In an electric power system, a substation is a facility at which voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse, using transformers. A Step-Down Transformer is used to decrease the voltage while maintaining the same current in a circuit.
A substation step-down transformer is a device that transforms high-voltage electricity from the power grid into lower voltages that are used by businesses and homes. The transformer reduces the voltage so that it can be safely used by appliances, lights, and other devices.
substation step-down transformer plays an important role in the power grid.
It transforms high-voltage electricity from the grid into lower voltages that can be used by businesses and homes. The transformer is a critical piece of equipment because it helps to ensure that electricity can be safely used by appliances, lights, and other devices.
Without a substation step-down transformer, the voltage of electricity would be too high for most devices to use.
This could lead to damage or even fires. The transformer helps to protect against this by reducing the voltage so that it is safe for use.
substation step-down transformers are typically located near power plants or other major sources of electricity.
They are usually placed in underground vaults or on poles near these sources. The transformers are designed to withstand extreme weather conditions and earthquakes so that they can continue to provide power even in emergency situations.
If you have ever wondered how your home or business gets its electricity, then you should know about substation step-down transformers!
These devices play an important role in our power grid by transforming high-voltage electricity into lower voltages that we can use safely in our everyday lives.
Step down Transformer Example
A step-down transformer is a type of electrical transformer that steps down the voltage from its primary winding to its secondary winding. The most common use for a step-down transformer is to convert high voltage, low current electricity from the power grid into the lower voltage, higher current electricity needed to run most household appliances.
The first thing to understand about transformers is that they don’t actually create any new electricity.
Rather, they take the electricity that’s already there and change it in some way. In a step-down transformer, this change is accomplished by having more turns of wire on the secondary coil than on the primary coil. This means that the secondary coil has less resistance than the primary coil, so it can carry more current.
But because there are fewer volts per turn on the secondary coil, the overall voltage is reduced.
It’s important to note that not all transformers work in exactly this way. Some have different numbers of turns on their coils, while others use special cores made of materials like ferrite or iron instead of just air.
But at their core (pun intended), all transformers work by inductively coupling two circuits together and changing either the voltage or current (or both) in one or both circuits as a result.
Step-Down Transformer Voltage
Most of the time when we talk about electricity, we think about it in terms of voltage. Voltage is the force that drives current through a circuit. It’s what makes your light bulbs light up and your motors run.
But there are times when we need to change the voltage of an electrical signal. That’s where transformers come in.
A transformer is a device that takes an incoming AC voltage and transforms it into a different AC voltage.
The most common type of transformer is the step-down transformer. As the name implies, a step-down transformer steps down the voltage of an incoming signal. For example, if you have an incoming 220 volt AC signal, a step-down transformer can transform it into 110 volts AC.
Why would we want to do this? Well, often times 110 volt equipment is less expensive than 220 volt equipment. And sometimes we need to use equipment that isn’t rated for high voltages.
In either case, a step-down transformer can be used to safely power our equipment without damaging it or causing it to overheat.
Step-down transformers are relatively simple devices and they’re very easy to use. Just connect the primary winding (the side with the higher voltage) to your power source and connect the secondary winding (the side with the lower voltage) to your load.
The number of turns on each winding will determine the amount of voltage transformation that takes place. More turns on the secondary winding will result in a greater transformation (i.e., a bigger drop in voltage).
Step-Up Transformer Example
A step-up transformer is a type of transformer that increases the voltage of an alternating current (AC). The input voltage is fed into the primary winding, and the output voltage is taken from the secondary winding. The number of turns in the secondary winding is greater than the number of turns in the primary winding, which results in a higher output voltage.
The most common use for a step-up transformer is to increase the voltage from a low-voltage power source, such as a battery, to a high-voltage power grid. For example, transformers are used to convert 120 volt AC from household outlets to 240 volt AC used by electric utilities.
Another example where step-up transformers are used is in wind turbines.
The blades of a wind turbine rotate at high speeds, which generates low-voltage AC electricity. This electricity needs to be converted to high-voltage AC before it can be sent to the power grid. To do this, a step-up transformer is used.
Step-Down Transformer Working Principle
A step-down transformer is an electrical device that transforms alternating current (AC) from a higher voltage to a lower voltage. It is a type of power transformer. The input side of the transformer is called the primary winding, and the output side is called the secondary winding.
The primary winding has more turns of wire than the secondary winding. This means that the secondary voltage will be lower than the primary voltage.
The working principle of a step-down transformer is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in a conductor when there is a change in magnetic flux through the conductor.
The EMF causes current to flow in the conductor. In a step-down transformer, AC flows through the primary winding, and this generates a magnetic field. The secondary winding is placed in this magnetic field, and this induces an EMF in the secondary winding.
The number of turns in each winding determines the ratio of voltages between the primary and secondary windings; for example, if there are 100 turns on the primary winding and 50 turns on the secondary winding, then the ratio of voltages would be 2:1 (100:50). This means that if you have 120 volts on your primary side, you would have 60 volts on your secondary side – thus “stepping down” from 120 volts to 60 volts.
