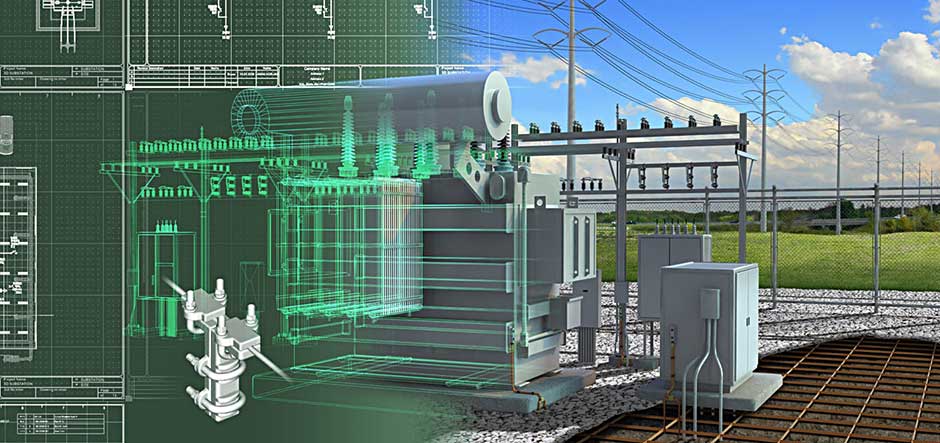
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power infrastructure. It is a high-voltage switching station where electricity is received from generation plants and transmitted to distribution networks. The design of an electrical substation must consider many factors such as system voltage, capacity, reliability, safety, and cost.
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electric power grid. It serves as a switching and/or transforming point in the distribution of electricity from the high-voltage transmission system to the lower voltage distribution system. A substation can also be used to interconnect two different voltage levels within the same network.
There are many factors that go into designing an electrical substation, such as determining the equipment needed, sizing transformers and circuit breakers, and creating a layout that will ensure safe and reliable operation. The design process must take into account the specific needs of each individual project.
As with any electrical system, safety is paramount when designing a substation.
Careful consideration must be given to clearance requirements, fire protection, and security measures. The layout of the substation must allow for easy access to key components for maintenance and repair.
With modern technology, there are many different ways to design an electrical substation.
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is frequently used to create detailed drawings and models of proposed designs. This allows for accurate calculations and simulations to be performed before any construction takes place.
Electrical Substation Design Book
As an electrical engineer, one of the most important things you can do is learn how to design efficient and effective substations. A substation is a critical component in any electrical grid, and its design can have a major impact on the overall performance of the system.
There are many different factors to consider when designing a substation, including power demand, voltage levels, transformer capacity, switchgear type, and more.
It can be a challenge to juggle all of these elements while also ensuring that the substation is safe and reliable.
Fortunately, there are resources available to help you with this task. One such resource is the Electrical Substation Design Book from IEEE Press.
This book provides detailed information on all aspects of substation design, from planning and siting to equipment selection and protection schemes. It also includes case studies of real-world projects, so you can see how theory translates into practice.
If you’re looking to improve your substation design skills, the Electrical Substation Design Book is an essential resource.
Electrical Substation Design Pdf
Electrical substation design is a critical part of ensuring the reliable operation of the electrical grid. Substation designers must take into account a variety of factors to ensure that the substation will meet the needs of the utility and its customers.
The first step in substation design is to determine the purpose of the substation.
Substations can be used for a variety of purposes, including generation, transmission, distribution, or load control. Each type of substation has different requirements. For example, a generation substation must be able to handle high voltages and currents, while a distribution substation must be designed to provide power to customers with minimal interruptions.
After the purpose of the substation has been determined, designers must select the proper equipment. This includes selecting transformers, switchgear, cables, and other electrical equipment. The selection of this equipment is based on many factors such as voltage levels, current levels, environmental conditions, and customer demands.
Once all of the necessary equipment has been selected, it must be installed in accordance with local building codes and safety regulations. This includes running cables and installing support structures in compliance with code requirements.
