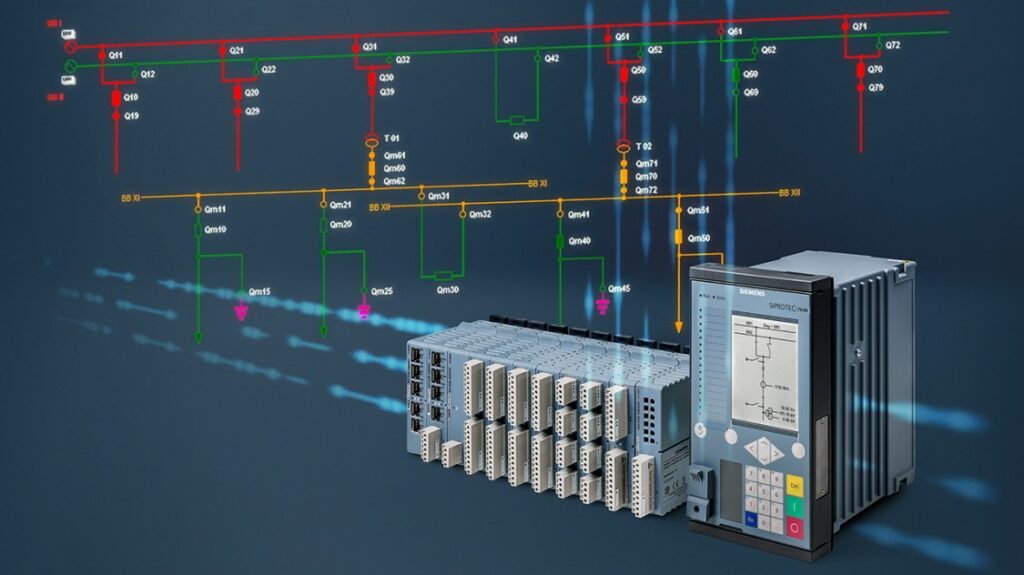
A substation is an electrical facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. A Scada system monitors and controls the equipment in a substation remotely. It includes sensors that measure various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate.
The data collected by the Scada system is used to optimize the performance of the equipment and ensure its safety.
HOW TO WORK SCADA, SCADA SYSTEM, 132/33 SUBSTATION, NEW SCADA SYSTEM
The modern substation is a complex and critical part of the power grid. And while they have been traditionally managed manually, advances in technology are leading more and more utilities to adopt substation automation systems, or Substation SCADA.
Substation SCADA systems provide many benefits over traditional manual methods of operation and control.
Perhaps most importantly, they allow for remote monitoring and control of substations, which can help reduce operational costs and improve response times in the event of an incident. Additionally, Substation SCADA systems can provide improved visibility into the health and status of equipment, helping to identify potential problems before they cause an outage.
While there are many benefits to implementing Substation SCADA systems, there are also some challenges that need to be considered.
One of the biggest challenges is cybersecurity; as these systems become increasingly connected to networked computers, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Additionally, Substations SCADA systems can be complex to implement and manage; utilities will need to ensure they have adequate staffing and training in place before making the switch from manual operations.
Overall, Substations SCADA offer a number of advantages over traditional methods of operation and control.
But as with any new technology implementation, there are some challenges that need to be considered before making the switch.
Scada System for Substation Pdf
A Scada system is a process control system that monitors and controls industrial equipment such as pumps, valves, motors, and other devices. It typically includes a central computer system that collects data from remote devices, displays information on operator screens, and stores data in databases. A Scada system can be used to control a wide variety of equipment in a substation, including:
-Circuit breakers
-Transformers
-Capacitors
-Reactors
Substation Automation System Ppt
Substation Automation System Ppt is a presentation that covers the basics of substation automation. It covers topics such as what is a substation, what are its components, and how it functions. Additionally, the presentation covers the benefits of automating a substation and some of the challenges associated with it.
Substation Automation System Tutorial
A substation automation system (SAS) is a computer-based system used to remotely monitor and control electric power substations. SASs are typically used by utilities to improve grid reliability, operational efficiency, and safety.
In this tutorial, we will provide an overview of substation automation systems, including their key components and features.
We will also discuss some of the benefits and challenges associated with implementing these systems.