Step-down transformers are used in many applications where it is necessary to reduce voltage; for example, they are used to provide 110/120 volts for domestic appliances such as televisions and hair dryers from 230/240 volt mains supplies.
Step-Down Transformer Pdf
A step-down transformer is an electrical device that transforms voltage from a higher level to a lower level. It is also known as a bucking transformer. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the high-voltage source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
The number of turns on the secondary winding will be greater than on the primary winding, resulting in a lower output voltage.
The most common use for a step-down transformer is to convert 240 volts down to 120 volts so that it can be used in standard household outlets in North America. These transformers are typically small and can be plugged into a wall outlet.
Larger step-down transformers are used in industrial applications, such as converting high-voltage transmission lines down to levels that can be used by factories or office buildings.
Step-Up And Step-Down Transformer Formula
A transformer is a device that converts alternating current (AC) from one voltage to another. It is composed of two or more coils of wire called the primary coil and the secondary coil. The primary coil is wound around an iron core and the secondary coil is wound around a separate iron core.
The two cores are either separated by an air gap or they are linked together by a magnetic material.
The transformer relies on Faraday’s law of induction, which states that when a conductor is moved through a magnetic field, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced in the conductor. This EMF causes a current to flow in the conductor.
The direction of the induced EMF and resulting current depend on the direction of movement of the conductor relative to the magnetic field.
If the primary coil is connected to an AC source and the secondary coil is not connected to anything, then no current will flow in the secondary coil because there is no closed circuit for it to flow in. However, if we connect a load across the terminals of the secondary coil, then current will flow in the secondary winding and through the load resistance.
The size of this current will depend on boththe number of turns in each windingandthe ratioof turns between them:
Np = number of turns in primary windingNs = number o fturns inthesecondarywindingVp = applied voltage tomagnetizing(primary)windingVse=voltageatsecondarywindingterminalsIse=currentflowinginthesecondarycircuitRl=loadresistanceconnectedtosecondarywindingterminals
Assuming ideal transformers with no energy losses:

Credit: www.webpages.uidaho.edu
What is Step down Transformer Used For?
A step down transformer is used to convert high-voltage, low-current electricity into low-voltage, high-current electricity. This type of transformer is often used in electrical devices that require a lower voltage, such as cell phone chargers and laptop computers.
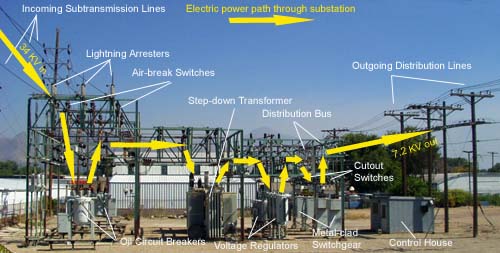
What is a Step down Substation?
In an electric power system, a substation is a facility where voltage is transformed from high to low, or the reverse. A substation may also include transformers to change the voltage levels between transmission and distribution systems.
The primary function of a substation is to switch equipment on or off, and to protect equipment from faults in the system.
Substations are also used to change the voltage level of electricity being sent through the power grid. This is done by either increasing or decreasing the voltages using transformers.
A step-down substation reduces the voltage from transmission levels to distribution levels.
The most common voltages used in transmission systems are 115 kV, 138 kV, 161 kV, and 230 kV. The typical voltage for a distribution system is 25 kV or lower.
Most step-down substations are located near load centers because it is more efficient to distribute electricity at lower voltages.
A step-up substation increases the voltage from distribution levels to transmission levels so that electricity can be sent over long distances without significant losses.
What is Stepdown Transformer?
A stepdown transformer is a type of transformer that steps down the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. The primary winding has more turns of wire than the secondary winding, which causes the voltage to be stepped down. The transformer also steps up the current in the secondary winding, because there are fewer turns of wire in the secondary than in the primary.
What Transformer is Used in Substation?
There are many different types of transformers that are used in substations, but the most common type is the power transformer. This type of transformer is responsible for taking the high-voltage electricity from the power lines and transforming it into a lower voltage that can be used by households and businesses. The power transformer is typically located near the top of the substation, where it can easily tap into the high-voltage power lines.
Electrical Substation | 33/11KV & 11/0.4KV Step Down Auto Tap Changing Transformer
Conclusion
A substation step down transformer is a device that is used to convert high-voltage electricity into low-voltage electricity. This type of transformer is typically found in electrical substations. The primary winding of the transformer is connected to the high-voltage side of the circuit, while the secondary winding is connected to the low-voltage side.
The substation step down transformer reduces the voltage of the electricity so that it can be safely used by household appliances and other devices. Without this type of transformer, the voltage would be too high and could damage these devices. In addition, the transformer also helps to regulate the flow of electricity so that it does not fluctuate too much.