Electrical Substation Design Calculations Pdf
Are you an electrical engineer? Do you design substations? If so, then you know that there are many factors to consider when it comes to designing a substation.
You must take into account the voltage, the amperage, the power factor, and the impedance. These calculations can be complex, but they are essential in ensuring that your substation is designed correctly.
In this blog post, we will discuss how to perform electrical substation design calculations.
We will cover topics such as voltage drop and short-circuit current calculations. After reading this blog post, you should have a better understanding of how to properly design a substation.
Voltage Drop Calculations
The first calculation that we will discuss is voltage drop. Voltage drop is the difference in voltage between two points in an electric circuit. The formula for voltage drop is:
Voltage Drop = IRDrop
Electrical Substation Design Course
An electrical substation is a critical part of the electricity infrastructure. It is a place where various types of equipment are used to change the voltage and current levels of electricity before it is supplied to homes and businesses. A well-designed substation can help to ensure the reliable supply of electricity, while a poorly designed one can lead to blackouts and other problems.
A new course from eTraining Inc., Electrical Substation Design, covers all aspects of designing safe and reliable substations. The course begins with an overview of the different types of substations and their components, then goes on to discuss the principles of electrical power transmission and distribution. Students will learn about the different types of transformers and how to select the right one for each application.
They will also learn about switchgear, circuit breakers, and other key components. The course includes several case studies that illustrate real-world applications of these concepts.
Whether you are a professional engineer who wants to brush up on your substation design skills or a student who is just starting out, this course will give you the knowledge you need to design safe and reliable electrical substations.
Substation Design Standards
There are many different types of substation designs and the specific design standards that need to be met can vary depending on the application. In general, substation design standards focus on ensuring the safety of both workers and the public, as well as minimizing risks to equipment. Some of the specific design elements that need to be considered include:
– The layout of the substation, including clear delineations between public and private areas
– The location of critical equipment, such as transformers and switchgear, in order to minimize fire hazards
– The use of barriers and fencing to protect against electrical shock hazards
– Adequate ventilation for all enclosed spaces in order to prevent dangerous build-ups of heat or fumes
Substation Design Engineer
Substation Design Engineer
A substation design engineer is responsible for the electrical design of substations and other high voltage power system facilities. The position requires a bachelor’s degree in engineering and a minimum of five years’ experience in the field.
The engineer must be knowledgeable about the National Electrical Code, industry standards, and best practices. He or she must also be able to use computer-aided design software to create accurate drawings and models. The substation design engineer works closely with project managers, clients, and other engineers to ensure that the project meets all requirements.
Substation Design Companies
There are a variety of substation design companies out there that can provide the services you need to get your substation up and running. Here is a look at some of the top companies in this field:
1. ABB: ABB is a global leader in power and automation technologies.
They offer a wide range of products and services for substations, including design, engineering, supply, installation, commissioning, and maintenance.
2. Siemens: Siemens is another global leader in electrical engineering and technology. They offer a comprehensive portfolio of products and solutions for substations, including design, manufacturing, supply, installation, testing, and commissioning.
3. Eaton: Eaton is a world-leading provider of electrical products and services for substations. They offer complete turnkey solutions for substation projects, from design to commissioning. Their product offerings include circuit breakers, transformers, switchgear assemblies, cabling systems, monitoring & control equipment, etc.
4. Alstom: Alstom is a leading supplier of infrastructure solutions for substations. Their offerings include engineering services (design & project management), manufacturing (equipment & materials), construction (installation & commissioning), as well as operation & maintenance services.

Credit: oelectrical.com
How Do You Design a Substation?
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid, and the design must take into account many factors to ensure reliability and safety. The first step is to determine the size and capacity of the substation based on the load it will be serving. The next step is to select the location of the substation, taking into account factors such as proximity to power sources, transmission lines, and distribution lines.
Once the location is selected, engineers will design the substation layout, which includes determining the placement of equipment such as transformers, switches, and circuit breakers. The final step in designing a substation is to develop protection schemes that safeguard equipment and prevent outages.