Substation Automation System Abb
An substation automation system is a computer-based system for monitoring and controlling electric power substations. It is usually installed at high-voltage substations and integrated with the supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system of the power grid.
The substation automation system gathers data from various equipment in the substation, such as circuit breakers, transformers, and voltage regulators.
This data is then processed and used to generate alarms, reports, and control signals. The system also provides a user interface for operator control and interaction.
Operators can use the substation automation system to remotely monitor and control equipment in the substation.
This allows them to carry out tasks such as opening or closing circuit breakers, changing transformer tap settings, or adjusting voltage regulator setpoints.
The benefits of using a substation automation system include improved safety, reduced downtime, increased efficiency, and better asset management.
What is Substation Automation
Substation automation is the process of automating the operation and control of electric power substations. Substation automation systems are used to monitor, control, and protect substation equipment and to improve overall efficiency and reliability.
A substation automation system typically includes a variety of sensors, controllers, communication devices, and other components that are connected together to form a complete system.
Sensors are used to detect conditions within the substation, such as voltage levels, current levels, temperature levels, etc. Controllers are used to execute commands based on the sensor data and can be used to automatically operate switches, breakers, transformers, etc. Communication devices are used to connect the various components of the system together and allow for remote monitoring and control of the substation.
Substation automation systems offer many benefits over traditional manual or semi-automatic methods of operation. They can provide real-time monitoring of conditions within the substation, which can help identify problems before they cause equipment damage or failures. They can also automate routine tasks such as switch operations, breaker operations, transformer tap changes, etc., which can improve efficiency and reduce operator error.
Additionally, substation automation systems can provide enhanced security by restricting access to authorized personnel only.
If you’re considering implementing a substation automation system in your facility, there are a few things you should keep in mind. First, you’ll need to determine what type of system best meets your needs – there are several different architectures available on the market today.
Second, you’ll need to consider what level of integration you require – some systems offer more integration than others. Finally ,you’ll need to make sure that your existing infrastructure is compatible with the new system – if not ,you may need to make some upgrades before proceeding .
Substation Automation System Siemens
Introduction
The Siemens Substation Automation System (SAS) is a complete, integrated solution that helps utilities manage and protect their substations. The system includes hardware, software, and services for substation automation and protection, as well as communications and integration with other systems.
SAS provides utilities with the ability to remotely monitor and control substations, reducing the need for on-site personnel. The system also helps improve the reliability of the power grid by providing accurate information about grid conditions in real time.
The heart of SAS is the Substation Control Center (SCC), which is a PC-based application that runs on Windows or Linux operating systems.
The SCC provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for configuring, monitoring, and controlling all aspects of the SAS system.
In addition to the SCC, SAS includes a variety of hardware devices such as RTUs, IEDs, sensors, gateways, and more. These devices are used to collect data from substation equipment and relay it back to the SCC for monitoring and analysis.
Sensors – measure parameters such as voltage, current, temperature, pressure, etc.
RTUs – remote terminal units that provide an interface between field equipment and the control center
IEDs – intelligent electronic devices that perform various functions such as protection relaying
Gateways – enable communication between different protocols used in SAS
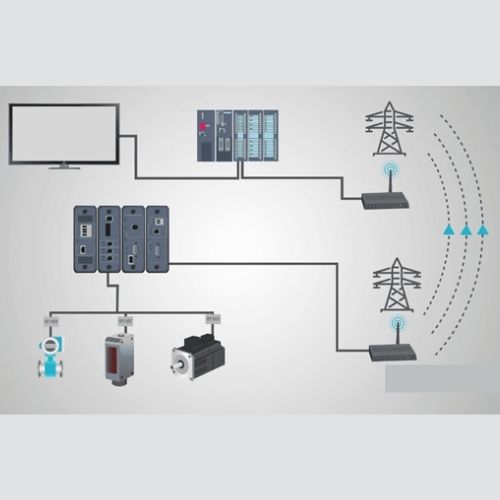
Substation Automation System Architecture
In a substation, there are many pieces of equipment that must work together to provide power to customers. This equipment includes transformers, circuit breakers, switches, and other devices. To make sure this equipment works together smoothly, a substation automation system is used.
The substation automation system architecture can be divided into three main parts: the control center, field devices, and communications network.
