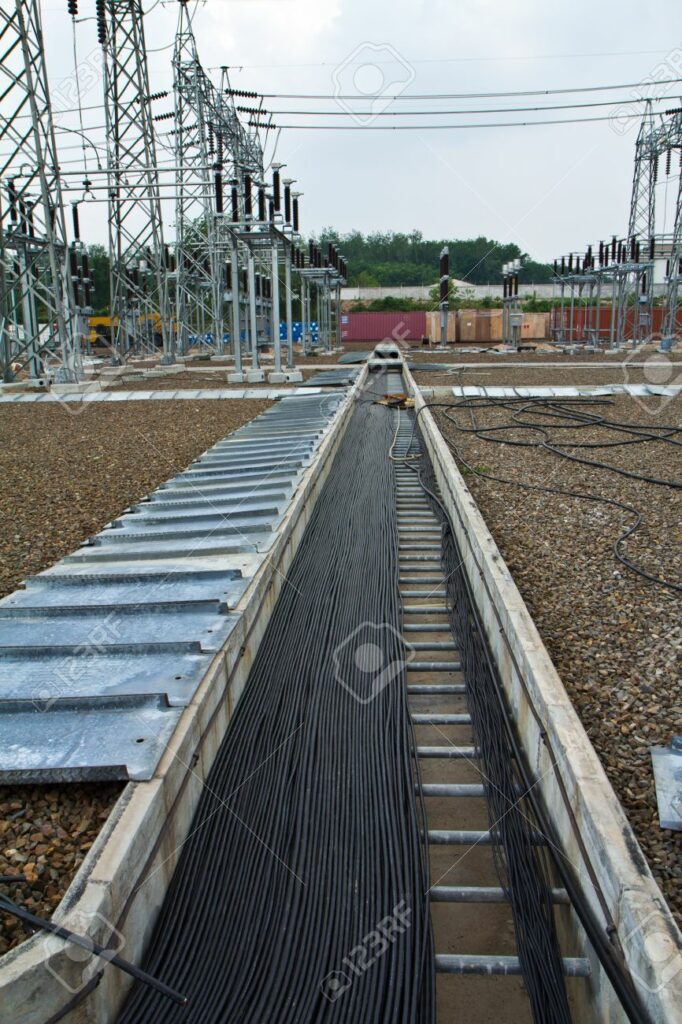
A cable trench is a narrow, shallow ditch used to bury electrical cables underground. The trench is dug using a trencher, and the cables are laid in the bottom of the trench before it is filled back in. Cable trenches are typically between 12 and 18 inches deep, and they may be lined with gravel or other material to protect the cables from damage.
The first thing to consider when planning a cable trench is the type of soil you are dealing with. Sandy soil is easy to work with and doesn’t require as much support for the walls of the trench. Clay soil, on the other hand, is more difficult to work with and requires more support.
The next thing to consider is the depth of the trench. A deeper trench will require more support than a shallow one.
Once you have considered these factors, you can start planning the actual details of the trench.
The width of the trench should be at least 2 feet wide, but 3 feet is ideal. The walls of the trench should be sloped so that they are stable and won’t collapse in on themselves. It’s also important to make sure that there is proper drainage in the trench so that water doesn’t build up and cause problems.
When it comes time to actually digging the trench, it’s important to take your time and do it right. If you rush, you could end up with a dangerous situation on your hands. Make sure to call 811 before you start digging so that you don’t accidentally damage any underground utilities.
Once you’ve started digging, be careful not to cave in the sides of the trench or create any air pockets . . . both could be very dangerous for anyone working in or around the area.
By following these simple tips, you can ensure that your substation cable trench project goes smoothly and safely!
Substation Cable Size
Substation cables are an integral part of the power grid, responsible for transmitting electricity from generation facilities to substations. The size of these cables is a critical factor in determining the capacity and efficiency of the grid.
There are a variety of factors that go into determining the size of substation cables.
The primary factor is the voltage of the electricity being transmitted. Higher voltages require larger cables, as they can carry more current without losing efficiency. The length of the transmission line also plays a role, as longer lines require larger cables to minimize resistance and losses.
Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature and humidity can impact cable size, as extreme conditions can cause damage to smaller cables.
The size of substation cables is thus a complex issue that must be carefully considered in order to ensure efficient and reliable operation of the power grid.
Cable Laying Procedure Pdf
The process of cable installation can be a daunting and time-consuming task, especially if you’re not familiar with the ins and outs of the procedure. However, by following these simple tips, you can ensure that your cable installation goes off without a hitch.
1. First and foremost, make sure that you have all of the necessary tools and materials on hand before beginning the installation process.
This includes things like a spade or shovel, tape measure, level, string line, conduit (if necessary), and of course, the cable itself.
2. Once you have everything gathered together, take some time to plan out the route that the cable will take. This is particularly important if you’re running multiple cables or if there are any obstacles in the way (trees, shrubs, etc.).
By having a clear plan ahead of time, you can avoid any potential problems down the road.
3. When you’re ready to start digging trenches for the conduit (if necessary), be sure to use a level so that your trenches are nice and straight. This will make it much easier to install the conduit later on.
Also, be sure to dig your trenches at least 6 inches deep in order to accommodate for both the conduit and the cable itself.
4. After your trenches are dug andLeveled lled , it’s time to start installingthe conduit . If you’re using PVC pipe , simply glue each section together using PVC cement .
