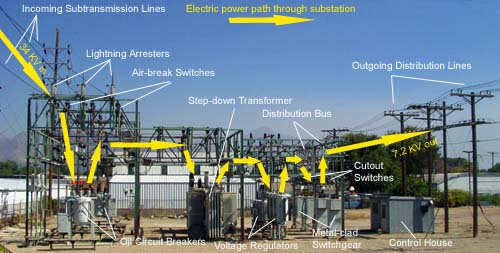
A Step Down Substation changes the voltage from high to low. The high voltage is brought in from the transmission line and goes through a transformer where it is reduced to a lower voltage that can be used on the distribution lines.
Classification Of Power Substations | Distribution | Step Up | Step Down Station | System Stations
The substation is the first line of defense against power surges and voltage fluctuations. It steps down high-voltage electricity from the transmission lines to a level that can be safely used in your home or business.
Distribution Substation
The distribution substation is the last stop for electricity before it reaches the customer. It steps down the voltage from the high-voltage transmission system to a lower voltage that can be used by businesses and residences. Many distribution substations have transformers to change the voltage levels.
The type of equipment used in a distribution substation depends on many factors, including whether it is an urban or rural area, what kind of loads are served by the substation, and how much space is available.
Electrical Substation
An electrical substation is a facility where electricity is generated, transformed, or switched. Substations may be connected to each other by transmission lines for the purpose of stepping voltage up or down in order to improve the efficiency of power distribution. They are also used to connect two or more alternating current or direct current circuits.
Substations are typically located where multiple circuits come together, such as at a crossroads in an electrical grid. A typical substation includestransformers to convert between high-voltage transmission levels and lowerdistribution levels, circuit breakers and switches to control the flowof electricity, measuring equipment, and busbars to connect differentcircuits within the substation.
In very large substations, oil-filled transformers may be used toprevent fire hazards arising from arcing during switching operations.Gas-insulated switchgear is often used in place of air-insulatedequipment due to its superior reliability and safety record.
Substation Components
Substations are an essential part of the electric grid, providing a safe and reliable way to switch electricity between different parts of the system. substation components include transformers, circuit breakers, and other equipment that helps to control the flow of electricity.
Substation Voltage Levels
A substation is a crucial link in the electrical power system. It is a collection of equipment that receive, transform and deliver electrical energy from one part of the network to another. The voltage level in a substation can range from low (1 kV) to extremely high (765 kV).
The most common voltages used in substations are 13.8 kV, 34.5 kV, 115 kV and 230 kV. The primary purpose of a substation is to step-down or step-up the voltage levels as required by the system load. A typical suburban distribution network may have several 34.5/13.8 kV substations while a large city grid may have 345/138 kV or even higher voltages at its core with numerous 115/69kv and lower voltage levels at outlying areas
The receiving end of a transmission line or circuit typically has a slightly higher voltage than the sending end due to line losses along the way. In order to maintain uniformity throughout the system, it is necessary to raise (or boost) the voltage at the receiving end of long transmission lines so that once line losses are taken into account, both ends will be operating at approximately equal voltages. This function is performed by what is called a “step-up transformer.”
Function of Substation
A substation is a critical part of the electrical grid. It transforms voltage from high to low, or vice versa, and also serves as a switchyard where power can be routed from one line to another. Substations are typically located near power plants or large industrial facilities.
Substations come in a variety of shapes and sizes, but all have three basic components: transformers, switches, and circuit breakers. The transformer changes the voltage so that it can be used by consumers. The switch controls the flow of electricity, and the circuit breaker protects against overloads by automatically shutting off the power if necessary.
In addition to these three components, substations also have various other pieces of equipment that help to keep everything running smoothly. For example, there may be devices that monitor the flow of electricity or provide backup power in case of an outage.
Types of Substation Pdf
There are many different types of substations and the design varies depending on the intended use. The three most common types of substations are:
1) Transmission Substation
A transmission substation connects two or more electricity generation plants to an electricity grid. These types of substations are typically very large with high voltage equipment. The purpose of a transmission substation is to step up the voltage from the generating plant so that it can be transmitted across long distances through high-voltage power lines.
2) Distribution Substation
A distribution substation connects an electricity grid to individual consumers. These substations typically have lower voltages than transmission substations.
The purpose of a distribution substation is to step down the voltage so that it can be used safely by individual consumers.
3) Industrial Substation
An industrial substation is used to supply power to an industrial facility such as a factory, mine, or oil refinery.
Industrial substations typically have voltages that are higher than distribution substations but lower than transmission Substations.
Transmission Substation
A transmission substation is a facility where electricity is transferred from one voltage to another. This can be done either by changing the voltage of the electricity (step-up or step-down transformer) or by connecting two different voltages together (transmission line). The substation also includes devices to protect the equipment from faults on the electrical system.
Classification of Substation
A substation is an energy facility where electricity is generated, transformed, or switched. Substations are typically located at the interface between transmission and distribution systems.
There are three types of substations:
-Generating stations
-Transmission substations
-Distribution substations
Generating stations convert forms of energy like coal, nuclear, solar, or wind into electricity. The electricity produced by generating stations is then transmitted to transmission substations through high voltage power lines. Transmission substations step down the voltage so that it can be distributed to consumers through lower voltage distribution lines.
Finally, distribution substations distribute the electricity to end users such as homes and businesses.

Credit: www.shutterstock.com
What are Types of Substations?
There are many types of substations, but the three most common are:
1. Transmission Substations
2. Distribution Substations
3. Generating Substations
Transmission substations step up the voltage from generation plants to the extremely high voltages needed for long-distance transmission on extra-high-voltage (EHV) power lines. They then step down the voltage for local distribution to customers.
A typical transmission substation has several hundred thousand volts (kV) incoming, and several outgoing kV levels for distribution at 34 kV, 115 kV, or more. The largest transmission substations can have voltages close to a million volts (1000 kV). These huge voltages allow electricity to be transmitted over very long distances with relatively low losses.
Distribution substations connect to the lower voltage network that delivers electricity directly to customers. They do not usually have high voltages like transmission substations, but may still carry tens of thousands of volts on some parts of the site. Most customer outages occur in distribution networks due to faults in equipment like switches and transformers at these locations.
Generating stations may have their own internal substation where generators are connected together before being stepped up to higher transmission voltages by a transformer for connection onto the grid system.
Where is the Step-Up Substation Installed?
A substation is an electrical installation where electricity is converted from one voltage to another. A step-up substation increases the voltage of an electrical circuit. The step-up substation is usually installed between the power plant and the transmission grid.
What is Step-Up Or Primary Substation?
A substation is a power system facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. A primary substation is a type of substation that steps up voltage from its incoming transmission line to a higher voltage for distribution to local consumers. The transformer in a primary substation typically steps up the voltage by a factor of 10 times or more.
What is the Difference between a Substation And a Transformer?
A substation is aname given to an electrical installation where there is a medium or high voltage switchgear and the transformers that supply power to the low voltage network. The function of a substation is to take electricity from the main grid, step it down in voltage so that it can be used by homes and businesses, then distribute it across lower voltage networks. A transformer is an electrical device that transforms the voltage of an alternating current (AC) at one voltages to another AC at a different voltage.
Conclusion
A substation is a crucial part of the electric power grid. It transforms voltage from high to low or the reverse, and also serves as a switchyard where circuits are connected and disconnected. Substations are typically located at a strategic point in the distribution system where electricity is generated, transmitted, and distributed.
A substation can be as small as a single transformer with associated switches and protection devices, or it can be much larger, housing hundreds of transformers along with associated equipment such as breakers, capacitors, and circuit breakers.