The control center is the heart of the substation automation system. It is responsible for monitoring and controlling all of the equipment in the substation.
The control center typically contains a human-machine interface (HMI), which is used by operators to monitor and control the substation equipment. The HMI can be a physical panel with buttons and displays, or it can be a software application running on a computer.
Field devices are the sensors and actuators that are installed in the substation equipment.
These devices collect information about the state of the equipment and allow operators to remotely control the equipment. Field devices include things like circuit breaker position sensors, transformer oil level sensors, switch status indicators, etc.
The communications network connects all of the different parts of the substation automation system together.
The network allows operators at the control center to communicate with field devices and vice versa. The communications network also allows different parts of the substation automation system to share data with each other.
Credit: www.reliservsolution.net
What are the Three 3 Types of Scada?
There are three main types of SCADA systems: centralized, distributed, and web-based. Centralized SCADA systems have a single server that collects data from all the remote sites. Distributed SCADA systems have multiple servers that collect data from different remote sites.
Web-based SCADA systems use a web browser to access the data collected by the server.
What is the Importance of Scada in Substation?
The Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system is a type of industrial control system (ICS). SCADA systems are used to monitor and control industrial processes that can include infrastructure systems such as water treatment plants, waste management facilities, oil and gas pipelines, electrical transmission grids, and large manufacturing plants.
The substation is the component of an electrical grid which regulates voltage and current levels, switches equipment on or off, protects against faults, measures power system parameters for metering and control purposes, and provides communications interfaces for remote monitoring and control.
Substations may be connected to each other by means of high-voltage transmission lines or extra-high-voltage (EHV) cables so as to form part of an interconnected grid. They may also be connected together with low-voltage distribution lines feeding domestic, commercial or light industrial premises.
A typical substation would have a number of fundamental components including:
• A step-down transformer to change the voltage from high transmission voltage to a lower distribution voltage;
• Circuit breakers or fuses to interrupt short circuits or overload currents;
• Capacitors or reactors used for power factor correction;
• Busbars carrying currents between outgoing feeders;
• Metering equipment such as voltmeters and ammeters;
• Protective relays to detect abnormal conditions within the substation so that appropriate action can be taken – this might involve automatically opening circuit breakers in order to isolate sections of the network.
What is Automatic Substation Control in Scada?
An automatic substation is a power system facility in which equipment is operated by remote control from a master control center. The two main types of automatic substations are remotely controlled and locally monitored.
In a remotely controlled substation, all operations are performed from the master control center.
This type of substation is typically used for high-voltage applications where safety is a concern. Remotely controlled substations are also used in cases where it is not practical to have personnel on site, such as in remote locations or in areas where conditions are hazardous.
In a locally monitored substation, some operations are performed locally while others are performed from the master control center.
This type of substation is typically used for low-voltage applications where safety is not as much of a concern. Locally monitored substations can also be used in cases where it is not practical to have personnel on site, but they can also be manned if necessary.
What is Scada in Electrical System?
In an electrical system, SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. It is a system that monitors and controls the equipment and processes in an industrial or commercial facility. The data acquisition part of SCADA collects data from sensors that are connected to the system, while the control part uses this data to operate equipment such as valves, pumps, and motors.
SCADA systems are used in a variety of industries, including water treatment facilities, power plants, oil and gas pipelines, and manufacturing plants. They can be used to monitor and control many different types of processes and equipment.
One advantage of using SCADA is that it can help reduce costs by automating tasks that would otherwise need to be done manually.
For example, if a pump needs to be turned on when a tank reaches a certain level, a SCADA system can be programmed to do this automatically. This can also help improve safety by reducing the need for people to work in potentially dangerous areas.
Another advantage of SCADA is that it can provide real-time information about the status of a process or piece of equipment.
This information can be used to make decisions about how to operate the system more efficiently or troubleshoot problems when they occur.
There are some disadvantages to using SCADA systems as well. One is that they can be complex and expensive to set up and maintain.
Another is that they rely on computers and other electronic components which can fail or become corrupted.
Conclusion
In a substation, the Scada system is responsible for monitoring and controlling the electrical equipment. This includes the switchgear, transformers, circuit breakers, and other devices. The Scada system also monitors the power flow and load levels in the substation.