What are the Three Types of Substations?
A substation is an electrical power switching and/or distribution station. A substation may be a step-down transformer that reduces voltage from high transmission voltages to the level used by local distribution systems, or it may be a step-up transformer that increases voltage from lower local levels to the high transmission voltages. Substations also include devices such as circuit breakers and disconnect switches, and often have controls to monitor power flows, voltage levels and equipment conditions at the site.
There are three types of substations:
1) Transmission Substation
2) Distribution Substation
3) Substations for Special Systems
Transmission substations connect parts of the high-voltage electric power transmission system. They usually transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, depending on whether they are connecting two parts of the system with different voltages.
These stations are located between generating plants and regional grids, or between regional grids. A typical configuration might include several 500 kV transformers feeding a few 225 kV busbars – which in turn feed 115 kV secondary circuits off each busbar. The outgoing 115 kV circuits feed distribution substations below them in the grid.
Transmission substations can range in size from simple to very complex facilities with dozens of large 500kv – 765kv GIS switchgear bays housed in multiple buildings; however most consist of one or two main switchgear buildings housing primary equipment fed from an outdoor yard full of various types HV/MV/LV bushings leading into each building where connections are made between circuit breakers (CBs), current transformers (CTs), potential transformers (PTs), instrument Transformers (ITs), line Reactors(LRs)and other miscellaneous equipment required for operation then exiting out another set bushings connected to various pieces secondary equipment like capacitor banks(CBs), reclosers(RCOs), sectionalizers(SECOs). Secondary control buildings house PLC & SCADA equipment along with associated monitoring & protection relays all interconnected allowing remote operation & monitoring of critical data points throughout facility via fiber optic cable running back to a central control room(CCR).
What are the Different Substation Design?
There are many different types of substation designs. The most common type is the step down transformer substation, which is used to convert high-voltage electricity from the power grid into lower voltages for distribution to homes and businesses. Other types of substations include those that use batteries or generators to provide backup power, or those that distribute electricity to a specific area or customer.
What Should I Consider in Substation Design?
When designing a substation, there are many factors to consider in order to ensure a safe and efficient installation. Here are some of the key considerations:
1. Location: The location of the substation is critical for several reasons.
First, it must be situated close enough to the power source (usually a power plant) to minimize transmission losses. Second, the site must have sufficient space to accommodate all of the substation components. And third, the location must be safe from potential hazards like flooding or earthquakes.
2. Equipment: Careful selection of equipment is essential for a well-functioning substation. Switchgear, transformers, circuit breakers and other electrical equipment must be appropriate for the voltage and current levels involved. In addition, this equipment must be compatible with each other so that they can operate safely and efficiently as a system.
3. Layout: The layout of a substation is important for two main reasons: safety and efficiency. All electrical equipment must be installed in accordance with local building codes and safety regulations. In addition, the layout should be designed to minimize energy losses through things like heat dissipation or electromagnetic interference.
4. Cabling: The cabling used in a substation must be able to handle the high voltages and currents involved without failure.
Substation design, Substation engineering, Substation drawings, Single line diagram, SLD.
Conclusion
An electrical substation is a crucial part of the electrical grid. It transforms high-voltage electricity from power plants into lower voltages that are safe for homes and businesses. Without substations, the electricity we use every day wouldn’t be possible.
Substation design is a complex process that involves many different factors. The first step is to determine the voltage level that the substation will need to operate at. This depends on the voltage of the power lines that will be feeding into the substation, as well as the desired voltage of the electricity that will be sent out to customers.
Once the voltage has been determined, engineers must design the substation equipment accordingly. This includes transformers, circuit breakers, and other switchgear. The layout of these components must be carefully planned so that they can all fit within the substation footprint and work together seamlessly.
After the equipment has been designed, it must be installed and tested before going live. This is an important step to ensure that everything works as intended and there are no safety hazards present. Once everything is up and running, electric utilities will monitor the substation closely to make sure it continues to operate safely and efficiently.