Be sure to apply pressure to each joint as you glue it so that there are no gaps or weak spots . Once allofyour sectionsare gluedtogether , lay them intothe trenchand use stakes every few feetto keep them Leveled lled in place whilethe cementcures . 5 Once yourconduitis installed , fishyourcable throughit byattachingsometypeoffishingline(monofilamentline works well)tocableandpullingitte throughtheconduitfromoneendtoanotheruntilitcomesoutoftheotherside .
. Youmayhavetocutawayanykinksorloopsinthecableasyougoalongsoithastheproperslackwhenpulled tight..
Finally , onceyourcableismadeittotheothersideofthetrench safelysecureittoapostortreeusingacableclampbeforefillinginthetrenchwithdirtagain .. Andthat’sit!
Ieee 518 Cable Separation
The IEEE 518 standard for cable separation provides guidance on the minimum separation between power and signal cables. This separation is important to prevent interference between the two types of cables, which can lead to electrical problems. The standard recommends a minimum separation of 3 inches (7.6 cm) between power and signal cables, but this may vary depending on the type and size of the cables involved.
Cable Cellar Meaning
Do you know what a cable cellar is? If not, you’re not alone. This term is not one that’s used often, but it’s an important part of your home if you have buried cables.
Here’s what you need to know about cable cellars.
What is a Cable Cellar?
A cable cellar is simply a below-ground room where cables and wires are stored.
This can include things like electrical wiring, telephone lines, and even fiber optic cables. Cable cellars are common in both residential and commercial properties.
Why Have a Cable Cellar?
There are several reasons why someone might want to have a cable cellar. First, it can help protect your wires and cables from the elements. If they’re underground, they’re less likely to be damaged by severe weather or other environmental factors.
Second, it can keep your cords and wires hidden from view. This can be helpful if you don’t want your property to look cluttered or messy. Finally, having a cable cellar can also deter thieves from stealing your valuable wiring or equipment.
Low Voltage Cable Installation Standards
There are several low voltage cable installation standards that are used in the industry today. The most common standard is the NEC, or National Electrical Code. This code provides guidelines for the safe installation of low voltage cables in homes and businesses.
Other standards include the NFPA, or National Fire Protection Association, and the UL, or Underwriters Laboratories. These standards provide similar guidelines as the NEC but may have different requirements based on their specific needs.
Cable Segregation Standard
Cable segregation is the practice of separating different types of cables in an installation so that they are not confused. It is important to segregate cables because some types of cable, such as power or control cables, must not be connected together or they will create a fire hazard. Other types of cable, such as communications or data cables, can be connected together but need to be kept separate from power and control cables to avoid interference.
There are two main ways to segregate cables: by type and by function. Cables can be segregated by type into categories such as power, control, communications, and data. They can also be segregated by function into categories such as analog and digital, voice and video, or high-speed and low-speed data.
The most common method of cable segregation is by type. Power cables are always segregated from other types of cable because they carry a higher risk of fire if they are connected together. Control cables are often segregated from other types of cable because they may carry a voltage that could damage other types of cable if they are connected together.
Communications and data cables can usually be connected together without problems, but it is important to keep them separated from power and control cables to avoid interference.
Some installations may also require segregation by function. For example, analog and digital signals should not be mixed together because they can cause interference.
Voice and video signals should also be kept separate to avoid any degradation in quality. High-speed and low-speed data signals should also be kept separate so that the high-speed signal does not interfere with the low-speed signal.
Credit: www.alamy.com
How Do You Size a Cable Trench?
When it comes to sizing a cable trench, there are a few things you need to take into account. First, you need to determine the width of the trench. The width will be based on the number of cables you need to run through the trench and the type of cables being used.
Then, you need to determine the depth of the trench. The depth will be based on the burial depth required for the cables being used. Finally, you need to determine the length of the trench.
The length will be based on where the trench needs to start and end.
How Should You Install a Cable in a Cable Trench?
If you are installing a cable in a cable trench, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. First, make sure the trench is clean and dry. Second, lay the cable in the trench and secure it with tape or clamps.
Third, fill the trench with sand or soil and compact it. Finally, finish by covering the trench with concrete or asphalt.
What is the Purpose of Cable Trench?
A cable trench is a type of underground conduit used to protect and route electrical cables and wiring. It is typically deeper and wider than a traditional ditch, and is often lined with concrete or other durable materials to prevent damage to the cables. Cable trenches are commonly used when running power lines or communication cables beneath roads or other paved surfaces.
The main purpose of a cable trench is to provide a safe and reliable pathway for electrical cables while protecting them from damage. This is especially important for buried cables, which are more vulnerable to physical damage and environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals. In some cases, cable trenches may also be used to improve the aesthetics of an area by hiding unsightly wires and cables from view.
Which Type of Cable is Used in Substation?
The type of cable used in a substation depends on the type of equipment being used and the voltage level. For example, at lower voltages, such as those found in distribution substations, cables are often made of copper or aluminum. However, at higher voltages found in transmission substations, cables are typically made of high-voltage insulated wire.
33kv substation cable trench casting.
Conclusion
If you’re working on a substation project, you need to be aware of the many potential hazards that exist. One hazard is the cable trench. This is a trenches that contains high-voltage cables and other electrical equipment.
If you’re not careful, you can easily become electrocuted. Here are some important details about cable trenches:
• The depth of the trench should be at least 1 metre.
• The width of the trench should be at least 0.5 metres.
• The walls of the trench should be vertical and smooth.
• The bottom of the trench should be level and free of debris.



